Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Rheumatoid arthritis
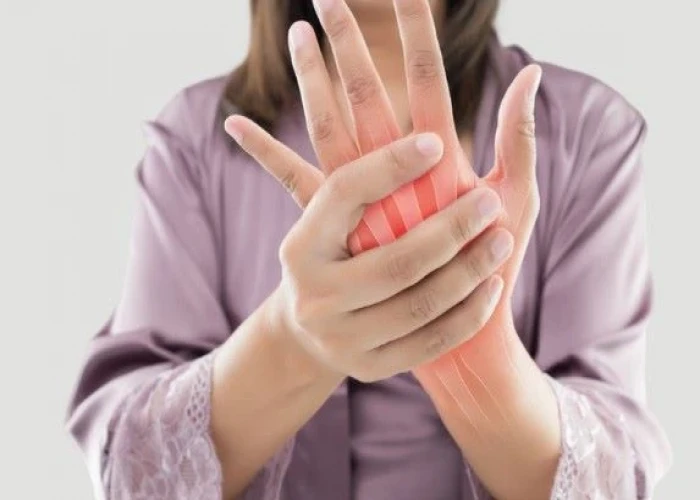
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, but can also impact other parts of the body. In RA, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, leading to inflammation, pain, and joint damage.
The symptoms of RA can vary from person to person but may include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, especially in the hands, wrists, and feet. Other symptoms can include fatigue, fever, and weight loss. RA can also cause deformities of the joints over time.
There is no cure for RA, but treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage. Treatment may involve a combination of medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biological therapies. In addition, physical therapy and occupational therapy may be recommended to help maintain mobility and function in the affected joints.
Lifestyle changes can also help manage symptoms of RA. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises can all help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important for managing RA and preventing long-term joint damage. Regular medical follow-up is important to monitor the progression of the disease and adjust treatment as needed.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen joint
- Joint stiffness
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Joint stiffness that is usually worse in the mornings and after inactivity
Disease Causes
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. Normally, your immune system helps protect your body from infection and disease. In rheumatoid arthritis, your immune system attacks healthy tissue in your joints. It can also cause medical problems with your heart, lungs, nerves, eyes and skin.
Doctors don't know what starts this process, although a genetic component appears likely. While your genes don't actually cause rheumatoid arthritis, they can make you more likely to react to environmental factors — such as infection with certain viruses and bacteria — that may trigger the disease.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. But clinical studies indicate that remission of symptoms is more likely when treatment begins early with medications known as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Medications
The types of medications recommended by your doctor will depend on the severity of your symptoms and how long you've had rheumatoid arthritis.
- NSAIDs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Over-the-counter NSAIDs include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve). Stronger NSAIDs are available by prescription. Side effects may include stomach irritation, heart problems and kidney damage.
- Steroids. Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, reduce inflammation and pain and slow joint damage. Side effects may include thinning of bones, weight gain and diabetes. Doctors often prescribe a corticosteroid to relieve symptoms quickly, with the goal of gradually tapering off the medication.
- Conventional DMARDs. These drugs can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and save the joints and other tissues from permanent damage. Common DMARDs include methotrexate (Trexall, Otrexup, others), leflunomide (Arava), hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) and sulfasalazine (Azulfidine). Side effects vary but may include liver damage and severe lung infections.
- Biologic agents. Also known as biologic response modifiers, this newer class of DMARDs includes abatacept (Orencia), adalimumab (Humira), anakinra (Kineret), certolizumab (Cimzia), etanercept (Enbrel), golimumab (Simponi), infliximab (Remicade), rituximab (Rituxan), sarilumab (Kevzara) and tocilizumab (Actemra).
- Biologic DMARDs are usually most effective when paired with a conventional DMARD, such as methotrexate. This type of drug also increases the risk of infections.
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs. Baricitinib (Olumiant), tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and upadacitinib (Rinvoq) may be used if conventional DMARDs and biologics haven't been effective. Higher doses of tofacitinib can increase the risk of blood clots in the lungs, serious heart-related events and cancer.
Therapy
Your doctor may refer you to a physical or occupational therapist who can teach you exercises to help keep your joints flexible. The therapist may also suggest new ways to do daily tasks that will be easier on your joints. For example, you may want to pick up an object using your forearms.
Assistive devices can make it easier to avoid stressing your painful joints. For instance, a kitchen knife equipped with a hand grip helps protect your finger and wrist joints. Certain tools, such as buttonhooks, can make it easier to get dressed. Catalogs and medical supply stores are good places to look for ideas.
Surgery
If medications fail to prevent or slow joint damage, you and your doctor may consider surgery to repair damaged joints. Surgery may help restore your ability to use your joint. It can also reduce pain and improve function.
Rheumatoid arthritis surgery may involve one or more of the following procedures:
- Synovectomy. Surgery to remove the inflamed lining of the joint (synovium) can help reduce pain and improve the joint's flexibility.
- Tendon repair. Inflammation and joint damage may cause tendons around your joint to loosen or rupture. Your surgeon may be able to repair the tendons around your joint.
- Joint fusion. Surgically fusing a joint may be recommended to stabilize or realign a joint and for pain relief when a joint replacement isn't an option.
- Total joint replacement. During joint replacement surgery, your surgeon removes the damaged parts of your joint and inserts a prosthesis made of metal and plastic.
Surgery carries a risk of bleeding, infection and pain. Discuss the benefits and risks with your doctor.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Aspirin
Pills should be powdered and mixed with water.
First 1 pill 3 times a day after meals. Then 2 pills 3 times a day.
-
Paracetamol
1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Indomethacin (Oral)
Aspirin and paracetamol do not reduce the pain.
1 capsule 3 times a day after meals.
-
Ibuprofen
1 tablet of 400 mg 3 times a day.
-
Ketoprofen (Oral & injection)
1 capsule 1/2 time a day 1 to 2 hours before or 2 hours after meals, between meals or after meals.
-
Celecoxib
1+0+1 or 0+0+200mg after meals.
-
Mefenamic acid
Elderly patients 500 mg 1 tablet 2/3 times a day after or between meals. Cannot be used for more than 7 days.
-
Naproxen Sodium
Medicines containing naproxen can be used in rheumatoid arthritis.
Adult 500mg 1 time between or after meals 2 times a day.
-
Ketorolac Tromethamine
1+0+1 or 1+1+1.
-
Tramadol Hydrochloride
1+0+1 or 1+1+1 (10/15 days).
-
Tolperisone Hydrochloride
1+0+1
-
Leflunomide
100 mg daily for 3 days.
-
Prednisolone
1 pill 3 times a day for 5/7 days.
-
Dexamethasone
1 pill 3 times a day for 5/7 days.
-
Betamethasone
First, increase and then decrease gradually.
-
Ranitidine Hydrochloride
150 mg pill 2 times a day.
-
Famotidine
1 pill of 20/40mg in the morning and 1 pill at night.
- Diclofenac Sodium
-
Fluoxetine Hydrochloride
1 pill every morning after breakfast for 1 month.
-
Nortriptyline
Take 1 pill at night before going to bed.
-
Vitamin B complex
Take 1 pill daily after food.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Rheumatoid arthritis and Learn More about Diseases

Wheat allergy
Acromegaly

Borderline personality disorder

Tuberculosis
Myasthenia gravis
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
Salpingitis
Rhabdomyosarcoma
rheumatoid arthritis, রিউম্যাটয়েড বাত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.