 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Loading...
Mucus or phlegm Generics
Mucus or phlegm - Yoga remedies
Mucus or phlegm is a thick, sticky substance produced by the mucous membranes that line the respiratory tract, including the nose, throat, and lungs. It plays an important role in protecting the respiratory system from harmful irritants, such as dust, bacteria, and viruses.
However, excessive production of mucus or phlegm can be a symptom of an underlying condition, such as:
- Cold or flu: During a cold or flu, the body produces more mucus to help flush out the virus.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to pollen, dust, or pet dander can cause the body to produce more mucus.
- Sinusitis: Sinusitis is a condition that causes inflammation of the sinuses and excessive mucus production.
- Asthma: Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that can cause excess mucus production and difficulty breathing.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): COPD is a progressive lung disease that can cause excess mucus production and difficulty breathing.
To manage excess mucus or phlegm, you can try the following:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water and herbal tea, can help thin out mucus and make it easier to cough up.
- Use a humidifier: Using a humidifier can help moisten the air, making it easier to breathe and reducing mucus production.
- Nasal irrigation: Nasal irrigation, also known as a saline rinse, can help flush out excess mucus from the nasal passages.
- Over-the-counter medication: Over-the-counter medications, such as decongestants and expectorants, can help reduce mucus production and make it easier to cough up.
- Address underlying conditions: Treating the underlying condition that is causing excess mucus or phlegm is important for managing this symptom.
If excess mucus or phlegm persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, cough, or difficulty breathing, it is important to seek medical attention.
Bronchitis
N/A

Arthritis in hand
N/A
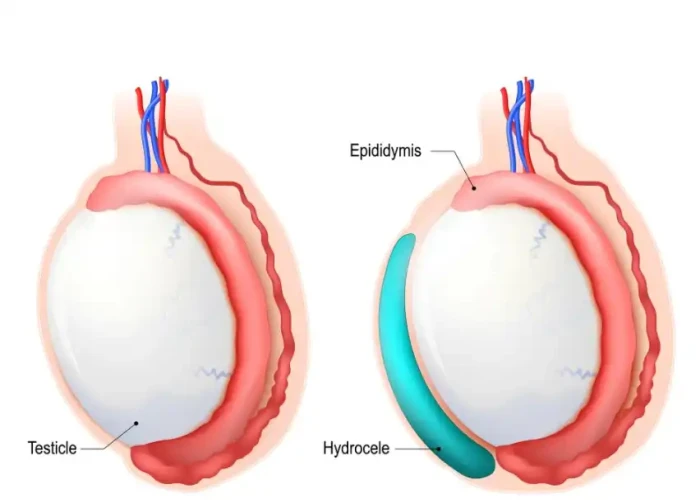
Hydrocele
N/A
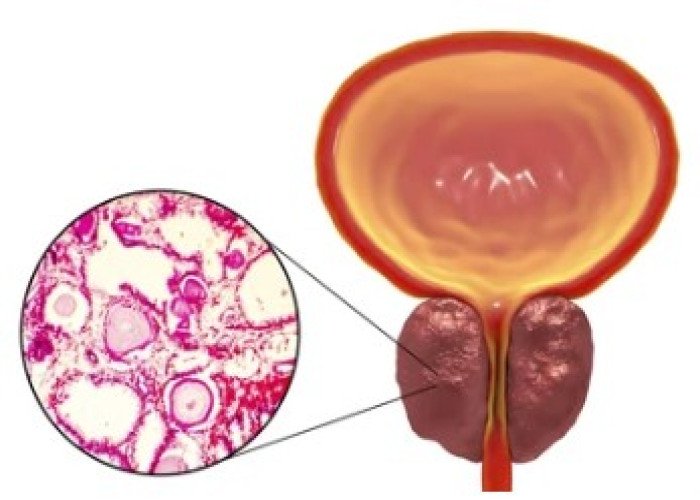
Prostate gland enlargemen...
N/A
Colon inflammation
N/A
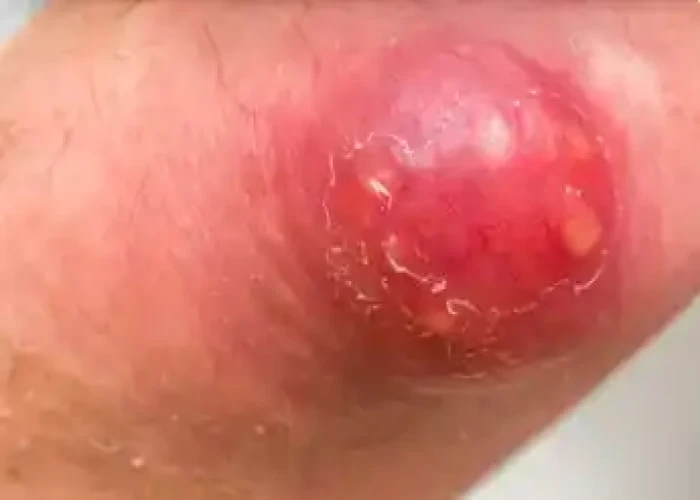
Boil
N/A

Maternal gland is weak
N/A

Sick
N/A
Searching Keywords Idea
Mucus or phlegm, শ্লেষ্মা বা কফ
Bangladesh is Number One in Digital Medical Management.
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
