 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Adenomyosis
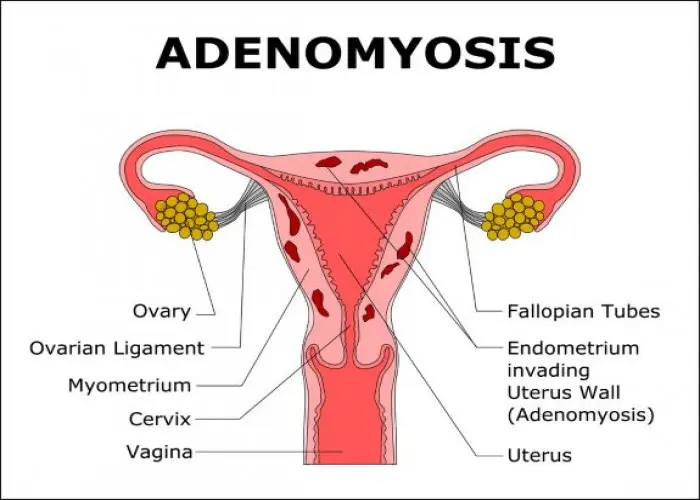
Adenomyosis is a medical condition that occurs when endometrial tissue, which normally lines the uterus, grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. This can cause the uterus to enlarge and the wall to thicken, leading to pain and heavy menstrual bleeding.
Adenomyosis is most commonly diagnosed in women who have been through menopause, but it can occur at any age. The exact cause of adenomyosis is not known, but it may be related to hormonal changes, injury to the uterus, or previous uterine surgery.
The symptoms of adenomyosis can vary from woman to woman, but may include:
- Heavy, prolonged, or painful menstrual periods
- Pelvic pain or discomfort, especially during menstruation
- Bloating or swelling of the lower abdomen
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Constipation or urinary frequency
Diagnosis of adenomyosis is usually made based on a woman's symptoms and a physical examination, although imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for adenomyosis depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, a woman's age, and whether or not she wants to have children in the future. Options may include medication, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or hormonal therapy, or surgery, such as a hysterectomy.
It's important for women with adenomyosis to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of action and to manage their symptoms. With proper treatment and management, most women are able to find relief from the symptoms of adenomyosis and live healthy, active lives.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Heavy menstrual period or bleeding
- Severe cramping or sharp, knife like pelvic pain during menstruation (dysmenorrhea)
- Pelvic pain
- Painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
Disease Causes
Adenomyosis
The cause of adenomyosis isn't known. There have been many theories, including:
- Invasive tissue growth. Some experts believe that endometrial cells from the lining of the uterus invade the muscle that forms the uterine walls. Uterine incisions made during an operation such as a cesarean section (C-section) might promote the direct invasion of the endometrial cells into the wall of the uterus.
- Developmental origins. Other experts suspect that endometrial tissue is deposited in the uterine muscle when the uterus is first formed in the fetus.
- Uterine inflammation related to childbirth. Another theory suggests a link between adenomyosis and childbirth. Inflammation of the uterine lining during the postpartum period might cause a break in the normal boundary of cells that line the uterus.
- Stem cell origins. A recent theory proposes that bone marrow stem cells might invade the uterine muscle, causing adenomyosis.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Adenomyosis often goes away after menopause, so treatment might depend on how close you are to that stage of life.
Treatment options for adenomyosis include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Your doctor might recommend anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), to control the pain. By starting an anti-inflammatory medicine one to two days before your period begins and taking it during your period, you can reduce menstrual blood flow and help relieve pain.
- Hormone medications. Combined estrogen-progestin birth control pills or hormone-containing patches or vaginal rings might lessen heavy bleeding and pain associated with adenomyosis. Progestin-only contraception, such as an intrauterine device, or continuous-use birth control pills often cause amenorrhea — the absence of your menstrual periods — which might provide some relief.
- Hysterectomy. If your pain is severe and no other treatments have worked, your doctor might suggest surgery to remove your uterus. Removing your ovaries isn't necessary to control adenomyosis.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Adenomyosis and Learn More about Diseases

Tape Worm

Transverse myelitis
Autonomic neuropathy
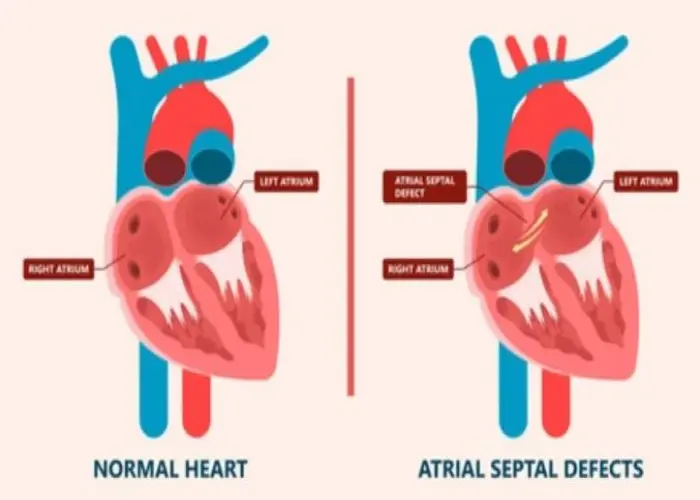
Atrial septal defect (ASD)
Post-polio syndrome

Popliteal artery aneurysm

Ear infection (middle ear)
Merkel cell carcinoma
Adenomyosis, Adenomyosis treatment, Adenomyosis uterus, Adenomyosis gallbladder, অ্যাডেনোমায়োসিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
