 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis

A drug allergy is an adverse reaction that occurs when the immune system overreacts to a medication. In other words, it is an allergic reaction to a drug that leads to symptoms such as rash, hives, itching, swelling, or breathing difficulties.
Drug allergies are not the same as side effects, which are more common and less severe. Side effects are often predictable and can be anticipated, whereas drug allergies are unpredictable and can occur even with a very small dose of the medication.
It's important to note that not all adverse reactions to medications are due to drug allergies. Some reactions may be caused by other factors such as drug interactions, the medication itself, or underlying medical conditions.
If you suspect that you have a drug allergy, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to confirm the diagnosis and receive appropriate treatment. In some cases, an allergy to one medication may indicate a higher risk of developing an allergy to other medications in the same class, so it's important to be aware of any known drug allergies and inform healthcare providers before taking new medications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Joint pain
- Swollen joint
- Swollen knee
- Knee pain
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Joint swelling is common but is often first noticed in larger joints such as the knee.
- In some cases, high fever, swollen lymph nodes or a rash on the trunk may occur which is usually worse in the evenings.
- A fever that is often is higher than 102.2 F (39 C) and lasts more than three days
Disease Causes
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis occurs when the body's immune system attacks its own cells and tissues. It's not known why this happens, but both heredity and environment seem to play a role.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment for juvenile idiopathic arthritis focuses on helping your child maintain a normal level of physical and social activity. To accomplish this, doctors may use a combination of strategies to relieve pain and swelling, maintain full movement and strength, and prevent complications.
Medications
The medications used to help children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis are chosen to decrease pain, improve function and minimize potential joint damage.
Typical medications include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These medications, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve), reduce pain and swelling. Side effects include stomach upset and, much less often, kidney and liver problems.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Doctors use these medications when NSAIDs alone fail to relieve symptoms of joint pain and swelling or if there is a high risk of damage in the future.
- DMARDs may be taken in combination with NSAIDs and are used to slow the progress of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The most commonly used DMARD for children is methotrexate (Trexall, Xatmep, others). Side effects of methotrexate may include nausea, low blood counts, liver problems and a mild increased risk of infection.
- Biologic agents. Also known as biologic response modifiers, this newer class of drugs includes tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers, such as etanercept (Enbrel, Erelzi, Eticovo), adalimumab (Humira), golimumab (Simponi) and infliximab (Remicade, Inflectra, others). These medications can help reduce systemic inflammation and prevent joint damage. They may be used with DMARDs and other medications.
- Other biologic agents work to suppress the immune system in slightly different ways, including abatacept (Orencia), rituximab (Rituxan, Truxima, Ruxience), anakinra (Kineret) and tocilizumab (Actemra). All biologics can increase the risk of infection.
- Corticosteroids. Medications such as prednisone may be used to control symptoms until another medication takes effect. They are also used to treat inflammation when it is not in the joints, such as inflammation of the sac around the heart.
- These drugs can interfere with normal growth and increase susceptibility to infection, so they generally should be used for the shortest possible duration.
Therapies
Your doctor may recommend that your child work with a physical therapist to help keep joints flexible and maintain range of motion and muscle tone.
A physical therapist or an occupational therapist may make additional recommendations regarding the best exercise and protective equipment for your child.
A physical or occupational therapist may also recommend that your child make use of joint supports or splints to help protect joints and keep them in a good functional position.
Surgery
In very severe cases, surgery may be needed to improve joint function.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis and Learn More about Diseases
Rocky Mountain spotted fever

Reactive attachment disorder

Retrograde ejaculation
Amoebic Dysentry
Gout
Hemifacial spasm
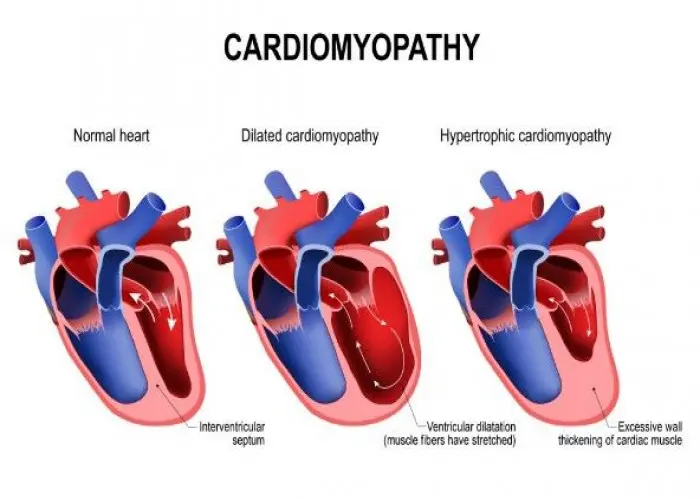
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Heart palpitations
juvenile idiopathic arthritis, কিশোর ইডিয়োপ্যাথিক বাত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
