Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Acute sinusitis
Acute sinusitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the sinuses, which are air-filled cavities in the skull. It is typically caused by an infection, such as a viral or bacterial infection, that blocks the normal flow of mucus from the sinuses and causes the sinuses to become inflamed.
The symptoms of acute sinusitis may include:
- Nasal congestion or stuffiness
- Pain or pressure in the face, especially around the eyes, cheeks, or forehead
- Headache
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Toothache
- A thick, yellow or green discharge from the nose
- Reduced sense of smell
Acute sinusitis is usually diagnosed based on a person's symptoms and a physical examination, although a CT scan may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for acute sinusitis typically involves self-care measures, such as nasal decongestants, pain relievers, and warm compresses, as well as antibiotics if the cause is bacterial. In some cases, a procedure such as nasal irrigation or the use of a nasal steroid spray may also be recommended.
In most cases, acute sinusitis resolves within two to four weeks. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, it's important to see a doctor for further evaluation and treatment. Severe or persistent sinusitis can lead to complications, such as a sinus infection or orbital cellulitis (an infection of the eye socket), so prompt treatment is important.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Headaches
- Toothache
- Cough
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Fever
- Red eyes (conjunctivitis)
- Swollen eye (Conjunctivitis)
Disease Causes
Acute sinusitis
Acute sinusitis is most often caused by the common cold, which is an infection with a virus. In some cases, an infection with bacteria develops.
Disease Prevents
Acute sinusitis
Take these steps to help reduce your risk of getting acute sinusitis:
- Avoid upper respiratory infections. Try to stay away from people who have colds or who are sick with other infections. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before your meals.
- Manage your allergies. Work with your doctor to keep symptoms under control.
- Avoid cigarette smoke and polluted air. Tobacco smoke and other pollutants can irritate and inflame your lungs and nasal passages.
- Use a humidifier. If the air in your home is dry, such as it is if you have forced-air heat, adding moisture to the air may help prevent sinusitis. Be sure the humidifier stays clean and free of mold with regular, thorough cleaning.
Disease Treatments
Most cases of acute sinusitis get better on their own. Self-care techniques are usually all you need to ease symptoms.
Treatments to relieve symptoms
Your doctor may recommend treatments to help relieve sinusitis symptoms, including:
- Saline nasal spray, which you spray into your nose several times a day to rinse your nasal passages.
- Nasal corticosteroids. These nasal sprays help prevent and treat inflammation. Examples include fluticasone (Flonase Allergy Relief, Flonase Sensimist Allergy Relief, others), budesonide (Rhinocort Allergy), mometasone (Nasonex) and beclomethasone (Beconase AQ, Qnasl, others).
- Decongestants. These medications are available in over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription liquids, tablets and nasal sprays. Use nasal decongestants for only a few days. Otherwise they may cause the return of more-severe congestion (rebound congestion).
- Allergy medications. If your sinusitis is due to allergies, using allergy medications may help lessen allergy symptoms.
- OTC pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or aspirin.
- Use caution when giving aspirin to children or teenagers. Though aspirin is approved for use in children older than 3, children and teenagers recovering from chickenpox or flu-like symptoms should never take aspirin. This is because aspirin has been linked to Reye's syndrome, a rare but potentially life-threatening condition, in such children.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics usually aren't needed to treat acute sinusitis, because it's usually caused by a virus and not by bacteria. Even if your acute sinusitis is bacterial, it may clear up without treatment. Your doctor might wait and watch to see if your acute sinusitis worsens before prescribing antibiotics.
However, severe, progressive or persistent symptoms might require antibiotics. If your doctor prescribes an antibiotic, be sure to take the whole course, even after your symptoms get better. If you stop taking them early, your symptoms may recur.
Immunotherapy
If allergies are contributing to your sinusitis, allergy shots (immunotherapy) that help reduce the body's reaction to specific allergens may help treat your symptoms.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Acute sinusitis and Learn More about Diseases
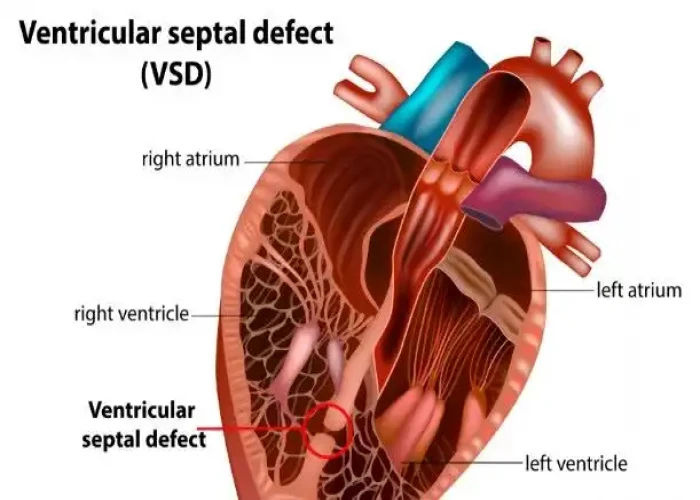
Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
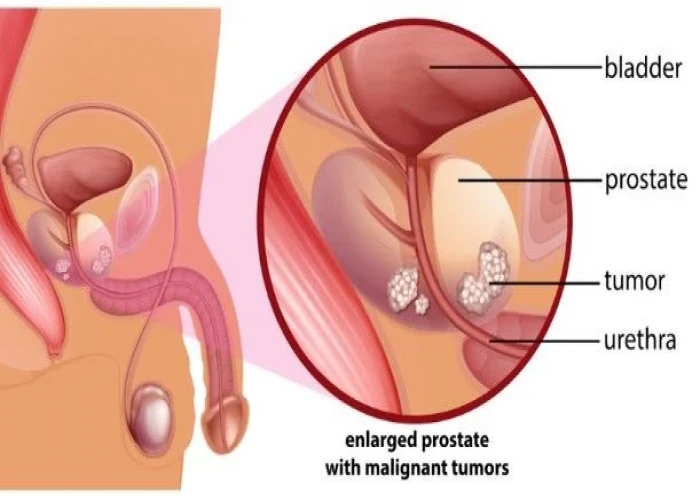
Prostate cancer
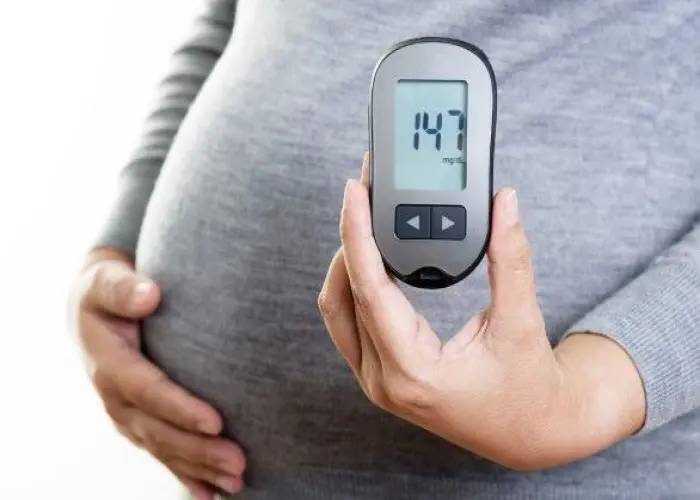

Gestational diabetes
Dry mouth
Blood in urine (Hematuria)

Retrograde ejaculation

Tricuspid valve disease
MRSA infection
Acute sinusitis, Bacterial sinusitis, Acute sinusitis treatment, তীব্র সাইনোসাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.