Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Hernia - Homeopathic remedies
Hernia refers to a medical condition characterized by the protrusion of an organ or tissue through the wall of the cavity that normally contains it. Hernias can occur in various parts of the body, including the abdomen, groin, diaphragm, and even the brain.
The most common type of hernia is an inguinal hernia, which occurs in the groin area. It happens when part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. Other types of hernias include femoral hernias, umbilical hernias, hiatal hernias, and incisional hernias.
The symptoms of hernias vary depending on the location and severity of the hernia. In general, people with hernias may experience pain, discomfort, or pressure in the affected area, as well as a visible bulge or swelling. Some people may also experience nausea, vomiting, or constipation if the hernia is obstructing the intestine.
Treatment for hernias typically involves surgery to repair the weakened area of the muscle wall. In some cases, a hernia may not need immediate treatment, especially if it is small and not causing any symptoms. However, hernias can worsen over time, and complications such as incarceration and strangulation can occur, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
To reduce the risk of developing a hernia, it is important to maintain a healthy weight, avoid heavy lifting or straining, and to address any underlying medical conditions that may increase the risk of hernias, such as chronic coughing or constipation.
Stiff feet

Hiccups
Whooping cough
Gland is hard as stone
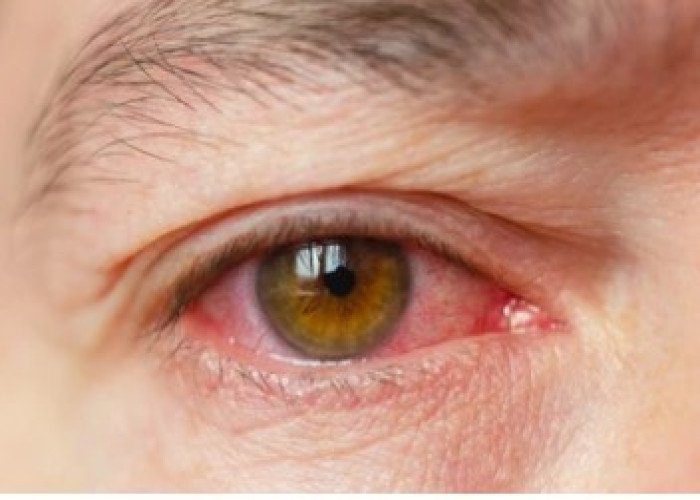
Eye inflammation
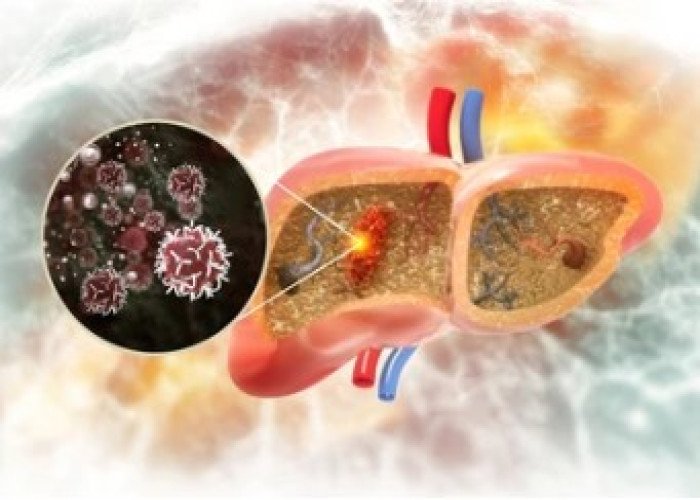
Liver cancer
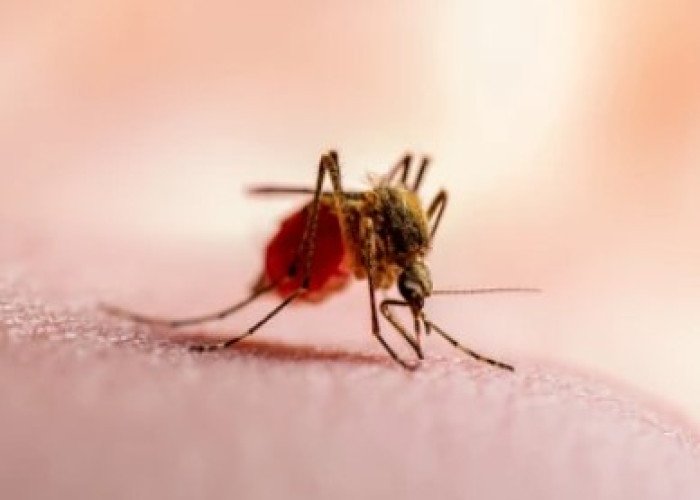
Malaria fever

Obesity
Hernia, হার্নিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.