Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Achalasia
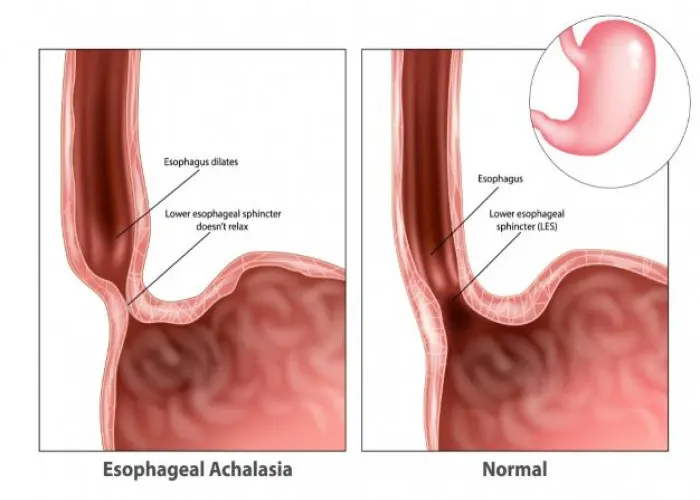
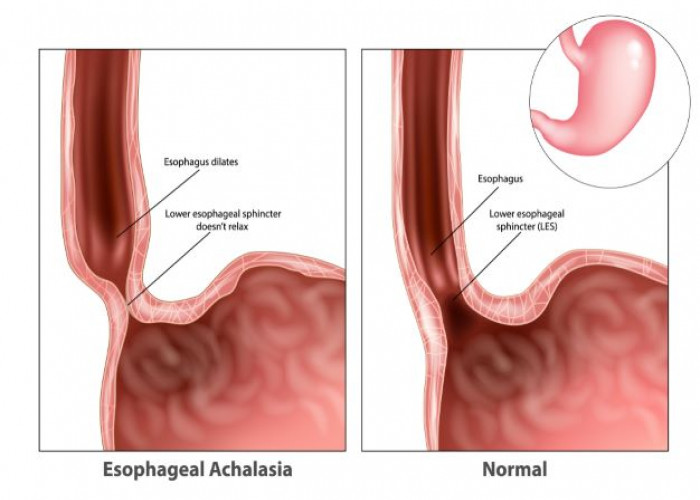
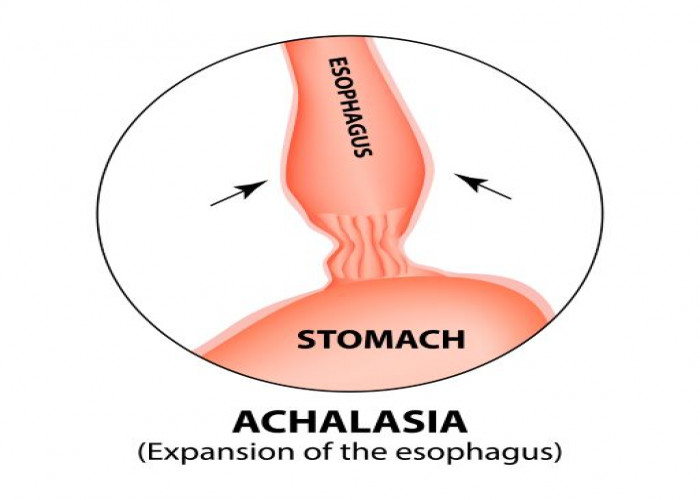
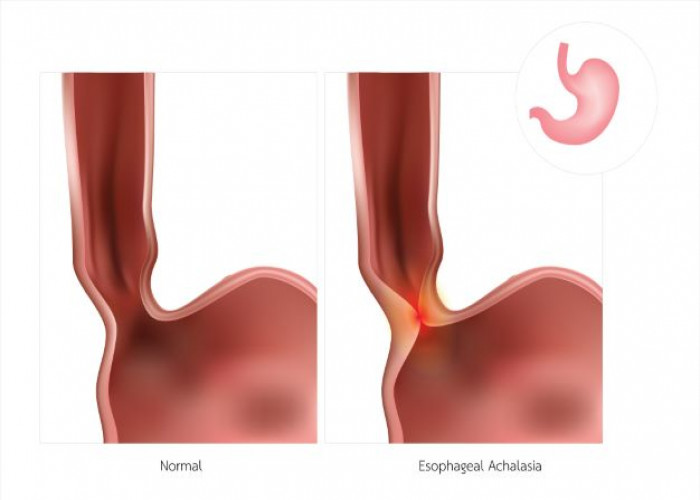
Achalasia is a rare disorder of the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. In achalasia, the lower esophageal sphincter, a ring of muscle at the bottom of the esophagus, fails to relax and open properly, making it difficult to swallow food and liquids.
The exact cause of achalasia is not known, but it is believed to involve a malfunction of the nerve fibers that control the esophageal muscles.
Symptoms of achalasia can include difficulty swallowing, regurgitation of food, chest pain, and weight loss. The condition can be diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and tests such as an X-ray, endoscopy, or manometry.
Treatment options for achalasia can include medications, dilation of the lower esophageal sphincter, and surgery. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, age, and overall health of the patient.
It's important to see a doctor if you experience symptoms of achalasia, as prompt treatment can help prevent complications and maintain good quality of life.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Inability to eat or drink
- Backflow of undigested food (regurgitation)
- Heartburn
- Sour belch
- Chest pain that comes and goes
- Cough increases in evening
- Weight loss
- Nausea or vomiting
Disease Causes
Achalasia
The exact cause of achalasia is poorly understood. Researchers suspect it may be caused by a loss of nerve cells in the esophagus. There are theories about what causes this, but viral infection or autoimmune responses have been suspected. Very rarely, achalasia may be caused by an inherited genetic disorder or infection.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Nonsurgical options include:
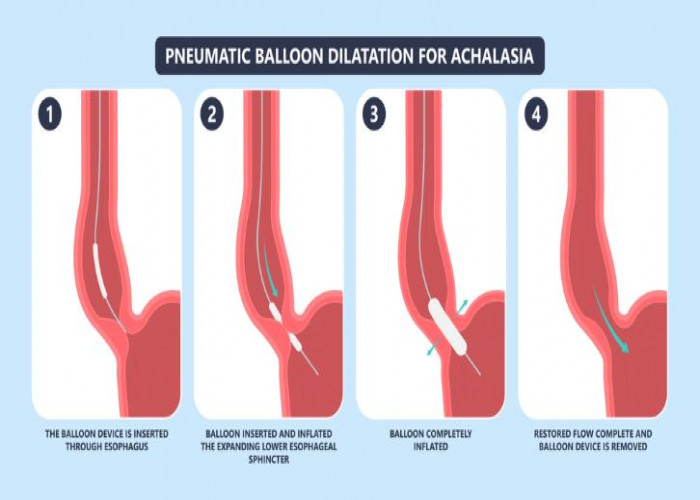
- Pneumatic dilation. A balloon is inserted by endoscopy into the center of the esophageal sphincter and inflated to enlarge the opening. This outpatient procedure may need to be repeated if the esophageal sphincter doesn't stay open. Nearly one-third of people treated with balloon dilation need repeat treatment within five years. This procedure requires sedation.
- Botox (botulinum toxin type A). This muscle relaxant can be injected directly into the esophageal sphincter with an endoscopic needle. The injections may need to be repeated, and repeat injections may make it more difficult to perform surgery later if needed.
- Botox is generally recommended only for people who aren't good candidates for pneumatic dilation or surgery due to age or overall health. Botox injections typically do not last more than six months. A strong improvement from injection of Botox may help confirm a diagnosis of achalasia.
- Medication. Your doctor might suggest muscle relaxants such as nitroglycerin (Nitrostat) or nifedipine (Procardia) before eating. These medications have limited treatment effect and severe side effects. Medications are generally considered only if you're not a candidate for pneumatic dilation or surgery, and Botox hasn't helped. This type of therapy is rarely indicated.
Surgery
Surgical options for treating achalasia include:
- Heller myotomy. The surgeon cuts the muscle at the lower end of the esophageal sphincter to allow food to pass more easily into the stomach. The procedure can be done noninvasively (laparoscopic Heller myotomy). Some people who have a Heller myotomy may later develop gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- To avoid future problems with GERD, a procedure known as fundoplication might be performed at the same time as a Heller myotomy. In fundoplication, the surgeon wraps the top of your stomach around the lower esophagus to create an anti-reflux valve, preventing acid from coming back (GERD) into the esophagus. Fundoplication is usually done with a minimally invasive (laparoscopic) procedure.
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). In the POEM procedure, the surgeon uses an endoscope inserted through your mouth and down your throat to create an incision in the inside lining of your esophagus. Then, as in a Heller myotomy, the surgeon cuts the muscle at the lower end of the esophageal sphincter.
- POEM may also be combined with or followed by later fundoplication to help prevent GERD. Some patients who have a POEM and develop GERD after the procedure are treated with daily oral medication.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Achalasia and Learn More about Diseases

Autism spectrum disorder
Interstitial lung disease
Seborrheic keratosis

Muscle cramp

Hiccups
Vitamin deficiency anemia
Ataxia
Hairy cell leukemia
Achalasia, Achalasia cardia, আছালাসিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.