 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Functional dyspepsia

Functional dyspepsia is a chronic digestive disorder that affects the upper digestive tract, including the stomach and small intestine. The condition is characterized by persistent or recurring pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen, bloating, and feelings of fullness after eating, even with small meals.
The exact cause of functional dyspepsia is not known, but it is believed to be related to abnormalities in the nerves and muscles that control the digestive tract. Stress, anxiety, and certain foods or medications may also trigger symptoms.
Symptoms of functional dyspepsia may include:
- Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen
- Feeling full after eating even small amounts of food
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Acid reflux
There is no cure for functional dyspepsia, but treatment can help manage symptoms. Treatment may include changes in diet and lifestyle, such as avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller and more frequent meals, and reducing stress. Over-the-counter antacids or prescription medications may also be used to manage symptoms.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or recurring symptoms of functional dyspepsia. A healthcare professional can help diagnose the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan. They may also refer you to a specialist if additional testing or treatment is needed.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Burning stomach pain
- Stomach bite
- Swollen abdomen (Ascites)
- An early feeling of fullness (satiety) when eating
Disease Causes
Functional dyspepsia
It's not clear what causes functional dyspepsia. Doctors consider it a functional disorder, which means that routine testing may not show any abnormalities. Hence, it is diagnosed based on symptoms.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Functional dyspepsia that is long lasting and isn't controlled by lifestyle changes may require treatment. What treatment you receive depends on your signs and symptoms. Treatment may combine medications with behavior therapy.
Medications
Medications that may help in managing the signs and symptoms of functional dyspepsia include:
- Over-the-counter gas remedies. Drugs that contain the ingredient simethicone may provide some relief by reducing intestinal gas. Examples of gas-relieving remedies include Mylanta and Gas-X.
- Medications to reduce acid production. Called H-2-receptor blockers, these medications are available over-the-counter and include cimetidine (Tagamet HB), famotidine (Pepcid AC) and nizatidine (Axid AR). Stronger versions of these medications are available in prescription form.
- Medications that block acid 'pumps.' Proton pump inhibitors shut down the acid "pumps" within acid-secreting stomach cells.
- Over-the-counter proton pump inhibitors include lansoprazole (Prevacid 24HR), omeprazole (Prilosec OTC) and esopremazole (Nexium 24HR). Proton pump inhibitors are also available by prescription.
- Antibiotics. If tests indicate that a common ulcer-causing bacterium called H. pylori is present in your stomach, your doctor may recommend antibiotics in combination with acid-suppressing medication.
- Low-dose antidepressants. Tricyclic antidepressants and drugs known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, taken in low doses, may help inhibit the activity of neurons that control intestinal pain.
- Prokinetics. Prokinetic agents help your stomach empty more rapidly and may help tighten the valve between your stomach and esophagus, reducing the likelihood of upper abdominal discomfort.
- Medications to relieve nausea (anti-emetics). If you feel nauseated after eating, your doctor may recommend an anti-emetic, such as promethazine, prochlorperazine or meclizine.
Behavior therapy
Working with a counselor or therapist may help relieve signs and symptoms that aren't helped by medications. A counselor or therapist can teach you relaxation techniques that may help you cope with your signs and symptoms. You may also learn ways to reduce stress in your life to prevent functional dyspepsia from recurring.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Pancreatin
Medicines containing pancreatin for digestion.
1 serving 2/3 times daily after meals.
-
Metronidazole
If there is mango in the stool, it is better to give dysentery pills with digestive medicine.
1 pill 3 times a day after meals for 7/10 days.
-
Loperamide Hydrochloride
Some people have loose stools.
Adults take 2 capsules for the first time and then 1 capsule after each bowel movement. Not more than 8 capsules in 24 hours. If you have an occasional upset stomach, it's best to treat it with a stool test.
-
Magnesium Hydroxide
For those who do not have irregular stools or bowel movements.
Take 3/4 teaspoon of the medicine with warm water at night.
-
Lactulose
2/3 teaspoon 2/3 times a day. The dose should be reduced gradually and stopped.
-
Hyoscine Butylbromide
1/2 pill 2/3 times daily.
-
Diazepam
Drugs containing diazepam to reduce physical and mental tension.
1 pill 1/2 time a day.
-
Metoclopramide Hydrochloride
If the patient has flatulence, flatulence, frothy vomiting, metoclopramide is given before meals.
1 pill 2/3 times a day before meals.
-
Domperidone Maleate
Medicines containing domperidone for non-ulcer indigestion, i.e. heartburn, abdominal heaviness, abdominal swelling, stomach contraction-dilation.
1 pill/1 spoonful 15 minutes before meals 3 times a day for 7-10 days.
-
Vitamin B complex
for strength.
1 capsule daily in the morning and evening after food.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Functional dyspepsia and Learn More about Diseases

Peyronie's disease
Atrial fibrillation
Seborrheic dermatitis

Chronic fatigue syndrome
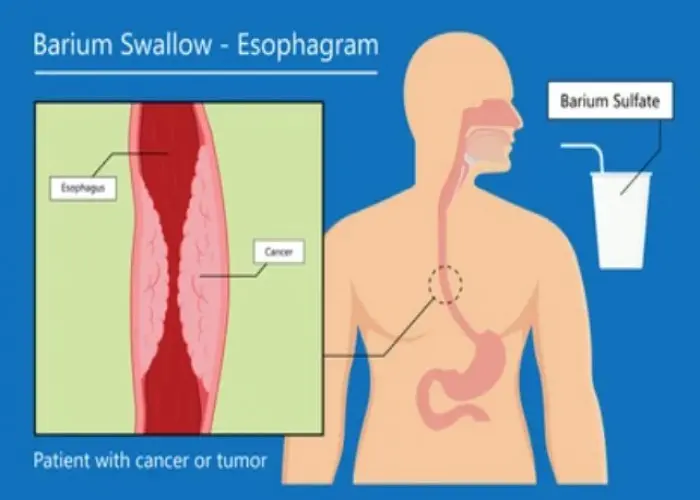
Barrett's esophagus

Hemorrhoids (Piles)

Presbyopia

Cellulitis
functional dyspepsia, কার্যকরী অজীর্ণ রোগ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
