 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
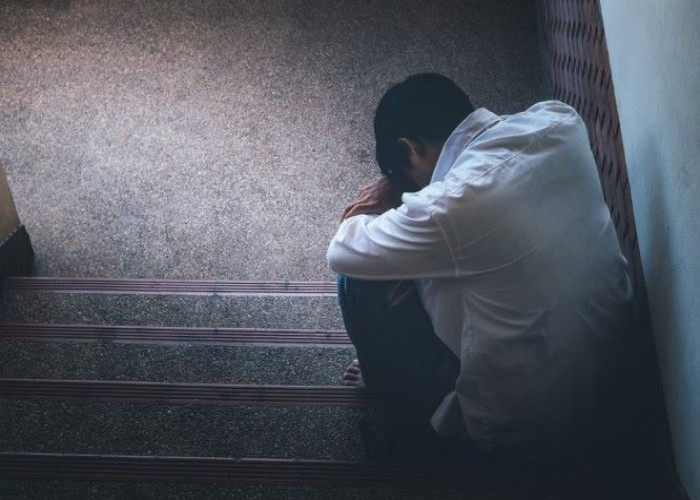
Depression (major depressive disorder)

Depression, also known as major depressive disorder, is a mental health condition that can affect a person's mood, thoughts, and behavior. It is a serious and common condition that can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life.
Symptoms of depression can include:
- Feelings of sadness, emptiness, or hopelessness
- Loss of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable
- Changes in appetite and weight
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or oversleeping
- Fatigue or loss of energy
- Feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
The causes of depression are complex and can include a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Some risk factors for developing depression include a family history of depression, experiencing a major life event or stressor, certain medical conditions, and certain medications.
Treatment for depression can involve a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. It is important for people with depression to seek help from a mental health professional, as depression can be a treatable condition with the right support and care.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Headaches
- People may feel generally miserable or unhappy without really knowing why.
- Frequent or recurrent thoughts of death
- Trouble thinking, concentrating, making decisions and remembering things
- Slowed thinking, speaking or body movements
- Reduced appetite and weight loss or increased cravings for food and weight gain
- Angry outbursts, irritability or frustration, even over small matters
- Loss of appetite
- Memory loss
- Attempts to suicide
- Anxiety, agitation or restlessness
- Anxiety
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Excessive anger
- Angry disposition
- Feelings of sadness, tearfulness, emptiness or hopelessness
- Strong depression
Disease Causes
Depression (major depressive disorder)
It's not known exactly what causes depression. As with many mental disorders, a variety of factors may be involved, such as:
- Biological differences. People with depression appear to have physical changes in their brains. The significance of these changes is still uncertain, but may eventually help pinpoint causes.
- Brain chemistry. Neurotransmitters are naturally occurring brain chemicals that likely play a role in depression. Recent research indicates that changes in the function and effect of these neurotransmitters and how they interact with neurocircuits involved in maintaining mood stability may play a significant role in depression and its treatment.
- Hormones. Changes in the body's balance of hormones may be involved in causing or triggering depression. Hormone changes can result with pregnancy and during the weeks or months after delivery (postpartum) and from thyroid problems, menopause or a number of other conditions.
- Inherited traits. Depression is more common in people whose blood relatives also have this condition. Researchers are trying to find genes that may be involved in causing depression.
Disease Prevents
Depression (major depressive disorder)
There's no sure way to prevent depression. However, these strategies may help.
- Take steps to control stress, to increase your resilience and boost your self-esteem.
- Reach out to family and friends, especially in times of crisis, to help you weather rough spells.
- Get treatment at the earliest sign of a problem to help prevent depression from worsening.
- Consider getting long-term maintenance treatment to help prevent a relapse of symptoms.
Disease Treatments
Medications and psychotherapy are effective for most people with depression. Your primary care doctor or psychiatrist can prescribe medications to relieve symptoms. However, many people with depression also benefit from seeing a psychiatrist, psychologist or other mental health professional.
If you have severe depression, you may need a hospital stay, or you may need to participate in an outpatient treatment program until your symptoms improve.
Here's a closer look at depression treatment options.
Medications
Many types of antidepressants are available, including those below. Be sure to discuss possible major side effects with your doctor or pharmacist.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Doctors often start by prescribing an SSRI. These drugs are considered safer and generally cause fewer bothersome side effects than other types of antidepressants. SSRIs include citalopram (Celexa), escitalopram (Lexapro), fluoxetine (Prozac), paroxetine (Paxil, Pexeva), sertraline (Zoloft) and vilazodone (Viibryd).
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Examples of SNRIs include duloxetine (Cymbalta), venlafaxine (Effexor XR), desvenlafaxine (Pristiq, Khedezla) and levomilnacipran (Fetzima).
- Atypical antidepressants. These medications don't fit neatly into any of the other antidepressant categories. They include bupropion (Wellbutrin XL, Wellbutrin SR, Aplenzin, Forfivo XL), mirtazapine (Remeron), nefazodone, trazodone and vortioxetine (Trintellix).
- Tricyclic antidepressants. These drugs — such as imipramine (Tofranil), nortriptyline (Pamelor), amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine (Surmontil), desipramine (Norpramin) and protriptyline (Vivactil) — can be very effective, but tend to cause more-severe side effects than newer antidepressants. So tricyclics generally aren't prescribed unless you've tried an SSRI first without improvement.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). MAOIs — such as tranylcypromine (Parnate), phenelzine (Nardil) and isocarboxazid (Marplan) — may be prescribed, typically when other drugs haven't worked, because they can have serious side effects. Using MAOIs requires a strict diet because of dangerous (or even deadly) interactions with foods ― such as certain cheeses, pickles and wines ― and some medications and herbal supplements. Selegiline (Emsam), a newer MAOI that sticks on the skin as a patch, may cause fewer side effects than other MAOIs do. These medications can't be combined with SSRIs.
- Other medications. Other medications may be added to an antidepressant to enhance antidepressant effects. Your doctor may recommend combining two antidepressants or adding medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Anti-anxiety and stimulant medications also may be added for short-term use.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is a general term for treating depression by talking about your condition and related issues with a mental health professional. Psychotherapy is also known as talk therapy or psychological therapy.
Different types of psychotherapy can be effective for depression, such as cognitive behavioral therapy or interpersonal therapy. Your mental health professional may also recommend other types of therapies. Psychotherapy can help you:
- Adjust to a crisis or other current difficulty
- Identify negative beliefs and behaviors and replace them with healthy, positive ones
- Explore relationships and experiences, and develop positive interactions with others
- Find better ways to cope and solve problems
- Identify issues that contribute to your depression and change behaviors that make it worse
- Regain a sense of satisfaction and control in your life and help ease depression symptoms, such as hopelessness and anger
- Learn to set realistic goals for your life
- Develop the ability to tolerate and accept distress using healthier behaviors
Alternate formats for therapy
Formats for depression therapy as an alternative to face-to-face office sessions are available and may be an effective option for some people. Therapy can be provided, for example, as a computer program, by online sessions, or using videos or workbooks. Programs can be guided by a therapist or be partially or totally independent.
Before you choose one of these options, discuss these formats with your therapist to determine if they may be helpful for you. Also, ask your therapist if he or she can recommend a trusted source or program. Some may not be covered by your insurance and not all developers and online therapists have the proper credentials or training.
Smartphones and tablets that offer mobile health apps, such as support and general education about depression, are not a substitute for seeing your doctor or therapist.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Depression (major depressive disorder) and Learn More about Diseases
Blastocystis hominis
Filaria

Bladder stones
Viral hemorrhagic fevers

Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)

Thoracic outlet syndrome

Cough headaches
Claudication
Depression, Major depressive disorder, Clinical depression, MDD disease, হতাশা, মেজর ডিপ্রেশিভ ডিসঅর্ডার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
