 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Urinary tract infection - Yoga remedies
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are infections that occur in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The most common cause of UTIs is bacteria, although they can also be caused by viruses or fungi.
Symptoms of UTIs include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, passing small amounts of urine frequently, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back.
UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics, which work by killing the bacteria causing the infection. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
Prevention measures for UTIs include drinking plenty of water, wiping from front to back after using the bathroom, urinating before and after sexual activity, and avoiding the use of irritating feminine products.
In some cases, UTIs can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney infections or sepsis. If you experience symptoms of a UTI, it is important to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.

Memory loss

Belly fat

Hemorrhoids
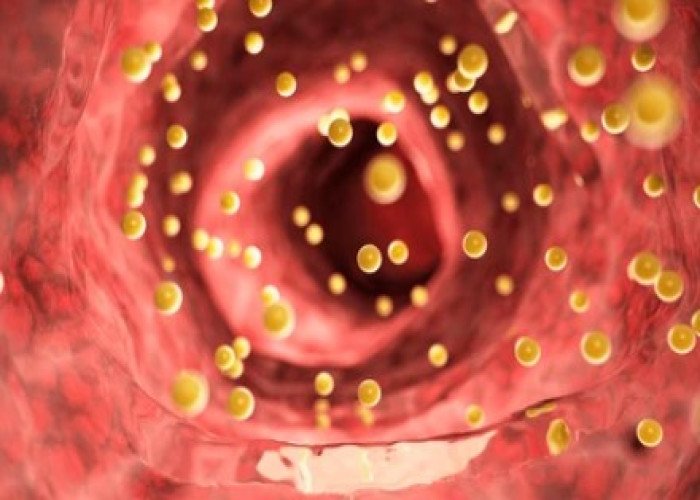
Colon inflammation
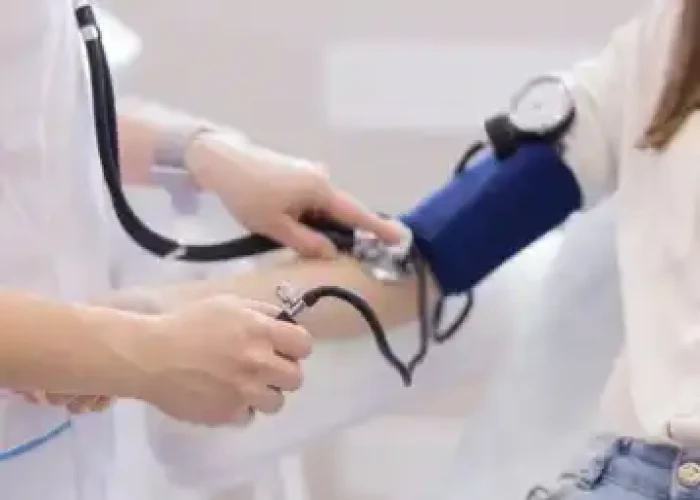
Low blood pressure
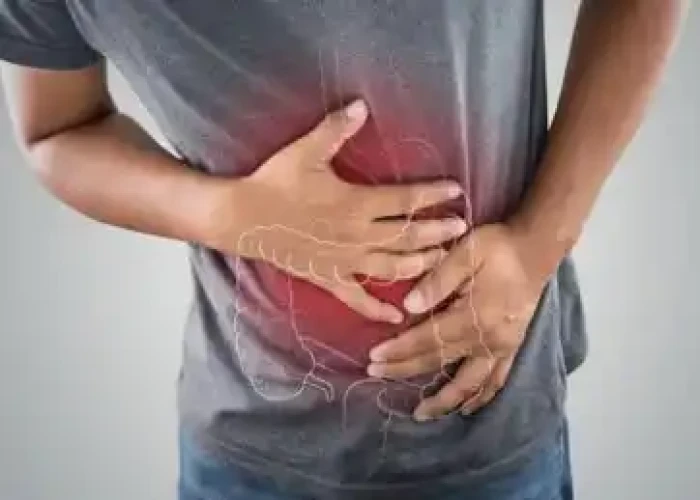
Diarrhea

Bile colic
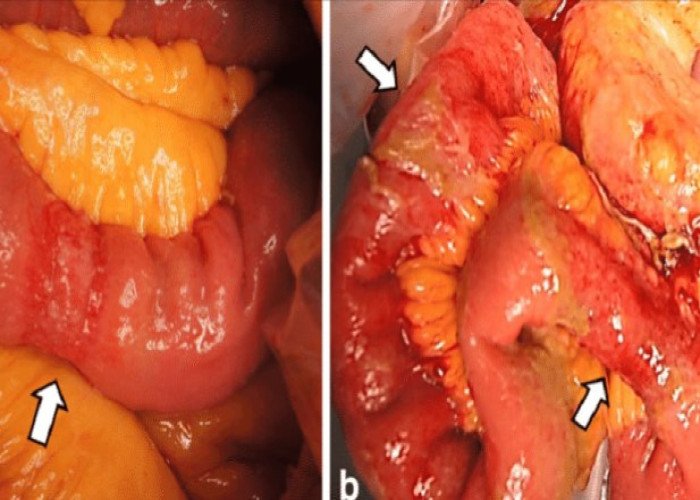
Intestinal boils
Urinary tract infection, মুত্র প্রদাহ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

