Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
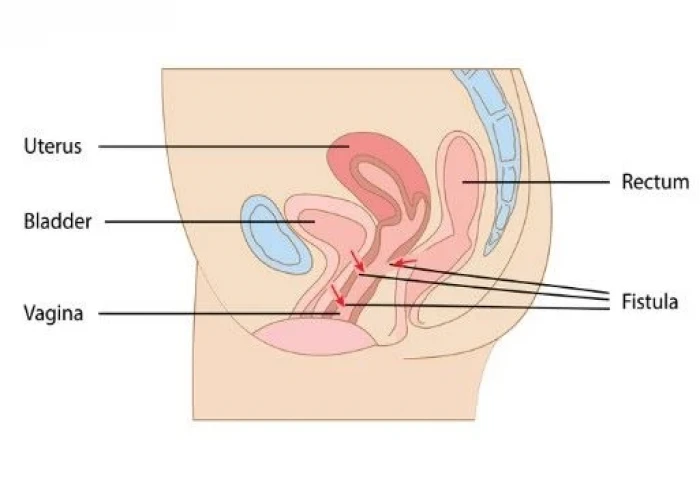
Rectovaginal fistula
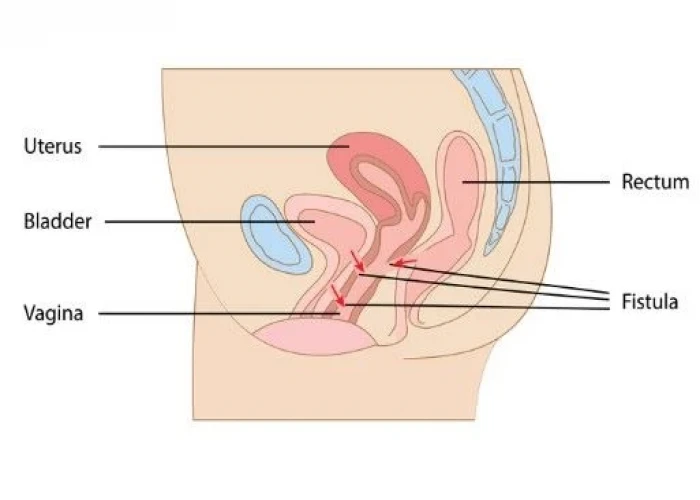
A rectovaginal fistula is an abnormal connection that develops between the rectum and the vagina, which can result in the passage of stool or gas through the vagina. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including childbirth injuries, inflammatory bowel disease, infections, or trauma.
Symptoms of a rectovaginal fistula may include fecal incontinence, vaginal discharge, recurrent urinary tract infections, pain during sex, and irritation or itching around the anus or vagina.
Treatment for rectovaginal fistula usually involves surgery to repair the connection between the rectum and vagina and restore normal bowel and vaginal function. The specific surgical procedure will depend on the size and location of the fistula and the individual's overall health and other factors.
Prevention of rectovaginal fistula involves addressing and managing underlying medical conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease or infections, that can increase the risk of developing the condition. It is also important to seek prompt medical attention if you experience symptoms of rectovaginal fistula, as early treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Gas
- Pus in stool
- Foul menstruation or vaginal discharge
- Frequent menstruation
- Painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Complication following surgery in the pelvic area
- Irritation or pain in the vulva, vagina and the area between your vagina and anus (perineum)
Disease Causes
Rectovaginal fistula
A rectovaginal fistula may form as a result of:
- Injuries during childbirth. Delivery-related injuries are the most common cause of rectovaginal fistulas. This includes tears in the perineum that extend to the bowel, or an infection of an episiotomy — a surgical incision to enlarge the perineum during vaginal delivery. These may happen following a long, difficult, or obstructed labor. These types of fistulas may also involve injury to your anal sphincter, the rings of muscle at the end of the rectum that help you hold in stool.
- Crohn's disease. The second most common cause of rectovaginal fistulas, Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease in which the digestive tract lining is inflamed. Most women with Crohn's disease never develop a rectovaginal fistula, but having Crohn's disease does increase your risk of the condition.
- Cancer or radiation treatment in your pelvic area. A cancerous tumor in your rectum, cervix, vagina, uterus or anal canal can result in a rectovaginal fistula. Radiation therapy for cancers in these areas can also put you at risk. A fistula caused by radiation usually forms within six months to two years after treatment.
- Surgery involving your vagina, perineum, rectum or anus. Prior surgery in your lower pelvic region, such as removal of your uterus (hysterectomy), in rare cases can lead to development of a fistula. The fistula may develop as a result of an injury during surgery or a leak or infection that develops afterward.
- Other causes. Rarely, a rectovaginal fistula may be caused by infections in your anus or rectum; infections of small, bulging pouches in your digestive tract (diverticulitis); long-term inflammation of your colon and rectum (ulcerative colitis); dry, hard stool that gets stuck in the rectum (fecal impaction); or vaginal injury unrelated to childbirth.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Symptoms of a rectovaginal fistula can be distressing, but treatment is often effective. Treatment for the fistula depends on its cause, size, location and effect on surrounding tissues.
Medications
Your doctor may recommend a medication to help treat the fistula or prepare you for surgery:
- Antibiotics. If the area around your fistula is infected, you may be given a course of antibiotics before surgery. Antibiotics may also be recommended for women with Crohn's disease who develop a fistula.
- Infliximab. Infliximab (Remicade) can help reduce inflammation and heal fistulas in women with Crohn's disease.
Surgery
Most people need surgery to close or repair a rectovaginal fistula.
Before an operation can be done, the skin and other tissue around the fistula must be healthy, without infection or inflammation. Your doctor may recommend waiting three to six months before having surgery to ensure the surrounding tissue is healthy and see if the fistula closes on its own.
Surgery to close a fistula may be done by a gynecologic surgeon, a colorectal surgeon or both working as a team. The goal is to remove the fistula tract and close the opening by sewing together healthy tissue. Surgical options include:
- Sewing an anal fistula plug or patch of biologic tissue into the fistula to allow your tissue to grow into the patch and heal the fistula.
- Using a tissue graft taken from a nearby part of your body or folding a flap of healthy tissue over the fistula opening.
- Repairing the anal sphincter muscles if they've been damaged by the fistula or by scarring or tissue damage from radiation or Crohn's disease.
- Performing a colostomy before repairing a fistula in complex or recurrent cases to divert stool through an opening in your abdomen instead of through your rectum. Most of the time, this surgery isn't needed. But you may need this if you've had tissue damage or scarring from previous surgery or radiation treatment, an ongoing infection or significant fecal contamination, a cancerous tumor, or an abscess. If a colostomy is needed, your surgeon may wait eight to 12 weeks before repairing the fistula. Usually after about three to six months and confirmation that your fistula has healed, the colostomy can be reversed and normal bowel function restored.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Rectovaginal fistula and Learn More about Diseases

Angiosarcoma
Aspergillosis
Wet macular degeneration
Roseola

Childhood asthma
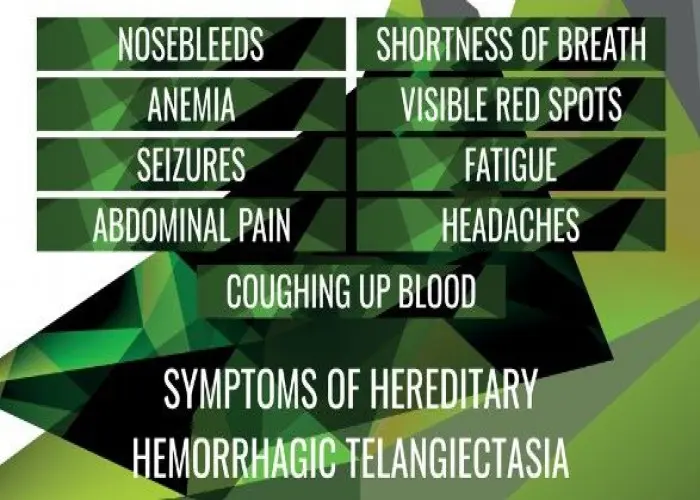
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia

Hair loss
Baby acne
rectovaginal fistula, রিকটোভজাইনাল ফিস্টুলা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.