 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Eosinophilic esophagitis
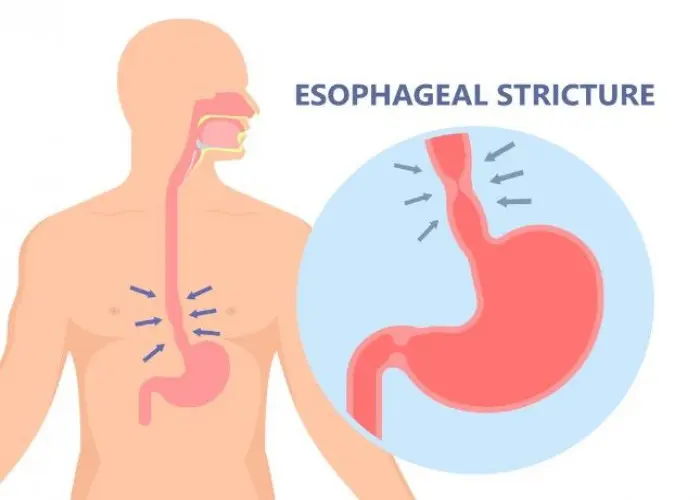
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the esophagus, which is the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. EoE is characterized by the presence of a high number of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the lining of the esophagus.
Symptoms of EoE may include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, heartburn, regurgitation, and food getting stuck in the throat. EoE can affect both children and adults, and may be associated with other conditions such as allergies, asthma, and eczema.
The exact cause of EoE is not well understood, but it is believed to be related to an abnormal immune response to certain foods or environmental allergens. Diagnosis is typically made through an upper endoscopy with biopsy, in which a small sample of tissue is taken from the lining of the esophagus and examined under a microscope.
Treatment for EoE may involve dietary changes, medications to control inflammation, or a combination of both. Elimination diets, in which specific foods are removed from the diet, are commonly used to identify trigger foods that may be causing symptoms. In some cases, a specialized formula diet may be recommended. Medications such as proton pump inhibitors, steroids, or immune modulators may also be used to manage symptoms and reduce inflammation.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider who specializes in the management of EoE to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on your individual needs and symptoms.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen (Edema)
- Failure to thrive (poor growth, malnutrition and weight loss)
- Chest pain that is often centrally located and does not respond to antacids
- Food getting stuck in the esophagus after swallowing (impaction)
- Weight loss
- Abdomen pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Backflow of undigested food (regurgitation)
- Chest pain
- A small, round bump under the skin, usually on the face, neck or trunk
Disease Causes
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophils are a normal type of white blood cells present in your digestive tract. However, in eosinophilic esophagitis, you have an allergic reaction to an outside substance. The reaction may occur as follows:
- Reaction of the esophagus. The lining of your esophagus reacts to allergens, such as food or pollen.
- Multiplication of eosinophils. The eosinophils multiply in your esophagus and produce a protein that causes inflammation.
- Damage to the esophagus. Inflammation can lead to scarring, narrowing and formation of excessive fibrous tissue in the lining of your esophagus.
- Dysphagia and impaction. You may have difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or have food become stuck when you swallow (impaction).
- Additional symptoms. You may have other symptoms, such as chest pain or stomach pain.
There has been a significant increase in numbers of people diagnosed with eosinophilic esophagitis in the past decade. At first, researchers thought this was due to an increase in awareness among doctors and greater availability of tests. However, studies now suggest that the disease is becoming increasingly common, parallel to the increase in asthma and allergies.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Eosinophilic esophagitis is considered a chronic relapsing disease, meaning that most people will require ongoing treatment to control their symptoms. Treatment will involve one or more of the following:
Dietary therapy
Depending on your response to tests for food allergies, your doctor may recommend that you stop eating certain foods, such as dairy or wheat products, to relieve your symptoms and reduce inflammation. A more limited diet is sometimes required.
Medication
- Proton pump inhibitor (PPI). Your doctor will likely first prescribe an acid blocker such as a PPI. This treatment is the easiest to use, but most people's symptoms don't improve.
- Topical steroid. If you do not respond to the PPI, your doctor will then likely prescribe a topical steroid, such as fluticasone or budesonide, which is a liquid that is swallowed to treat eosinophilic esophagitis. This type of steroid is not absorbed into the bloodstream, so you are unlikely to have the typical side effects often associated with steroids.
Dilation
If you experience severe narrowing (strictures) of your esophagus, your doctor may recommend dilation (stretching) to help make swallowing easier. Dilation may be used if steroids are not helpful. Or dilation may be a choice to avoid ongoing use of medication.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Eosinophilic esophagitis and Learn More about Diseases

Radiation enteritis

Anal cancer

Cold sore

Microcephaly
CSF leak (Cerebrospinal fluid leak)
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
Colon polyps

Reactive attachment disorder
eosinophilic esophagitis, ইওসিনোফিলিক খাদ্যনালী
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
