Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
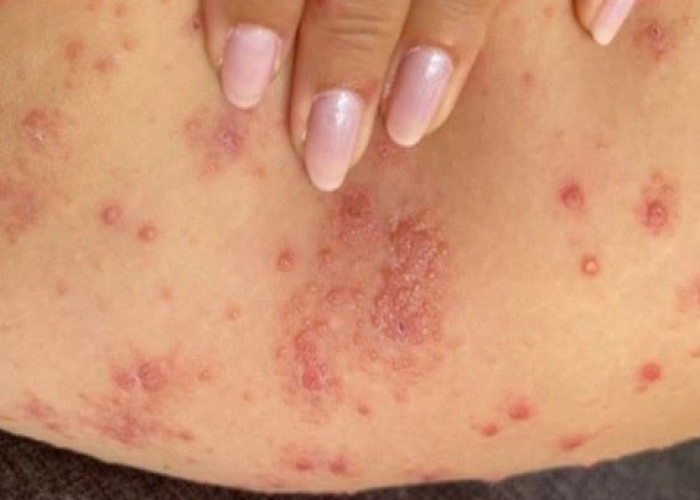
Chronic hives

Chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, is a skin condition characterized by the presence of itchy, red, and raised welts or hives on the skin that last for more than six weeks. The cause of chronic hives is often difficult to identify, but may be related to an underlying autoimmune or inflammatory condition, infection, or environmental factors. In some cases, chronic hives may be triggered by certain medications, foods, or other substances. Treatment for chronic hives typically involves medications to relieve symptoms, such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, and immune-modulating drugs. It is also important to identify and avoid triggers, such as certain foods or medications, and to manage underlying conditions that may be contributing to the development of hives. If you experience chronic hives, it is important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Red skin
- Itching
- Swollen skin
- Swollen throat
- Swollen facial
- Batches of red or skin-colored welts (wheals), which can appear anywhere on the body
- Welts that vary in size, change shape and appear and fade repeatedly as the reaction runs its course
- Painful swelling (angioedema) of the lips, eyelids and inside the throat
- A tendency for signs and symptoms to flare with triggers such as heat, exercise and stress
Disease Causes
Chronic hives
The welts that come with hives arise when certain cells release histamine and other chemicals into your bloodstream.
Doctors often can't identify the reason for chronic hives or why acute hives sometimes turn into a long-term problem. The skin reaction may be triggered by:
- Pain medications
- Insects or parasites
- Infection
- Scratching
- Heat or cold
- Stress
- Sunlight
- Exercise
- Alcohol or food
- Pressure on the skin, as from a tight waistband
In some cases, chronic hives may be related to an underlying illness, such as a thyroid disease or, rarely, cancer.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Your doctor will likely recommend you treat your symptoms with home remedies, such as over-the-counter antihistamines. If self-care steps don't help, talk with your doctor about finding the prescription medication or combination of drugs that works best for you. Usually, an effective treatment can be found.
Antihistamines
Taking nondrowsy antihistamine pills daily helps block the symptom-producing release of histamine. They have few side effects. Examples include:
- Loratadine (Claritin)
- Fexofenadine (Allegra)
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- Desloratadine (Clarinex)
If the nondrowsy antihistamines don't help you, your doctor may increase the dose or have you try the type that tends to make people drowsy and is taken at bedtime. Examples include hydroxyzine pamoate (Vistaril) and doxepin (Zonalon).
Check with your doctor before taking any of these medications if you are pregnant or breast-feeding, have a chronic medical condition, or are taking other medications.
Other medications
If antihistamines alone don't relieve your symptoms, other drugs may help. For example:
- Histamine (H-2) blockers. These medications, also called H-2 receptor antagonists, are injected or taken orally. Examples include cimetidine (Tagamet HB) and famotidine (Pepcid).
- Anti-inflammation medications. Oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can help lessen swelling, redness and itching. These are generally for short-term control of severe hives or angioedema because they can cause serious side effects if taken for a long time.
- Antidepressants. The tricyclic antidepressant doxepin (Zonalon), used in cream form, can help relieve itching. This drug may cause dizziness and drowsiness.
- Asthma drugs with antihistamines. Medications that interfere with the action of leukotriene modifiers may be helpful when used with antihistamines. Examples are montelukast (Singulair) and zafirlukast (Accolate).
- Man-made (monoclonal) antibodies. The drug omalizumab (Xolair) is very effective against a type of difficult-to-treat chronic hives. It's an injectable medicine that's usually given once a month.
- Immune-suppressing drugs. Options include cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, others) and tacrolimus (Astagraft XL, Prograf, Protopic).
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Chronic hives and Learn More about Diseases

Seasonal affective disorder (SAD)

Tendinitis

Mild cognitive impairment (MCI)

Wilson's disease
Dystonia
Myofascial pain syndrome
Dehydration

Tongue-tie (ankyloglossia)
Chronic hives, Chronic urticaria, করোনিক হাইভ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.