 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Bone and Joint Infections - Generics
Bone and joint infections, also known as musculoskeletal infections, refer to infections that occur in bones, joints, and surrounding tissues. These infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. Common bone and joint infections include osteomyelitis (infection of bone), septic arthritis (infection of joint), and soft tissue infections (infection of muscle, skin, or tendon).
Symptoms of bone and joint infections may include pain, redness, swelling, warmth, and stiffness in the affected area. In severe cases, the patient may also develop fever, chills, fatigue, and decreased mobility.
Treatment of bone and joint infections usually involves a combination of antibiotics, surgery, and supportive care. Antibiotics are used to eliminate the infection, while surgery may be needed to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue. Supportive care may include pain management, physical therapy, and rehabilitation.
Prevention of bone and joint infections involves good hygiene, proper wound care, and early treatment of infections or other conditions that increase the risk of developing these infections.

Corticosteroid-responsive...

Infiltration anesthesia

Superficial wounds

Infections
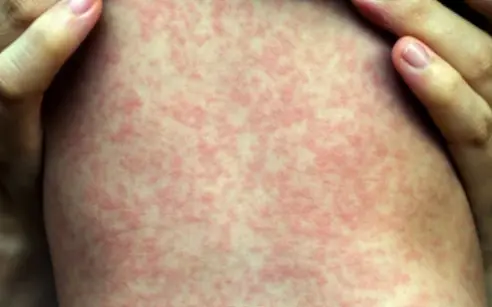
Prevention of measles

Myocardial infarction

Infantile eczema
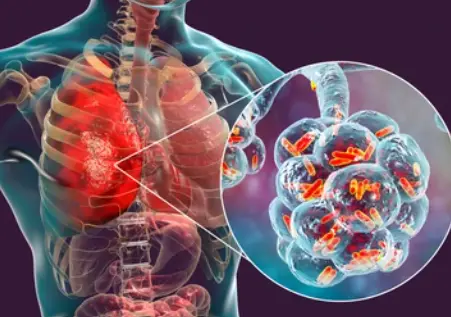
Aspiration pneumonia
Bone and Joint Infections, হাড় এবং জয়েন্ট ইনফেকশন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.