Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Gallstones
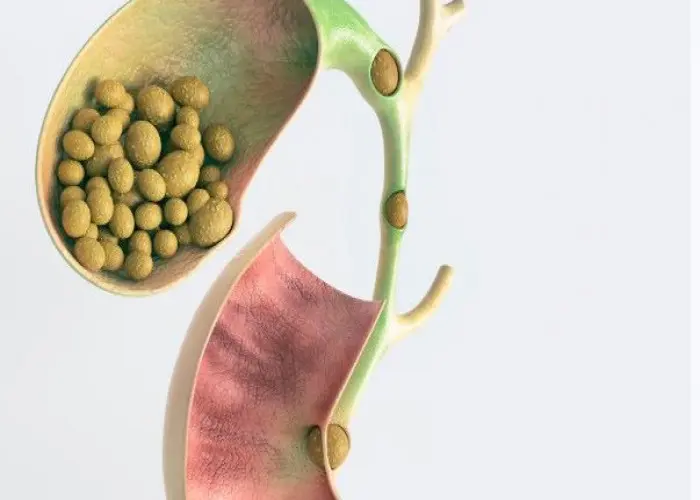
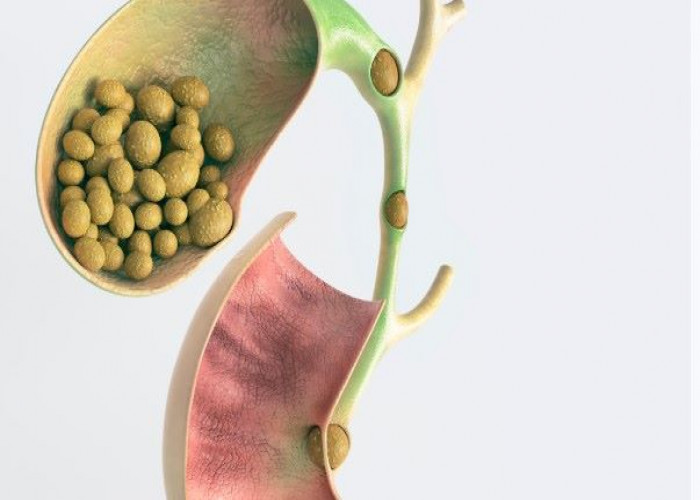
Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a fluid produced by the liver that helps digest fats in the small intestine. Gallstones can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.
There are two types of gallstones: cholesterol stones and pigment stones. Cholesterol stones are made up of hardened cholesterol, while pigment stones are made up of bilirubin and other substances. Cholesterol stones are the most common type of gallstone.
Gallstones often do not cause any symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during an imaging test for another condition. However, if a gallstone becomes lodged in the bile duct, it can cause severe pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and fever. This is known as a gallbladder attack.
Treatment for gallstones may involve medication to dissolve the stones, but in some cases, surgery to remove the gallbladder may be necessary. This is known as a cholecystectomy. Most people can lead a normal, healthy life without a gallbladder. However, they may need to make some dietary adjustments to help their body digest fat properly.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Abdomen pain
- Upper right or center abdomen pain
- Back pain
- Shoulder pain
- Nausea or vomiting
Disease Causes
Gallstones
It's not clear what causes gallstones to form. Doctors think gallstones may result when:
- Your bile contains too much cholesterol. Normally, your bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the cholesterol excreted by your liver. But if your liver excretes more cholesterol than your bile can dissolve, the excess cholesterol may form into crystals and eventually into stones.
- Your bile contains too much bilirubin. Bilirubin is a chemical that's produced when your body breaks down red blood cells. Certain conditions cause your liver to make too much bilirubin, including liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections and certain blood disorders. The excess bilirubin contributes to gallstone formation.
- Your gallbladder doesn't empty correctly. If your gallbladder doesn't empty completely or often enough, bile may become very concentrated, contributing to the formation of gallstones.
Types of gallstones
Types of gallstones that can form in the gallbladder include:
- Cholesterol gallstones. The most common type of gallstone, called a cholesterol gallstone, often appears yellow in color. These gallstones are composed mainly of undissolved cholesterol, but may contain other components.
- Pigment gallstones. These dark brown or black stones form when your bile contains too much bilirubin.
Disease Prevents
Gallstones
You can reduce your risk of gallstones if you:
- Don't skip meals. Try to stick to your usual mealtimes each day. Skipping meals or fasting can increase the risk of gallstones.
- Lose weight slowly. If you need to lose weight, go slow. Rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallstones. Aim to lose 1 or 2 pounds (about 0.5 to 1 kilogram) a week.
- Eat more high-fiber foods. Include more fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity and being overweight increase the risk of gallstones. Work to achieve a healthy weight by reducing the number of calories you eat and increasing the amount of physical activity you get. Once you achieve a healthy weight, work to maintain that weight by continuing your healthy diet and continuing to exercise.
Disease Treatments
Most people with gallstones that don't cause symptoms will never need treatment. Your doctor will determine if treatment for gallstones is indicated based on your symptoms and the results of diagnostic testing.
Your doctor may recommend that you be alert for symptoms of gallstone complications, such as intensifying pain in your upper right abdomen. If gallstone signs and symptoms occur in the future, you can have treatment.
Treatment options for gallstones include:
- Surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). Your doctor may recommend surgery to remove your gallbladder, since gallstones frequently recur. Once your gallbladder is removed, bile flows directly from your liver into your small intestine, rather than being stored in your gallbladder.
- You don't need your gallbladder to live, and gallbladder removal doesn't affect your ability to digest food, but it can cause diarrhea, which is usually temporary.
- Medications to dissolve gallstones. Medications you take by mouth may help dissolve gallstones. But it may take months or years of treatment to dissolve your gallstones in this way, and gallstones will likely form again if treatment is stopped.
- Sometimes medications don't work. Medications for gallstones aren't commonly used and are reserved for people who can't undergo surgery.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Pethidine Hydrochloride
Medicines containing pethidine hydrochloride for severe pain.
An injection should be given in the flesh.
-
Diclofenac Sodium
Medicines containing pethidine hydrochloride for severe pain.
An injection should be given in the flesh.
-
Ranitidine Hydrochloride
Diclofenac sodium is a medicine that contains ranitidine.
1 injection into the flesh for 3 days.
-
Metoclopramide Hydrochloride
Medicines containing metoclopramide for nausea or vomiting.
To be injected into the flesh.
-
Chlorpromazine Hydrochloride
Medicines containing metoclopramide for nausea or vomiting.
This injection can be given intramuscularly without using metoclomid medication. Do not use this medicine without knowing the adverse reactions or side effects.
-
Cephalexin
Medicines containing cephalexin for gall bladder infection.
1 250mg every 6 hours 1 500mg every 8 hours.
-
Cephradine
Medicines containing cephalexin for gall bladder infection.
250mg 1+1+1+1 or 500mg every 8/12 hours.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Calcarea carbonica
200 energy. Consume at hourly intervals with little water.
-
Chionanthus virginica
Q Mix 10/15 drops of the medicine in a glass of water and take one spoon every hour. Baby 4/5 drops.
-
Chelidonium majus
Q 4/5 drops.
-
Carduus marianus
Q Mix 10/15 drops of the medicine in a glass of water and take one spoon every 30 minutes.
-
Berberis vulgaris
Q Mix 10/15 drops of the medicine in a glass of water and take one spoon every hour. Children 4/5 drops.
-
Mentha piperita
6X power. 4/5 drops of medicine with little water every 5 minutes.
-
Digitalis purpurea
Q 8/10 drops in one ounce of water. Mix the medicine and take one spoon every hour. Children 3/4 drops.
Disease yoga
Gallstones and Learn More about Diseases
Colon polyps

Pet allergy
Spinal arteriovenous malformation (AVM)

Glomerulonephritis
Optic neuritis
Chagas disease
Snake bite

Pubic lice (crabs)
gallstones, পিত্ত পাথরী
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.