Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Amoebic Dysentry
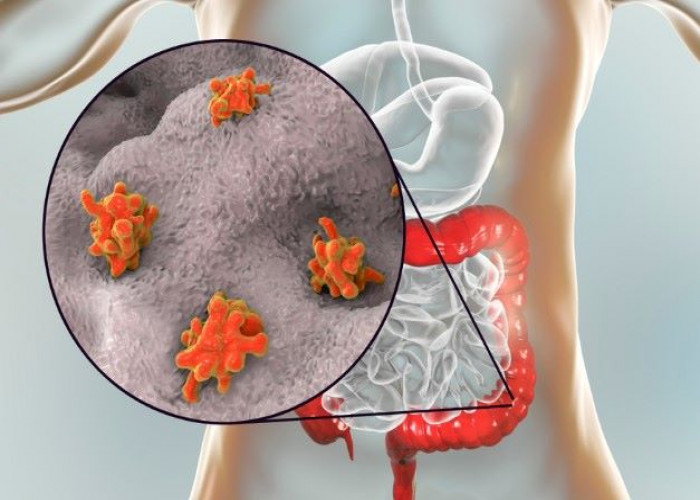
Amoebic dysentery, also known as amebiasis, is a parasitic infection of the intestines caused by the amoeba Entamoeba histolytica. It is a common cause of diarrhea in developing countries, and can also occur in travelers to these areas.
Symptoms of amoebic dysentery can include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stools, fever, and fatigue. In severe cases, the infection can cause liver abscesses, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Diagnosis of amoebic dysentery typically involves a stool test to detect the presence of the parasite, as well as blood tests and imaging tests to evaluate for complications such as liver abscesses.
Treatment of amoebic dysentery typically involves antibiotics to kill the parasite, as well as medications to control symptoms such as diarrhea and abdominal pain. In severe cases, drainage of liver abscesses may be necessary.
Prevention of amoebic dysentery involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly with soap and water, and avoiding drinking contaminated water or eating undercooked or raw food. Travelers to high-risk areas may also benefit from taking preventative medications to reduce the risk of infection.
In conclusion, amoebic dysentery is a parasitic infection of the intestines caused by the amoeba Entamoeba histolytica. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fever, and severe cases can lead to liver abscesses. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and supportive care, while prevention involves practicing good hygiene and avoiding contaminated food and water. If you suspect that you may have amoebic dysentery, it is important to seek medical attention immediately to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Abdomen pain before defecation
- Frequent toilet
- Mucus with stool
- Stinky stools
- Dysentery
Disease Causes
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Metronidazole
Medicines containing metronidazole in intestinal dysentery.
1+1+1.
-
Diloxanide Furoate
Intestinal dysentery with metronidazole followed by diloxenide furoate.
1 pill/ 1 teaspoon of syrup 3 times a day for 10 days.
-
Tetracycline Hydrochloride (Oral)
Drugs of tetracycline or oxytetracycline group work well in some cases acute, sub-acute and chronic. But it is not used for long as it is mixed with blood.
1 service every 6 hours.
-
Sulphamethoxazole + Trimethoprim
Co-trimoxazole-containing medicine in thick wounds.
1 pill a day 2 or 5/7 days or syrup 1 spoon 2 times a day 5/7 days.
-
Ciprofloxacin
1+0+1 (7-10 days)
-
Tinidazole
4 pills every night for 3 nights or 2 pills in the morning, 2 pills at night for 3 days.
-
Secnidazole
Combination therapy with secnidazole in acute intestinal amoebic dysentery.
Adults 2 tablets 1 time at night just before meals.
-
Chloroquine Phosphate
Treatment with chlorquine phosphate for chronic dysentery has good results.
2 pills 2 times a day for 2 days. Then 1 pill 2 times a day for 2/3 weeks.
-
Mebeverine Hydrochloride
Taking IBS medication reduces diarrhea.
1/2, 1 pill 2/3 times a day.
-
Hyoscine Butylbromide
1/2 pill 3 times a day.
-
Hyoscine Hydrobromide
1/2 pill 3 times a day.
-
Pancreatin
Medicines containing pancreatin for the patient's digestion and taste.
1 tablet daily after food.
-
Vitamin B complex
2cc medicine should be injected into the flesh after 1 day.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Ipecacuanha
3X strength 20/25 drops in 1 a. water with a spoonful recommended every hour.
-
Aloe socotrina
6 strength 2/3 drops of medicine every hour with a little water.
-
Podophyllum peltatum
Q Mix one dram of the medicine in one ounce of water and take one spoon every 30 minutes.
-
Pulsatilla
Mix one dram of medicine in 3X one ah water and take one spoon every hour.
-
Carbo vegetabilis
6 strength with a little water 3/4 drops of medicine every hour.
-
Colocynthis
Mix one dram of medicine in 3X one ah jar and use one spoon every hour. 10/15 mg intravenously for severe abdominal pain.
-
Mercurius solubilis
Mix 3/4 drop of medicine with 30 strength water and use every two hours.
-
Mercurius corrosivus
3 Shakti One dram of medicine in water one spoon every hour.
-
Nux vomica
3X 2/3 drop in a spoonful of water every two hours.
-
Hydrocotyle
3, 6 strength 2/3 drops three times a day with a little water.
-
Arsenicum
3X Mix 2/3 drops with little water and consume 4 times a day.
Disease yoga
Amoebic Dysentry and Learn More about Diseases
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
Posterior vaginal prolapse (Rectocele)

Mouth cancer

Stress fractures

Temporal lobe seizure

Rosacea
Keratosis pilaris

Nicotine dependence
amoebic dysentry, এ্যামিবিক আমাশয়
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.