Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
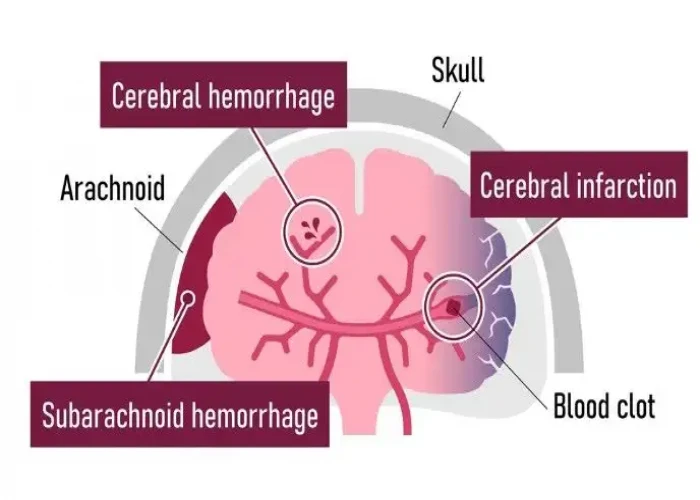
Subarachnoid hemorrhage

A subarachnoid hemorrhage is a type of bleeding that occurs in the space between the brain and the thin tissues that cover the brain, known as the subarachnoid space. This type of bleeding is typically caused by the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain and can be a life-threatening medical emergency.
Symptoms of a subarachnoid hemorrhage can include:
- A sudden, severe headache that is often described as the "worst headache of my life"
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stiff neck and sensitivity to light
- Confusion, drowsiness, or loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention, as a subarachnoid hemorrhage can lead to brain damage or even death.
Diagnosis of a subarachnoid hemorrhage typically involves a physical exam, imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI, and sometimes a lumbar puncture to test for blood in the cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment may involve medication to reduce the risk of complications such as seizures or vasospasm (narrowing of blood vessels in the brain), as well as measures to manage pain and other symptoms. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged blood vessel or drain excess fluid from the brain.
Recovery from a subarachnoid hemorrhage can be a long and challenging process and may involve rehabilitation to address any physical or cognitive deficits that result from the bleeding. It is important to follow your doctor's instructions and take any prescribed medications as directed to reduce the risk of further complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Bleeding in brain
- Headaches
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of consciousness (fainting)
Disease Causes
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Subarachnoid hemorrhage and Learn More about Diseases
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection

Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)

Ventricular tachycardia

Infertility (Sterility)
Ureteral cancer

Asthma attack

Anaphylaxis
Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome
subarachnoid hemorrhage, সুবারাচনয়েড রক্তক্ষরণ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.