 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Hair loss
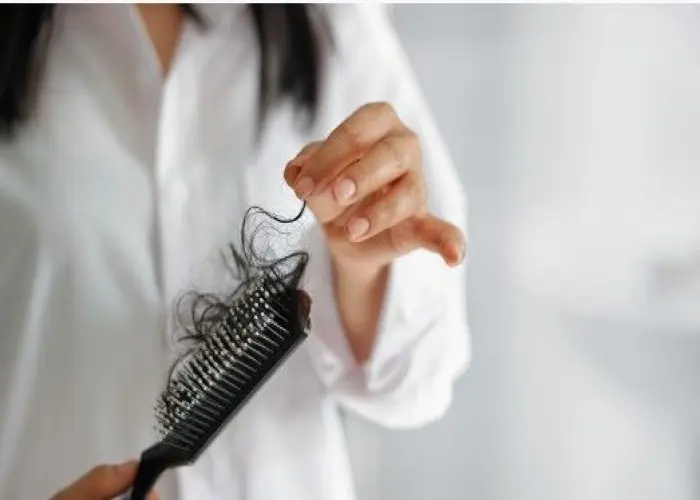

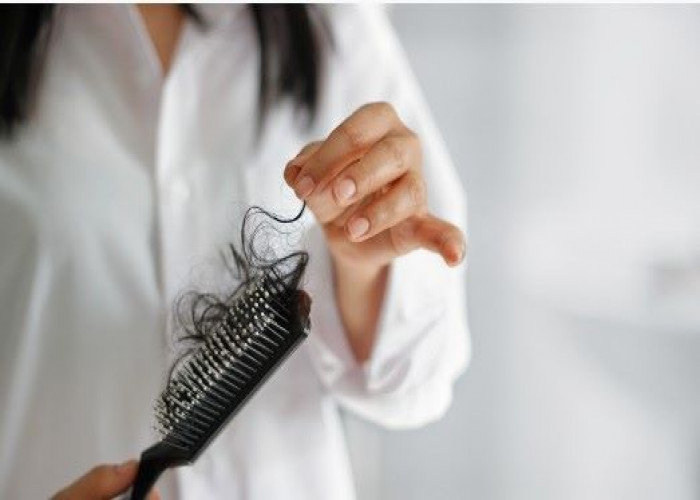
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, is a condition where an individual experiences a significant reduction in the amount of hair on their scalp or other parts of their body. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, aging, hormonal changes, certain medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors.
The most common form of hair loss in both men and women is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. This is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, which result in a gradual shrinking of hair follicles and a shorter growth phase of the hair cycle.
Other types of hair loss include alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder that causes patchy hair loss; telogen effluvium, which occurs when the body experiences significant stress or shock, causing a large number of hair follicles to enter the resting phase of the hair cycle; and traction alopecia, which is caused by repeated pulling or tension on the hair, often from tight hairstyles or hair extensions.
Treatment options for hair loss vary depending on the underlying cause. For androgenetic alopecia, medications such as minoxidil and finasteride may be used to slow down or stop hair loss, and hair transplantation surgery may be an option for those with more advanced hair loss. For other types of hair loss, treatment may include topical or oral medications, corticosteroid injections, or changes in lifestyle or hair care practices.
It's important to consult with a healthcare provider or a dermatologist if you are experiencing hair loss, as they can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Hair loss
- Hair gradual thinning on top of the head.
- In men, hair often begins to recede at the hairline on the forehead.
- Your skin may become itchy or painful before the hair falls out.
- Medical treatments, such as chemotherapy for cancer, can result in the loss of hair all over the body.
- A feeling of fullness in the abdomen that may make it uncomfortable to eat more than a little at a time
Disease Causes
Hair loss
People typically lose 50 to 100 hairs a day. This usually isn't noticeable because new hair is growing in at the same time. Hair loss occurs when new hair doesn't replace the hair that has fallen out.
Hair loss is typically related to one or more of the following factors:
- Family history (heredity). The most common cause of hair loss is a hereditary condition that happens with aging. This condition is called androgenic alopecia, male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness. It usually occurs gradually and in predictable patterns — a receding hairline and bald spots in men and thinning hair along the crown of the scalp in women.
- Hormonal changes and medical conditions. A variety of conditions can cause permanent or temporary hair loss, including hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause and thyroid problems. Medical conditions include alopecia areata (al-o-PEE-she-uh ar-e-A-tuh), which is immune system related and causes patchy hair loss, scalp infections such as ringworm, and a hair-pulling disorder called trichotillomania (trik-o-til-o-MAY-nee-uh).
- Medications and supplements. Hair loss can be a side effect of certain drugs, such as those used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, gout and high blood pressure.
- Radiation therapy to the head. The hair may not grow back the same as it was before.
- A very stressful event. Many people experience a general thinning of hair several months after a physical or emotional shock. This type of hair loss is temporary.
- Hairstyles and treatments. Excessive hairstyling or hairstyles that pull your hair tight, such as pigtails or cornrows, can cause a type of hair loss called traction alopecia. Hot-oil hair treatments and permanents also can cause hair to fall out. If scarring occurs, hair loss could be permanent.
Disease Prevents
Hair loss
Most baldness is caused by genetics (male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness). This type of hair loss is not preventable.
These tips may help you avoid preventable types of hair loss:
- Be gentle with your hair. Use a detangler and avoid tugging when brushing and combing, especially when your hair is wet. A wide-toothed comb might help prevent pulling out hair. Avoid harsh treatments such as hot rollers, curling irons, hot-oil treatments and permanents. Limit the tension on hair from styles that use rubber bands, barrettes and braids.
- Ask your doctor about medications and supplements you take that might cause hair loss.
- Protect your hair from sunlight and other sources of ultraviolet light.
- Stop smoking. Some studies show an association between smoking and baldness in men.
- If you're being treated with chemotherapy, ask your doctor about a cooling cap. This cap can reduce your risk of losing hair during chemotherapy.
Disease Treatments
Effective treatments for some types of hair loss are available. You might be able to reverse hair loss, or at least slow it. With some conditions, such as patchy hair loss (alopecia areata), hair may regrow without treatment within a year. Treatments for hair loss include medications and surgery.
Medication
If your hair loss is caused by an underlying disease, treatment for that disease will be necessary. If a certain medication is causing the hair loss, your doctor may advise you to stop using it for a few months.
Medications are available to treat pattern (hereditary) baldness. The most common options include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine). Over-the-counter (nonprescription) minoxidil comes in liquid, foam and shampoo forms. To be most effective, apply the product to the scalp skin once daily for women and twice daily for men. Many people prefer the foam applied when the hair is wet.
- Products with minoxidil help many people regrow their hair or slow the rate of hair loss or both. It'll take at least six months of treatment to prevent further hair loss and to start hair regrowth. It may take a few more months to tell whether the treatment is working for you. If it is helping, you'll need to continue using the medicine indefinitely to retain the benefits.
- Possible side effects include scalp irritation and unwanted hair growth on the adjacent skin of the face and hands.
- Finasteride (Propecia). This is a prescription drug for men. You take it daily as a pill. Many men taking finasteride experience a slowing of hair loss, and some may show new hair growth. It may take a few months to tell whether it's working for you. You'll need to keep taking it to retain any benefits. Finasteride may not work as well for men over 60.
- Rare side effects of finasteride include diminished sex drive and sexual function and an increased risk of prostate cancer. Women who are or may be pregnant need to avoid touching crushed or broken tablets.
- Other medications. Other oral options include spironolactone (Carospir, Aldactone) and oral dutasteride (Avodart).
Hair transplant surgery
In the most common type of permanent hair loss, only the top of the head is affected. Hair transplant, or restoration surgery, can make the most of the hair you have left.
During a hair transplant procedure, a dermatologist or cosmetic surgeon removes hair from a part of the head that has hair and transplants it to a bald spot. Each patch of hair has one to several hairs (micrografts and minigrafts). Sometimes a larger strip of skin containing multiple hair groupings is taken. This procedure doesn't require hospitalization, but it is painful so you'll be given a sedation medicine to ease any discomfort. Possible risks include bleeding, bruising, swelling and infection. You may need more than one surgery to get the effect you want. Hereditary hair loss will eventually progress despite surgery.
Surgical procedures to treat baldness are not usually covered by insurance.
Laser therapy
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a low-level laser device as a treatment for hereditary hair loss in men and women. A few small studies have shown that it improves hair density. More studies are needed to show long-term effects.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Hair loss and Learn More about Diseases
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)

Chronic fatigue syndrome

Lead poisoning
Personality disorders

Trigger finger
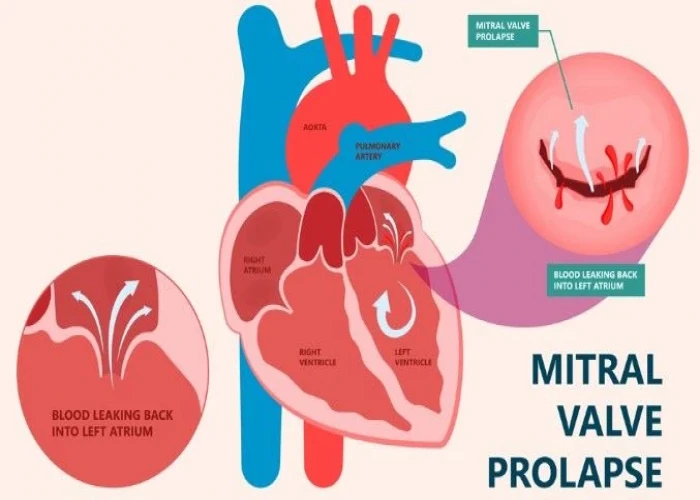
Mitral valve regurgitation

Uterine prolapse
Lupus nephritis
hair loss, চুল পরা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
