Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Hemangioma
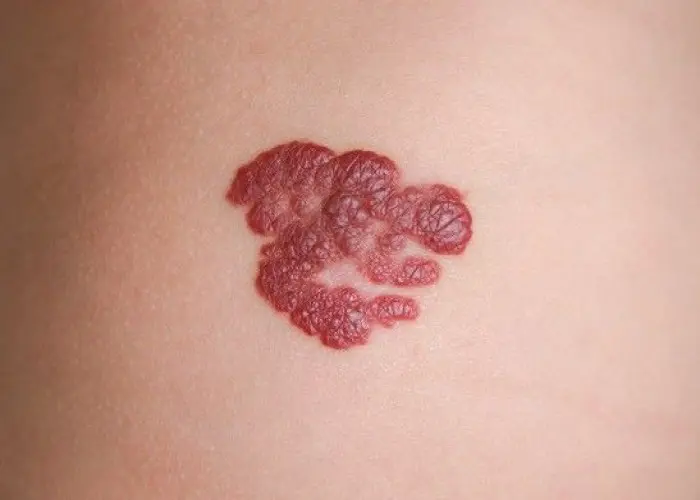
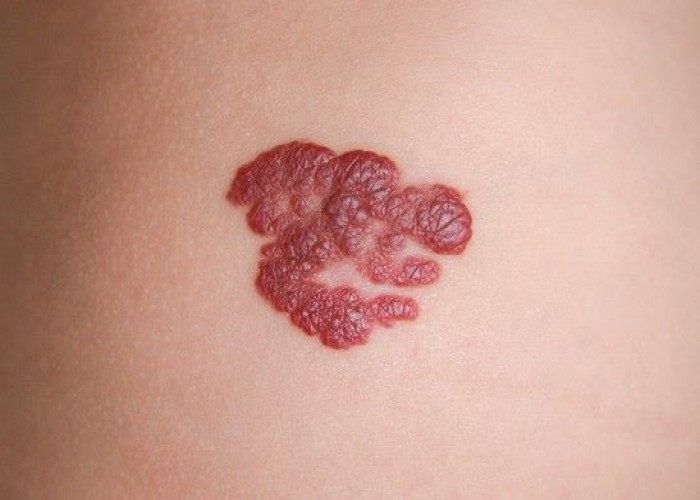
A hemangioma is a type of non-cancerous (benign) growth that is made up of an abnormal collection of blood vessels. It is a common type of birthmark that typically appears as a bright red or purple lesion on the skin, often on the face, scalp, or back of the neck.
Hemangiomas can occur in people of all ages, but they are most common in infants and young children. In most cases, hemangiomas are harmless and do not cause any symptoms. They often grow rapidly in the first few months of life, and then gradually shrink and disappear over time, usually by the age of 10 years old.
In some cases, a hemangioma can cause complications, particularly if it is located in certain areas of the body, such as the eyes, mouth, or airway. Complications can include visual impairment, feeding difficulties, breathing problems, and bleeding. If a hemangioma is causing significant symptoms or affecting normal function, medical treatment may be necessary.
Treatment for hemangiomas may involve medication or surgical intervention, depending on the location, size, and severity of the lesion. Some hemangiomas may be treated with topical or oral medications that can help to shrink the lesion, while others may require surgery to remove the affected tissue.
If you or your child has a hemangioma, it is important to have it evaluated by a healthcare provider. While most hemangiomas are harmless and do not require treatment, your healthcare provider can help to determine if any further evaluation or intervention is necessary.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Red skin
- Skin lesions
Disease Causes
Hemangioma
A hemangioma is made up of extra blood vessels that group together into a dense clump. What causes the vessels to clump isn't known.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treating hemangiomas usually isn't necessary because they go away on their own with time. But if a hemangioma affects vision or causes other problems, treatments include medications or laser surgery:
- Beta blocker drugs. In small, superficial hemangiomas, a gel containing the drug timolol may be applied to the affected skin. A severe infantile hemangioma may disappear if treated with an oral solution of propranolol. Treatment usually needs to be continued until about 1 year of age. Side effects can include high blood sugar, low blood pressure and wheezing.
- Corticosteroid medications. For children who don't respond to beta blocker treatments or can't use them, corticosteroids may be an option. They can be injected into the nodule or applied to the skin. Side effects can include poor growth and thinning of the skin.
- Laser surgery. Sometimes laser surgery can remove a small, thin hemangioma or treat sores on a hemangioma.
If you're considering treatment for your child's hemangioma, weigh the pros and cons with your child's doctor. Consider that most infantile hemangiomas disappear on their own during childhood and that treatments have potential side effects.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Hemangioma and Learn More about Diseases

Male breast cancer
Myelofibrosis

Throat cancer
Ureteral cancer

Dandruff
Adrenal cancer
Voice disorders

Reactive attachment disorder
hemangioma, হেম্যানজিওমা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.