Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Bursitis
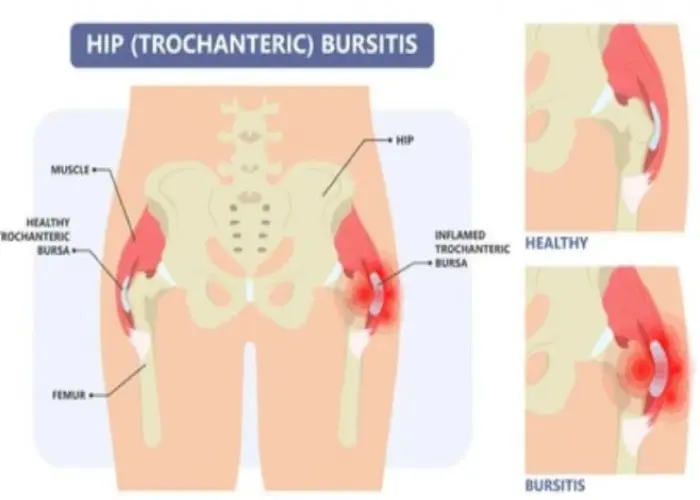
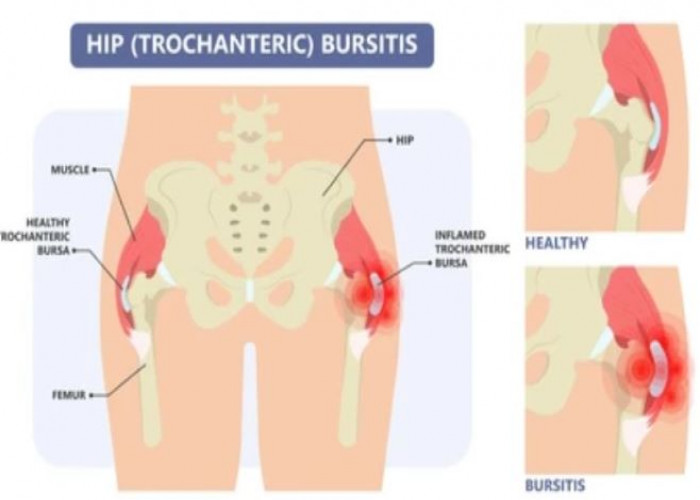
Bursitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae, which are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion and protect the joints. Bursitis can affect any joint in the body, but it is most commonly found in the shoulder, elbow, and hip. The condition can be caused by overuse or repetitive motion, injury, or infection. Symptoms of bursitis may include pain, swelling, tenderness, and limited range of motion in the affected joint. Treatment for bursitis may involve resting the affected joint, applying ice or heat, taking pain relievers, and physical therapy to improve the range of motion and strengthen the affected area. In some cases, a doctor may recommend the use of a splint or brace to immobilize the joint, or the use of corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected bursa.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen joint
- Joint pain
- Hurt more when you move it or press on it
Disease Causes
Bursitis
The most common causes of bursitis are repetitive motions or positions that put pressure on the bursae around a joint. Examples include:
- Throwing a baseball or lifting something over your head repeatedly
- Leaning on your elbows for long periods
- Extensive kneeling for tasks such as laying carpet or scrubbing floors
Other causes include injury or trauma to the affected area, inflammatory arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and infection.
Disease Prevents
Bursitis
While not all types of bursitis can be prevented, you can reduce your risk and the severity of flare-ups by changing the way you do certain tasks. Examples include:
- Using kneeling pads. Use some type of padding to reduce the pressure on your knees if your job or hobby requires a lot of kneeling.
- Lifting properly. Bend your knees when you lift. Failing to do so puts extra stress on the bursae in your hips.
- Wheeling heavy loads. Carrying heavy loads puts stress on the bursae in your shoulders. Use a dolly or a wheeled cart instead.
- Taking frequent breaks. Alternate repetitive tasks with rest or other activities.
- Maintaining a healthy weight. Being overweight places more stress on your joints.
- Exercising. Strengthening your muscles can help protect your affected joint.
- Warming up and stretching before strenuous activities to protect your joints from injury.
Disease Treatments
Bursitis generally gets better on its own. Conservative measures, such as rest, ice and taking a pain reliever, can relieve discomfort. If conservative measures don't work, you might require:
- Medication. If the inflammation in your bursa is caused by an infection, your doctor might prescribe an antibiotic.
- Therapy. Physical therapy or exercises can strengthen the muscles in the affected area to ease pain and prevent recurrence.
- Injections. A corticosteroid drug injected into the bursa can relieve pain and inflammation in your shoulder or hip. This treatment generally works quickly and, in many cases, one injection is all you need.
- Assistive device. Temporary use of a walking cane or other device will help relieve pressure on the affected area.
- Surgery. Sometimes an inflamed bursa must be surgically drained, but only rarely is surgical removal of the affected bursa necessary.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Bursitis and Learn More about Diseases
Pulmonary embolism
Cystitis
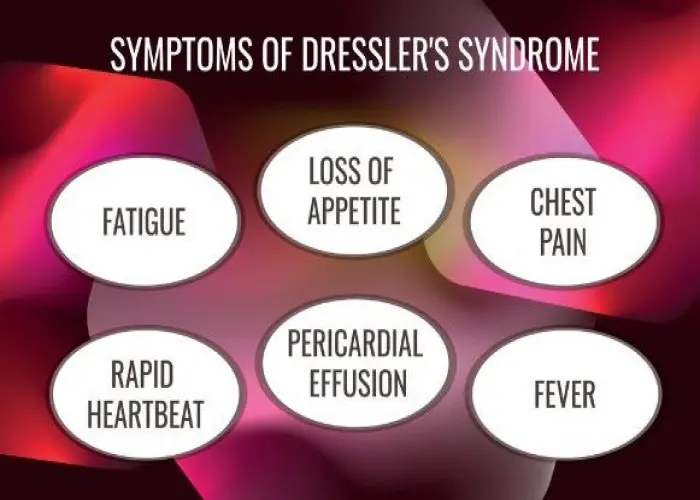
Dressler syndrome
Hepatitis C

Rett syndrome
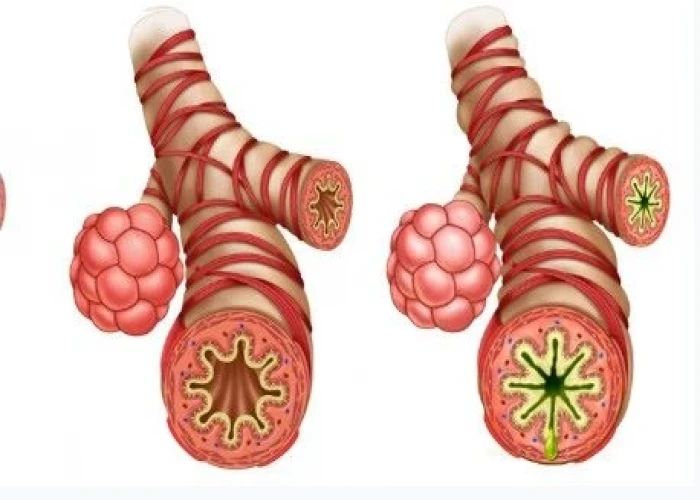
Occupational asthma
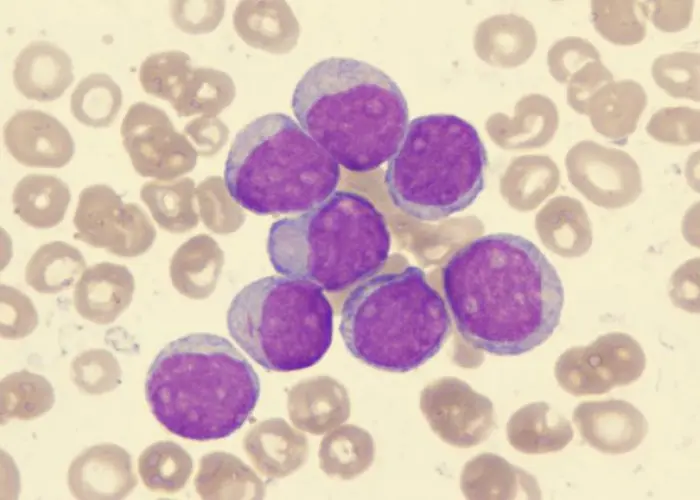
Acute myelogenous leukemia

Toe walking in children
Bursitis, Trochanteric, বার্সাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.