Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Whooping cough - Homeopathic remedies
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. It is characterized by severe coughing spells that are often followed by a "whoop" sound as the person gasps for air. The cough can be so severe that it may cause vomiting, exhaustion, and even broken ribs.
Whooping cough primarily affects infants and young children who have not yet been fully vaccinated. It is spread through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The incubation period for the disease is typically 7-10 days, but can range from 4-21 days.
Symptoms of whooping cough typically begin with a runny nose, sneezing, and a mild cough. After about a week or two, the cough becomes more severe and may be accompanied by thick mucus. The characteristic "whoop" sound is most common in children, but may not be present in adults. Infants under 6 months of age may not develop the typical symptoms, but may experience periods of apnea (pauses in breathing) or cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin).
Complications of whooping cough can be severe and life-threatening, particularly in infants and young children. These may include pneumonia, seizures, encephalopathy (brain inflammation), and even death. Treatment usually involves antibiotics to help clear the infection and reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent whooping cough, and is recommended for all children and adults.
In summary, whooping cough is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. It primarily affects infants and young children who have not yet been fully vaccinated, and is characterized by severe coughing spells that may be accompanied by a "whoop" sound. Complications can be severe and life-threatening, particularly in young children. Treatment involves antibiotics and vaccination is the most effective way to prevent the disease.

Vomiting bile

Squint eyed

Sadness
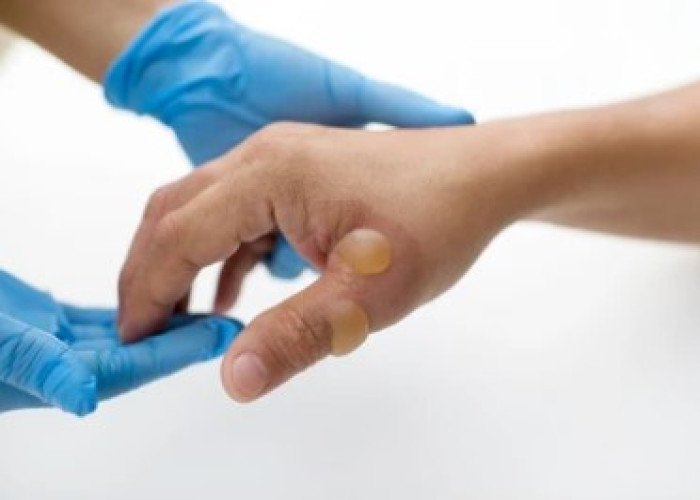
Blisters

Profuse sweating
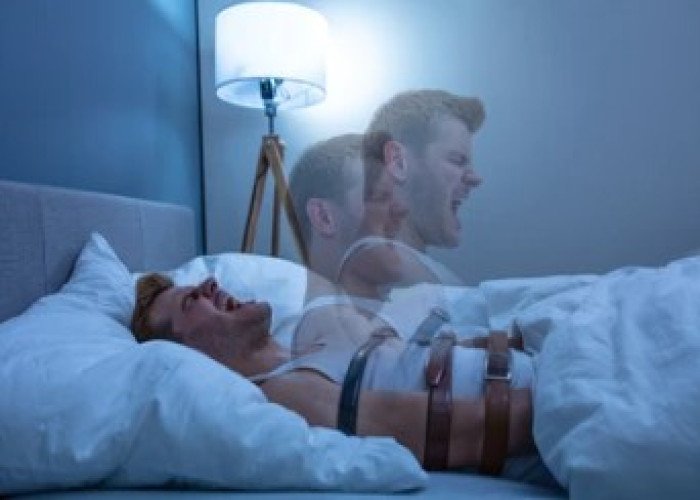

Sleep paralysis
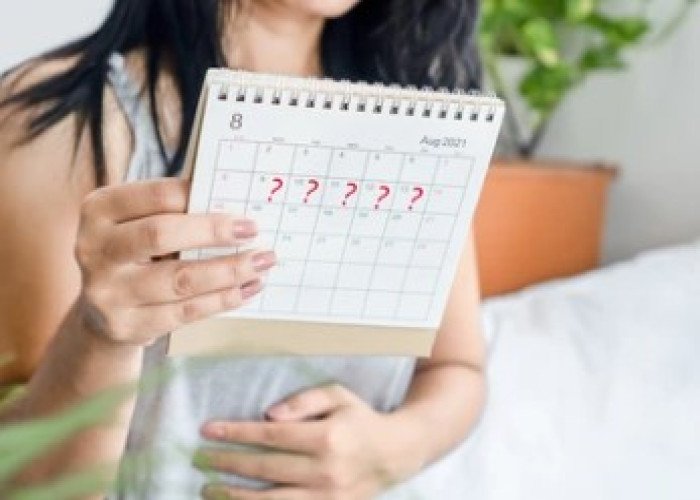

Irregular menstruation
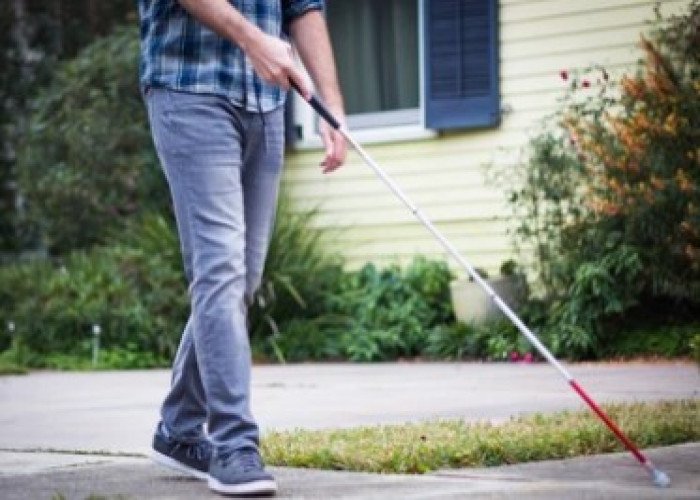

Blindness
Whooping cough, হুপিংকাশি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.