 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Ulcers - Yoga remedies
Ulcers are sores that can occur on the lining of the digestive tract, including the stomach, small intestine, and esophagus. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection with the bacteria Helicobacter pylori, long-term use of certain medications, and lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and stress.
Symptoms of ulcers can include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and changes in appetite. If left untreated, ulcers can lead to serious complications such as bleeding, perforation of the digestive tract, and an increased risk of stomach cancer.
Treatment for ulcers typically involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. Medications may include antibiotics to treat H. pylori infection, acid reducers to reduce stomach acid production, and drugs to protect the lining of the digestive tract. Lifestyle changes may include avoiding alcohol and smoking, reducing stress, and eating a healthy diet.
If you are experiencing symptoms of an ulcer, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. In some cases, additional testing such as endoscopy may be necessary to diagnose an ulcer or to monitor the healing process.
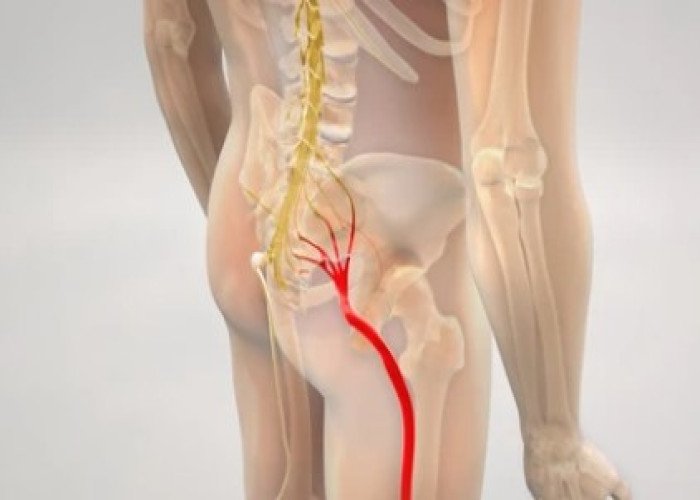
Sciatica
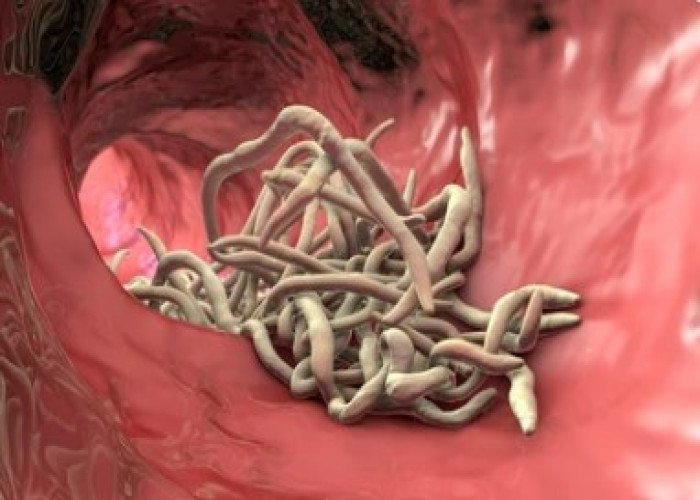
Worm
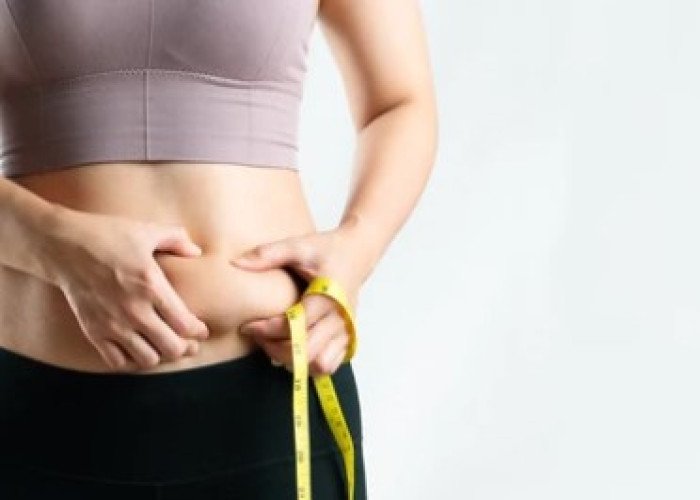

Belly fat
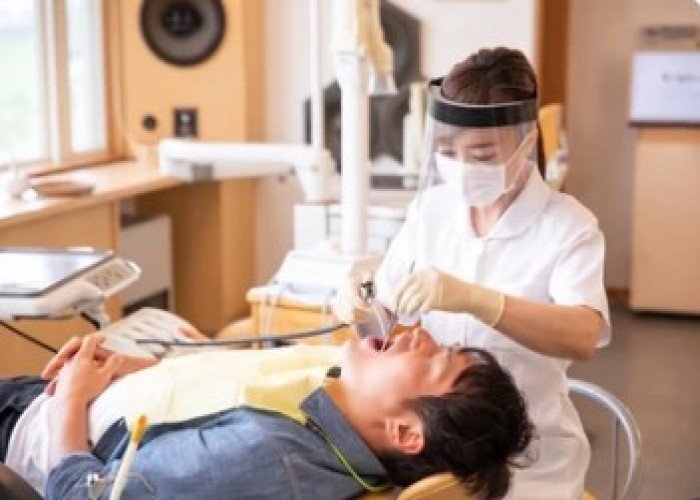
Pyorrhea

Anemia

N/A

Colic
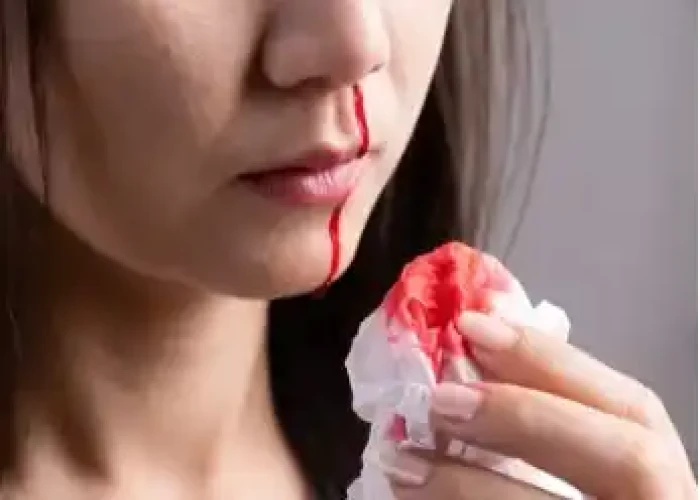

Bleeding from nose
Ulcers, অন্ত্রক্ষত, আলসার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
