 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Heart attack - Homeopathic remedies
A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of blood to the heart is blocked, resulting in damage to the heart muscle. This blockage is often caused by a buildup of plaque in the arteries that supply blood to the heart, a condition known as coronary artery disease. The plaque can rupture, causing a blood clot to form, which can completely block blood flow to the heart.
The symptoms of a heart attack can vary from person to person, but the most common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort: This is the most common symptom of a heart attack, and is often described as a feeling of pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the chest. The pain may also spread to the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder blades, or back.
- Shortness of breath: This can occur before or during chest discomfort, and may be accompanied by sweating, nausea, or lightheadedness.
- Nausea or vomiting: This can occur with or without chest pain.
- Sweating: This can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: This can be a symptom of a heart attack, especially if it is accompanied by chest pain or shortness of breath.
It is important to seek emergency medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as prompt treatment can help prevent further damage to the heart muscle.
Risk factors for heart attack include:
- Age: The risk of heart attack increases with age, especially in men over the age of 45 and women over the age of 55.
- Family history: If a close family member has had a heart attack, you are at increased risk.
- Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart attack, as it damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots.
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of heart attack.
- High cholesterol: High levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at increased risk of heart attack due to the damage that high blood sugar levels can cause to the blood vessels.
Treatment for a heart attack typically involves medications to help dissolve the blood clot and restore blood flow to the heart, as well as other medications to help reduce the workload on the heart and prevent further complications. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart.
Prevention of heart attack involves making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help identify and manage risk factors for heart attack.

Bed-sores

Sadness

Tone break

Skin disease
Blood dysentery

Dream of fear

Extreme hunger
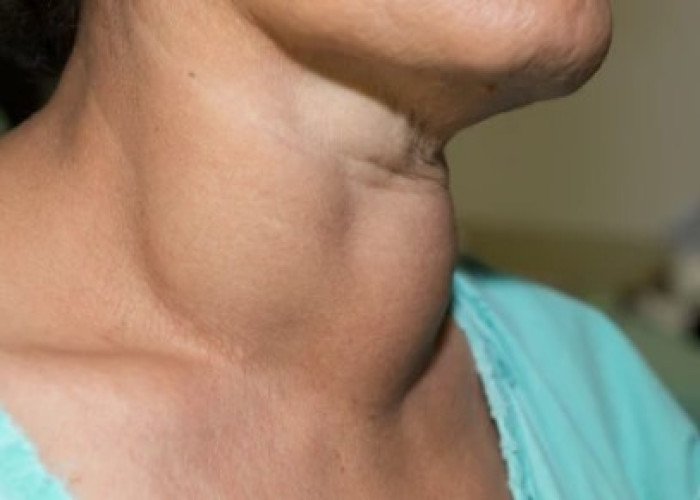
Goitre
Heart attack, হৃৎপিন্ডের পীড়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.



