Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Syphilis - Homeopathic remedies
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Syphilis can affect various parts of the body, including the genitals, anus, mouth, and skin. The infection is transmitted through direct contact with a syphilis sore during sexual activity.
Syphilis has four stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Symptoms vary depending on the stage of the infection.
In the primary stage, a painless sore or ulcer, called a chancre, appears at the site of infection. The sore may be located on the genitals, anus, or mouth. The sore usually heals on its own after a few weeks, even without treatment.
In the secondary stage, a rash may appear on the skin, along with flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. These symptoms may go away on their own, but without treatment, the infection can progress to the latent and tertiary stages.
During the latent stage, the infection is still present but there are no visible symptoms. However, the infection can still be transmitted to others during this stage.
In the tertiary stage, the infection can cause serious health problems, including damage to the heart, brain, nerves, and other organs. This stage can occur years or even decades after the initial infection.
Syphilis is treated with antibiotics, usually penicillin. The type and length of treatment depend on the stage of the infection. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you suspect that you may have syphilis or have been exposed to someone with syphilis. The earlier syphilis is diagnosed and treated, the more effective the treatment will be. Additionally, practicing safe sex can help prevent the spread of syphilis and other STIs.
Spleen and liver swelling
Meningitis
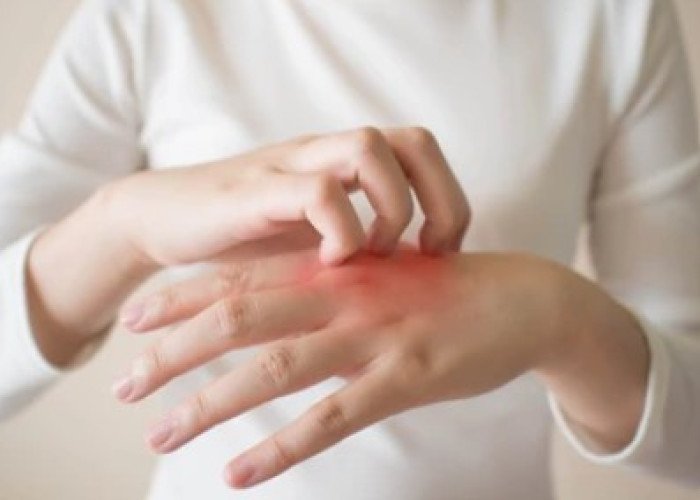
Itching

Erysipelas

Sensuality

Typhoid fever

Burned by fire
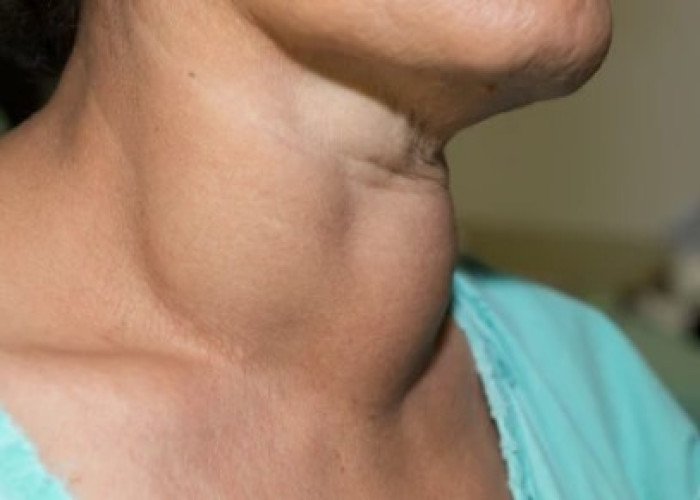
Goitre
Syphilis, সিফিলিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.