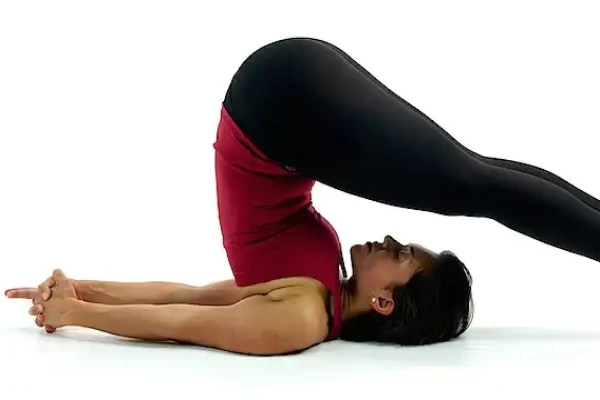
 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Heart disease - Yoga remedies
Heart disease is a broad term used to describe a variety of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. It is one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
The most common type of heart disease is coronary artery disease (CAD), which occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to chest pain (angina), heart attacks, and other serious complications.
Other types of heart disease include heart failure, arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), heart valve problems, and congenital heart defects.
Risk factors for heart disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, family history, and a sedentary lifestyle. These risk factors can be modified through lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
Diagnosis of heart disease typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies such as electrocardiograms (ECG) and echocardiograms, and cardiac catheterization.
Treatment for heart disease varies depending on the specific condition and severity. Medications such as statins, blood thinners, and blood pressure medications are commonly used to manage heart disease. In more severe cases, surgical procedures such as angioplasty, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), or heart valve replacement may be necessary.
Prevention of heart disease is key to reducing the risk of developing the condition. This involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying medical conditions, and working with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized prevention plan. It's important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of heart disease, as early detection and treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
Flatulence

Shortness of the body

Indigestion (Acidic)

One leg is short

Loss of health

Sperm loss

Colitis

Epilepsy
Heart disease, হৃদরোগ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

