 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Uterine displacement - Yoga remedies
Uterine displacement, also known as uterine prolapse, is a condition where the uterus descends from its normal position in the pelvis and protrudes into or out of the vagina. This can be a result of weakened pelvic muscles and ligaments that support the uterus, as well as other factors like pregnancy and childbirth, menopause, obesity, chronic coughing or straining, and heavy lifting.
There are several types of uterine displacement, depending on the degree of descent and the location of the prolapsed uterus. In a mild case, the uterus may only partially descend into the vaginal canal, while in severe cases, it may protrude outside the body.
Symptoms of uterine displacement include a feeling of pressure or fullness in the pelvic area, discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse, urinary incontinence or retention, constipation, and lower back pain. Women who have a prolapsed uterus may also experience recurring vaginal infections, discharge, or bleeding.
Treatment for uterine displacement depends on the severity of the condition and the symptoms experienced by the patient. In mild cases, pelvic floor exercises or physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the pelvic muscles and improve the support of the uterus. Pessaries, which are small devices inserted into the vagina to hold the uterus in place, may also be used.
In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the uterine displacement. There are several types of surgeries that can be performed, including hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), uterine suspension (repositioning of the uterus), and sacrocolpopexy (suspension of the uterus using mesh or other materials).
Prevention of uterine displacement involves maintaining good pelvic health through regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and seeking prompt treatment for conditions that may contribute to the development of uterine prolapse, such as chronic coughing or constipation.
It is important for women who experience symptoms of uterine displacement to seek medical attention promptly, as untreated prolapse can lead to complications like urinary tract infections, kidney damage, and other serious health issues.
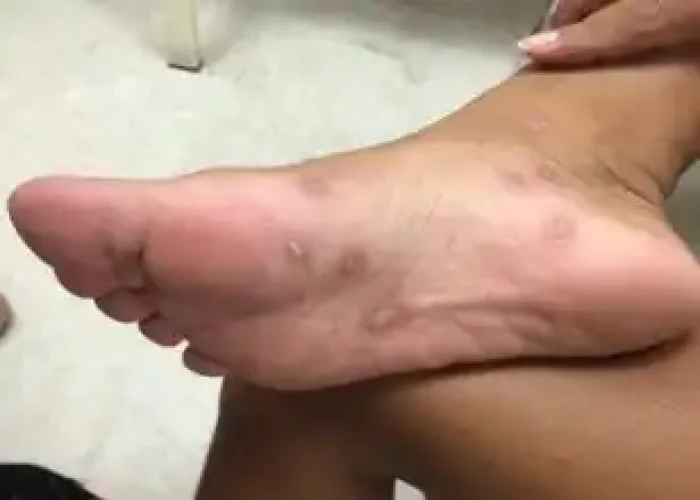
Syphilis
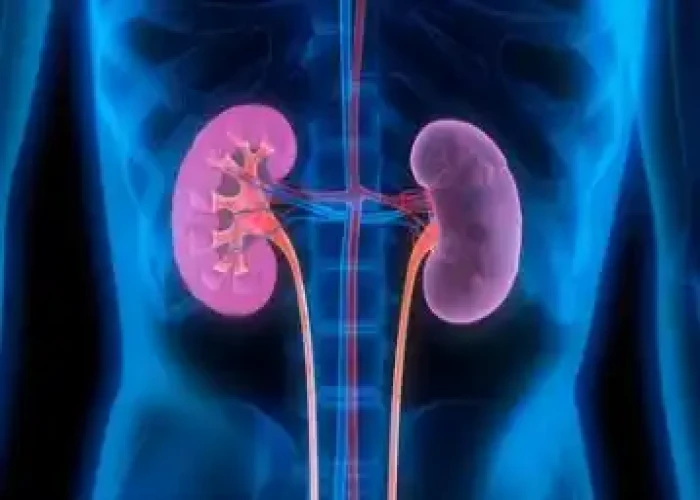
Kidney failure
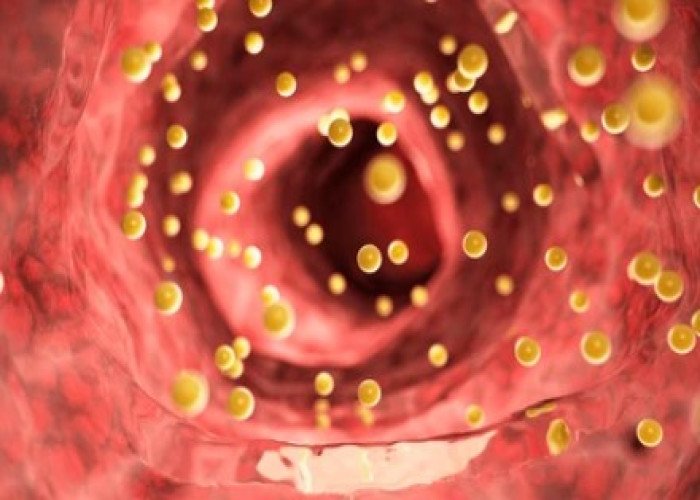
Colon inflammation

Indigestion (Acidic)

Itching

Fainting and hysteria

Inflammation of airways
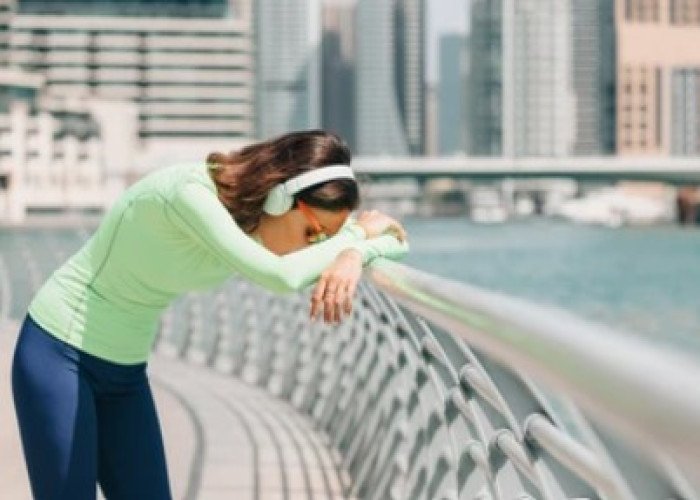

Decreased vitality
Uterine displacement, জরায়ুর স্থানচ্যুতি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
