 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Borderline personality disorder

Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a mental health condition characterized by persistent and unstable patterns of thinking, mood, and behavior. Individuals with BPD may experience intense and unstable emotions, have difficulty with interpersonal relationships, engage in impulsive or self-destructive behaviors, and have an unstable sense of self. The exact cause of BPD is not known, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic, neurobiological, and environmental factors. Treatment options may include psychotherapy, medication, or a combination of these approaches. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a type of psychotherapy that is often used to treat BPD, as it focuses on developing skills to regulate emotions, manage distress, and improve interpersonal relationships. It is important to work closely with a mental health professional to manage BPD and prevent potential complications, such as self-harm or suicide.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Unusual behavior
- Mental disorder
- Personality disorder
- Suicidal threats or behavior or self-injury, often in response to the fear of separation or rejection
- Wide mood swings lasting from a few hours to a few days, which can include intense happiness, irritability, shame or anxiety
- Ongoing feelings of emptiness
- Inappropriate, intense anger, such as frequently losing your temper, being sarcastic or bitter, or having physical fights
Disease Causes
Borderline personality disorder
As with other mental health disorders, the causes of borderline personality disorder aren't fully understood. In addition to environmental factors — such as a history of child abuse or neglect — borderline personality disorder may be linked to:
- Genetics. Some studies of twins and families suggest that personality disorders may be inherited or strongly associated with other mental health disorders among family members.
- Brain abnormalities. Some research has shown changes in certain areas of the brain involved in emotion regulation, impulsivity and aggression. In addition, certain brain chemicals that help regulate mood, such as serotonin, may not function properly.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Borderline personality disorder is mainly treated using psychotherapy, but medication may be added. Your doctor also may recommend hospitalization if your safety is at risk.
Treatment can help you learn skills to manage and cope with your condition. It's also necessary to get treated for any other mental health disorders that often occur along with borderline personality disorder, such as depression or substance misuse. With treatment, you can feel better about yourself and live a more stable, rewarding life.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy — also called talk therapy — is a fundamental treatment approach for borderline personality disorder. Your therapist may adapt the type of therapy to best meet your needs. The goals of psychotherapy are to help you:
- Focus on your current ability to function
- Learn to manage emotions that feel uncomfortable
- Reduce your impulsiveness by helping you observe feelings rather than acting on them
- Work on improving relationships by being aware of your feelings and those of others
- Learn about borderline personality disorder
Types of psychotherapy that have been found to be effective include:
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). DBT includes group and individual therapy designed specifically to treat borderline personality disorder. DBT uses a skills-based approach to teach you how to manage your emotions, tolerate distress and improve relationships.
- Schema-focused therapy. Schema-focused therapy can be done individually or in a group. It can help you identify unmet needs that have led to negative life patterns, which at some time may have been helpful for survival, but as an adult are hurtful in many areas of your life. Therapy focuses on helping you get your needs met in a healthy manner to promote positive life patterns.
- Mentalization-based therapy (MBT). MBT is a type of talk therapy that helps you identify your own thoughts and feelings at any given moment and create an alternate perspective on the situation. MBT emphasizes thinking before reacting.
- Systems training for emotional predictability and problem-solving (STEPPS). STEPPS is a 20-week treatment that involves working in groups that incorporate your family members, caregivers, friends or significant others into treatment. STEPPS is used in addition to other types of psychotherapy.
- Transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP). Also called psychodynamic psychotherapy, TFP aims to help you understand your emotions and interpersonal difficulties through the developing relationship between you and your therapist. You then apply these insights to ongoing situations.
- Good psychiatric management. This treatment approach relies on case management, anchoring treatment in an expectation of work or school participation. It focuses on making sense of emotionally difficult moments by considering the interpersonal context for feelings. It may integrate medications, groups, family education and individual therapy.
Medications
Although no drugs have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration specifically for the treatment of borderline personality disorder, certain medications may help with symptoms or co-occurring problems such as depression, impulsiveness, aggression or anxiety. Medications may include antidepressants, antipsychotics or mood-stabilizing drugs.
Talk to your doctor about the benefits and side effects of medications.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Borderline personality disorder and Learn More about Diseases
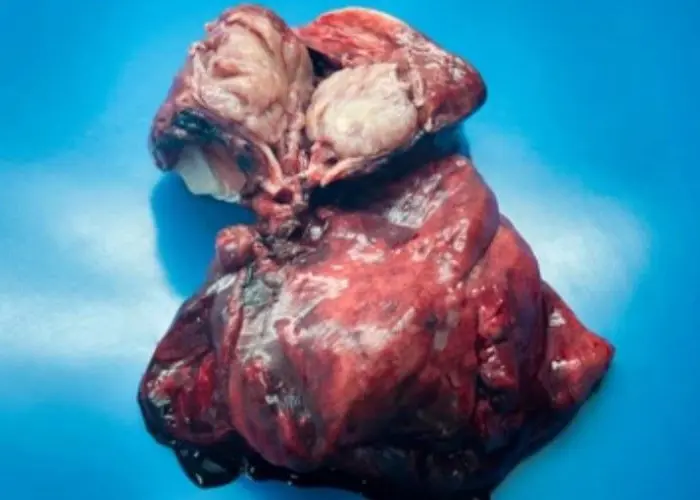
Carcinoid tumors

Selective IgA deficiency
Crohn's disease
Baby acne
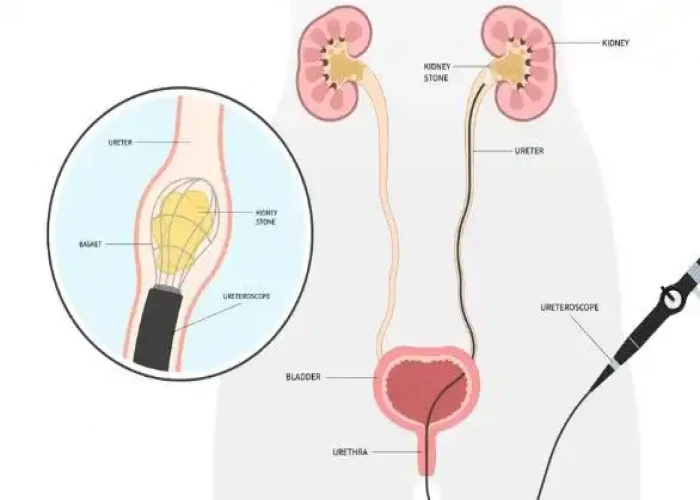
Ureteral obstruction
Erectile dysfunction

Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
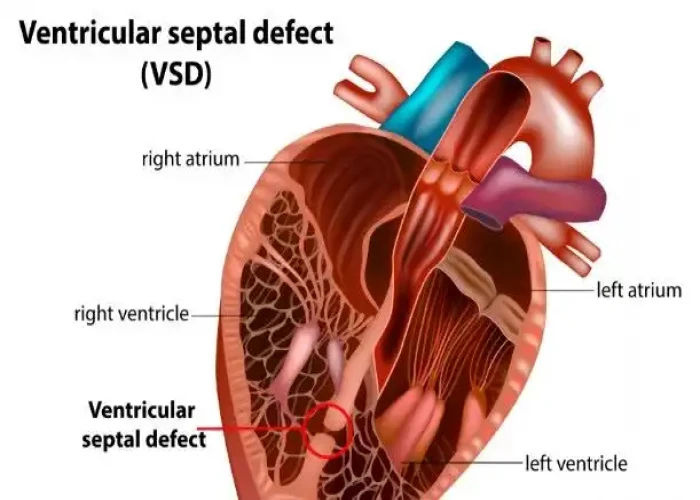
Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
Borderline personality disorder, BPD symptoms, Mentalization based treatment, বর্ডারলাইন পার্সোনালিটি ডিজঅর্ডার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
