 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Bronchitis - Yoga remedies
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that carry air to your lungs. It can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis usually develops from a cold or other respiratory infection and typically lasts a few days to a week or so. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is a long-term condition characterized by a persistent cough and excess mucus production.
The most common symptoms of bronchitis include coughing (with or without mucus), wheezing, chest discomfort or pain, fatigue, and sometimes fever. Acute bronchitis usually goes away on its own, but treatment may be needed for chronic bronchitis. Treatment options include medications to relieve symptoms, antibiotics (if the bronchitis is caused by a bacterial infection), and lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and avoiding irritants like air pollution or chemical fumes.

Nervousness
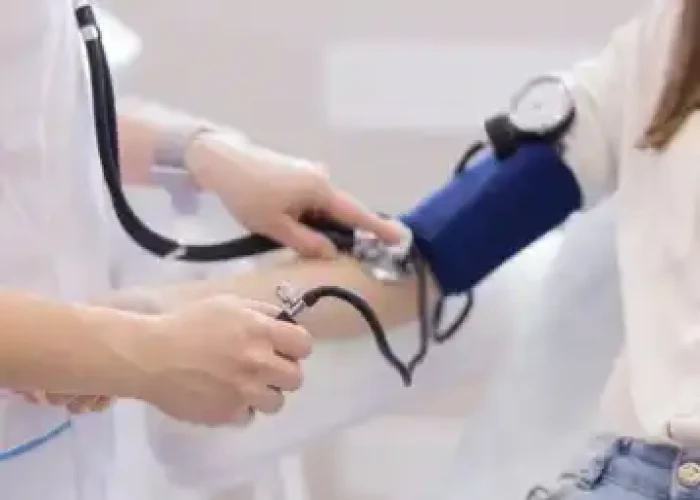
Low blood pressure
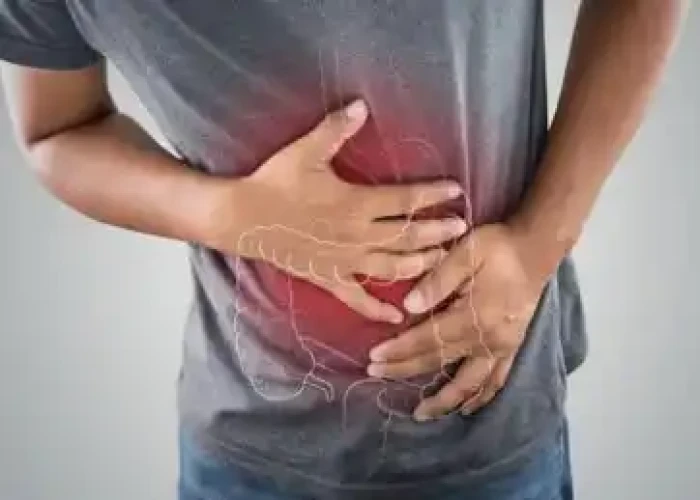
Diarrhea
Laziness

Loss of appetite

Cold
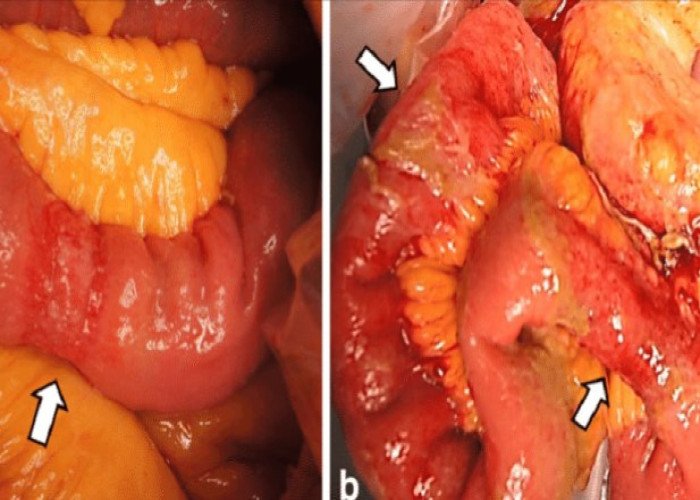
Intestinal boils

Slimness
Bronchitis, ব্রঙ্কাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.