Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Breast inflammation - Homeopathic remedies
Breast inflammation, also known as mastitis, is a condition in which the breast tissue becomes swollen and inflamed. It is most commonly seen in women who are breastfeeding, but can also occur in women who are not breastfeeding.
Symptoms of breast inflammation may include breast pain, redness, warmth, and swelling, as well as fever, chills, and fatigue. The breast may also feel hard and tender to the touch, and there may be a burning or itching sensation.
Breast inflammation is usually caused by an infection, which can occur when bacteria enter the breast tissue through a cracked or sore nipple. Other risk factors for breast inflammation include a history of breast infections, breastfeeding difficulties, and wearing tight-fitting clothing or bras.
Treatment for breast inflammation typically involves antibiotics to treat the underlying infection, as well as pain relievers and warm compresses to help alleviate symptoms. It is also important to continue breastfeeding or pumping breast milk, as this can help to clear the infection and prevent complications.
Preventing breast inflammation involves maintaining good breastfeeding hygiene, such as keeping the nipples clean and dry, and ensuring proper latch and positioning during breastfeeding. Women who are not breastfeeding can reduce their risk of breast inflammation by avoiding tight-fitting clothing and practicing good hygiene.

Ear infection

Premature hair ripe

Stammer
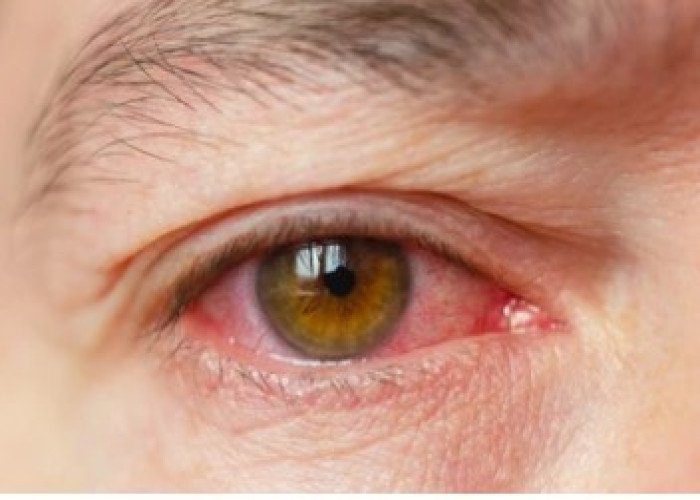
Eye inflammation

Dream of theft

Water dream
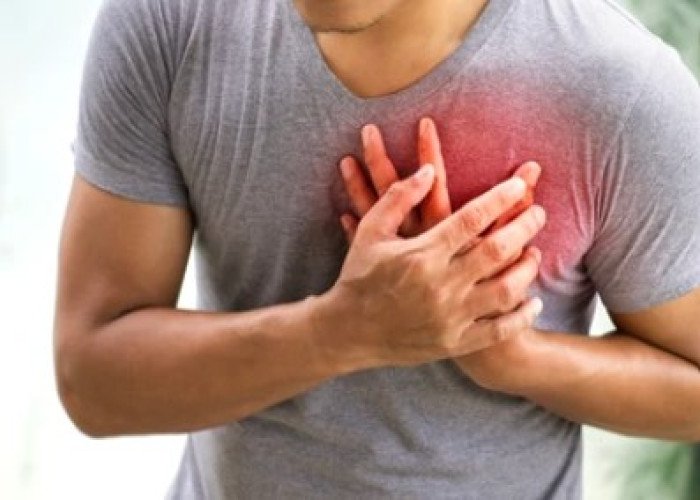

Heart attack
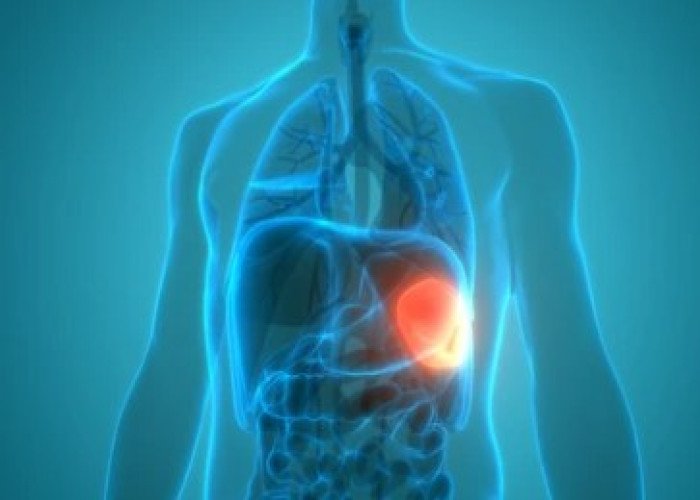
Spleen and liver swelling
Breast inflammation, স্তন প্রদাহ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.