 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Tonsils - Yoga remedies
Tonsils are two masses of tissue located at the back of the throat, one on each side. They are part of the body's immune system and help to filter out bacteria and other germs that enter through the mouth and nose. Tonsils can become infected or inflamed, a condition known as tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection. Symptoms may include sore throat, difficulty swallowing, swollen glands in the neck, fever, and a yellow or white coating on the tonsils. Treatment for tonsillitis typically involves rest, pain relief, and antibiotics if the cause is bacterial.
In some cases, recurrent or chronic tonsillitis may require tonsillectomy, which is the surgical removal of the tonsils. This procedure is usually reserved for cases where the tonsils are causing significant health problems, such as obstructive sleep apnea or frequent infections that do not respond to other treatments.
Tonsillitis is more common in children, but adults can also develop the condition. Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding contact with people who are sick, can help to prevent the spread of tonsillitis.

Mucus or phlegm
Laziness

Mind is restless
Ulcers

Asthma
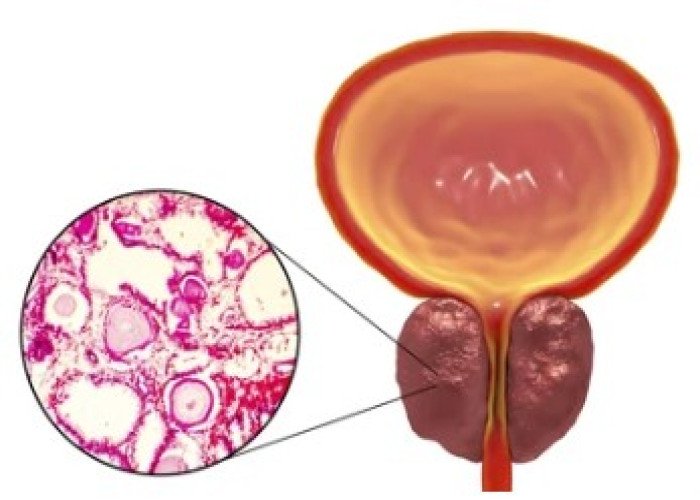
Prostate gland enlargemen...

Cough

Insanity
Tonsils, টনসিল
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.