Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Loading...
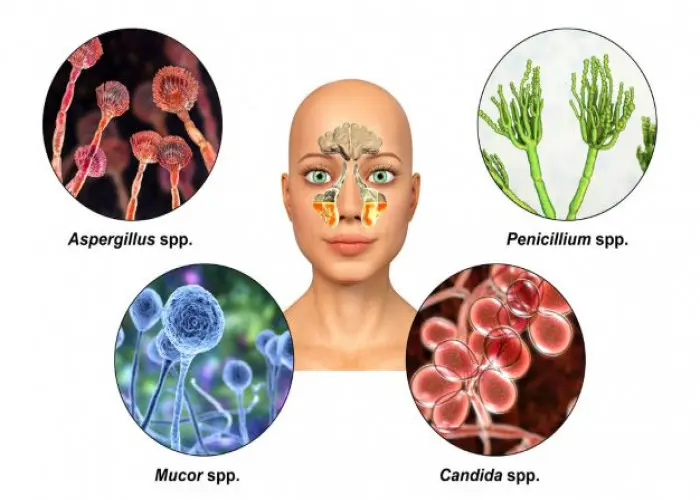
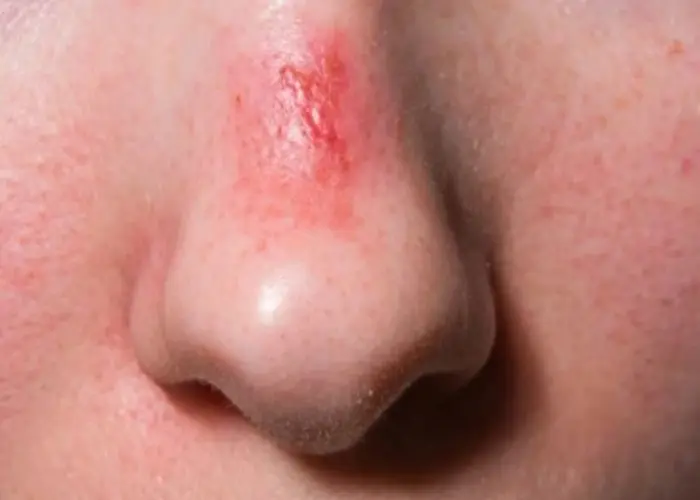
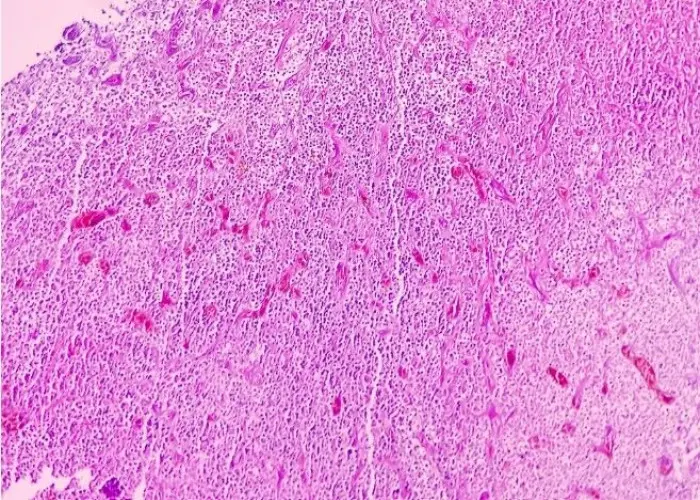
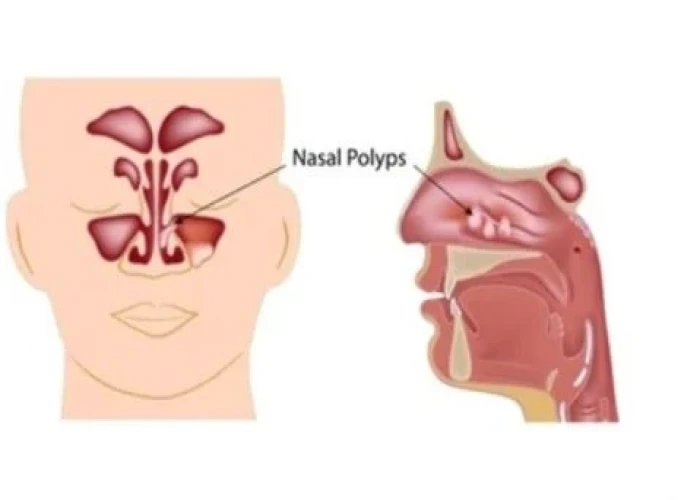
Nose Diseases
Nose - Diseases
The nose is a complex structure located on the face that is responsible for several important functions, including:
- Smell: The nose contains specialized cells called olfactory receptors, which detect different smells and send signals to the brain to interpret them.
- Breathing: The nose is the primary route for air to enter the body during breathing. As air passes through the nose, it is warmed, moistened, and filtered to remove dirt and other particles.
- Humidification: The nose helps to humidify the air as it enters the body, preventing the respiratory tract from drying out.
- Defense: The nose contains hairs and mucus that help to trap dirt, dust, and other particles, preventing them from entering the lungs.
The nose is made up of several structures, including:
- Nostrils: These are the openings on the outside of the nose that allow air to enter.
- Nasal cavity: This is a large, air-filled space inside the nose that is lined with a thin layer of mucus and tiny hairs called cilia.
- Sinuses: The nasal cavity is connected to several air-filled cavities in the skull, called sinuses. These cavities help to lighten the weight of the skull and may also play a role in sound resonance.
Disorders of the nose can include conditions such as allergies, sinusitis, and nasal polyps. Proper nasal hygiene, including regular cleaning and avoiding irritants, can help to prevent these conditions and maintain overall nasal health. Treatment for nasal disorders may include medications, surgery, or other medical interventions, depending on the specific condition and its underlying cause.
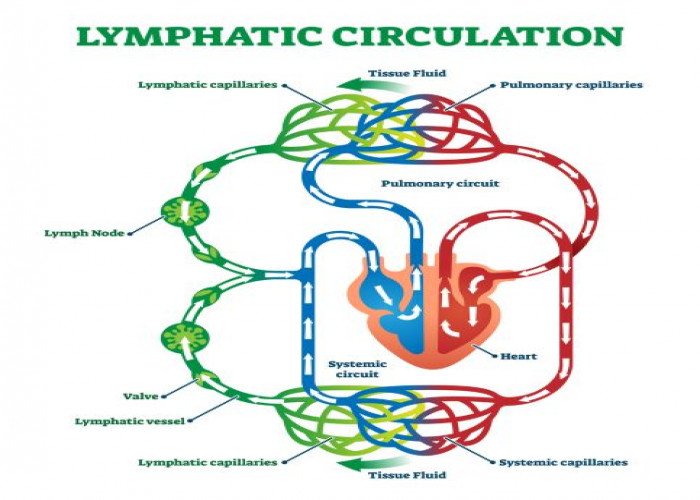
Lymphatic vessel
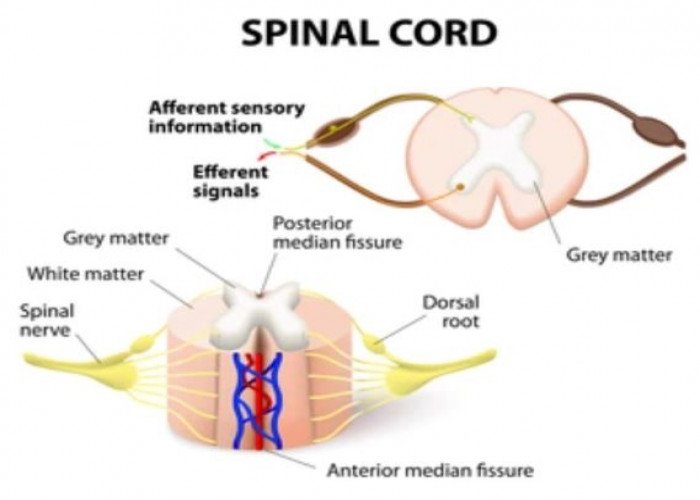
Spinal cord
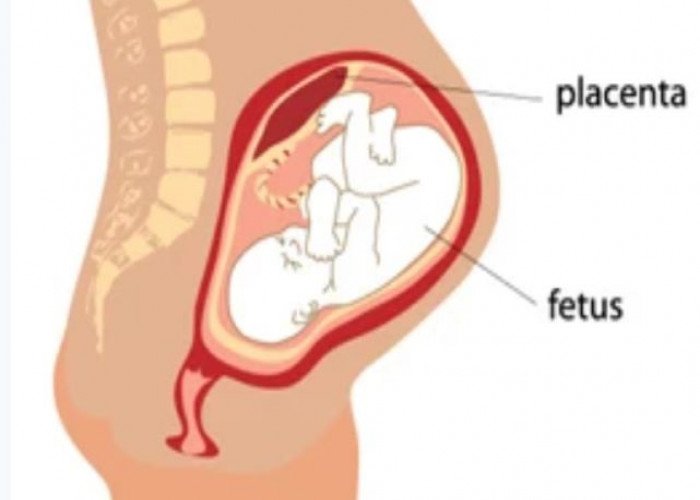
Placenta
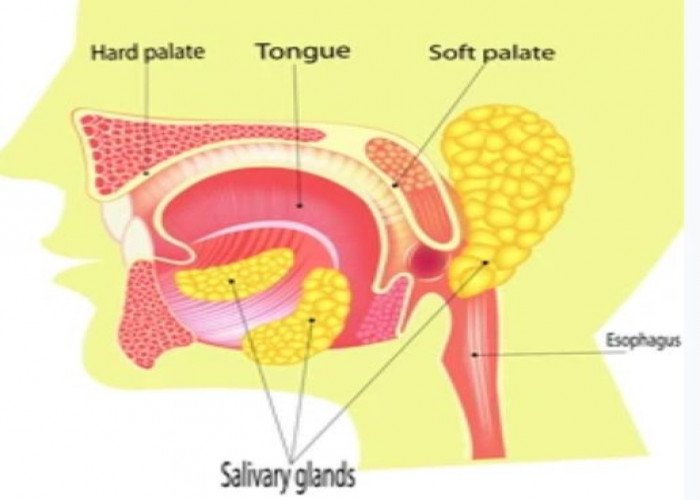
Salivary glands

Pelvic
Eye
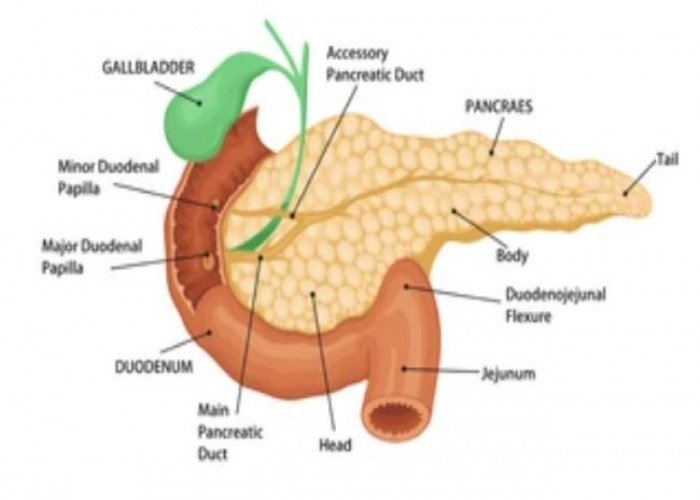
Pancreas
Nerves
Searching Keywords Idea
Nose, Deviated septum, নাক
Bangladesh is Number One in Digital Medical Management.
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.