 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Deafness - Yoga remedies
Deafness, or hearing loss, is a condition that affects a person's ability to hear sounds or speech. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, exposure to loud noise, aging, infections, and certain medications.
There are two main types of deafness: conductive deafness and sensorineural deafness. Conductive deafness occurs when there is a problem with the outer or middle ear that prevents sound from reaching the inner ear. Sensorineural deafness occurs when there is damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve, which can be caused by aging, exposure to loud noise, certain medications, or other factors.
Symptoms of deafness may include difficulty hearing sounds or speech, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and difficulty understanding speech in noisy environments. Deafness can also have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, causing social isolation, communication difficulties, and depression.
Treatment for deafness may include hearing aids, cochlear implants, or other assistive listening devices. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove damaged tissue in the ear. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have hearing loss, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and improve outcomes.
Preventing deafness involves protecting your ears from loud noise, such as by wearing earplugs or earmuffs when working in noisy environments, listening to music at a reasonable volume, and avoiding the use of earbuds or headphones for extended periods of time. It is also important to manage underlying medical conditions that may contribute to hearing loss, such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
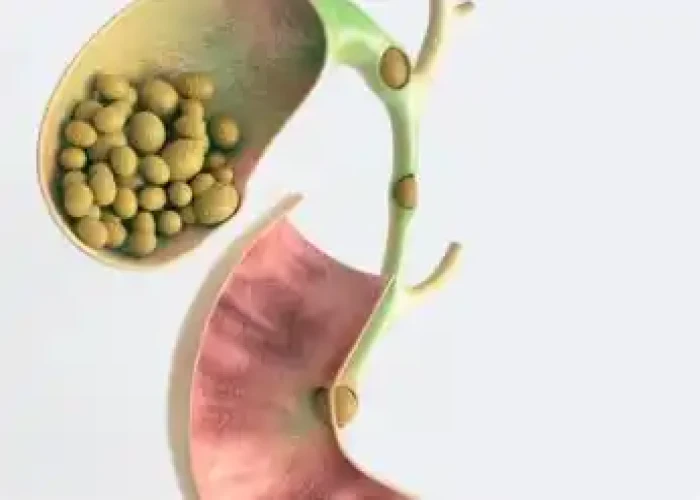

Gallstones

Muscle weakness
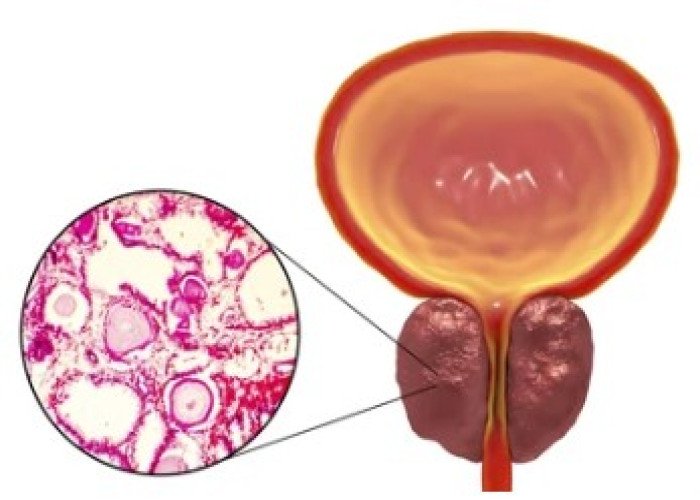
Prostate gland enlargemen...
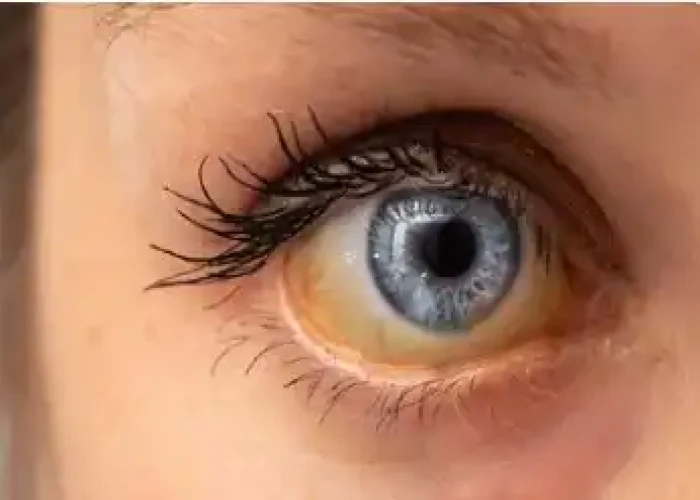
Jaundice

Muscle spasms
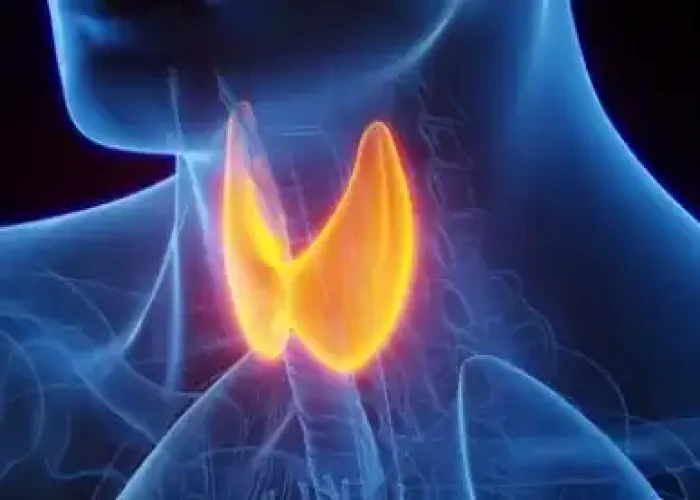
Glandular weakness

Predominant discharge
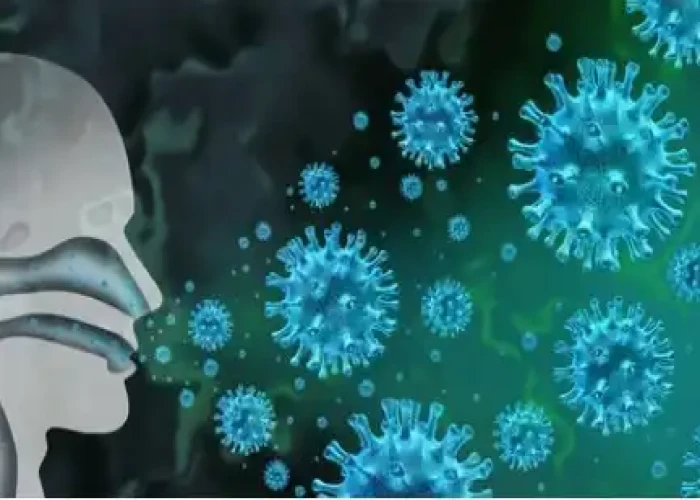

Influenza
Deafness, বধিরতা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.