 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Vulva - Diseases
The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia. It is located between the legs and includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vaginal opening, and urethral opening.
The vulva serves several functions, including protection of the internal reproductive organs, sexual pleasure, and urine elimination. It is also an important part of the female reproductive system and plays a role in childbirth.
The mons pubis is a rounded mound of fatty tissue located over the pubic bone. The labia majora are the outer folds of skin surrounding the vulva, and the labia minora are the inner folds of skin. The clitoris is a small, sensitive organ located at the front of the vulva, and it is important in sexual arousal and orgasm.
The vaginal opening is located between the labia minora and is the entrance to the vagina. The urethral opening is located above the vaginal opening and is the exit point for urine.
Various medical conditions can affect the vulva, including vulvitis, vulvodynia, and vulvar cancer. Treatment for these conditions may include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's circumstances. Good hygiene practices and regular gynecological exams are important for maintaining vulvar health.
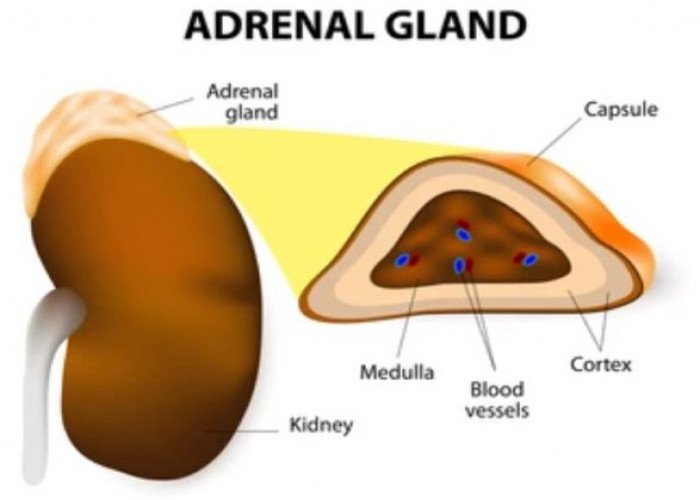
Adrenal glands
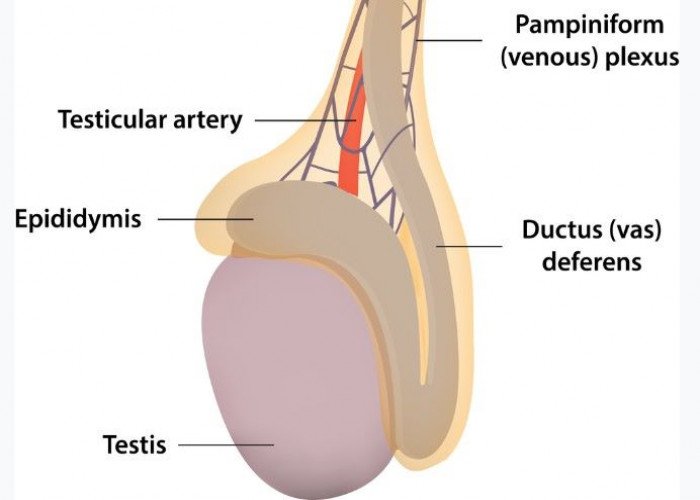
Vas deferens
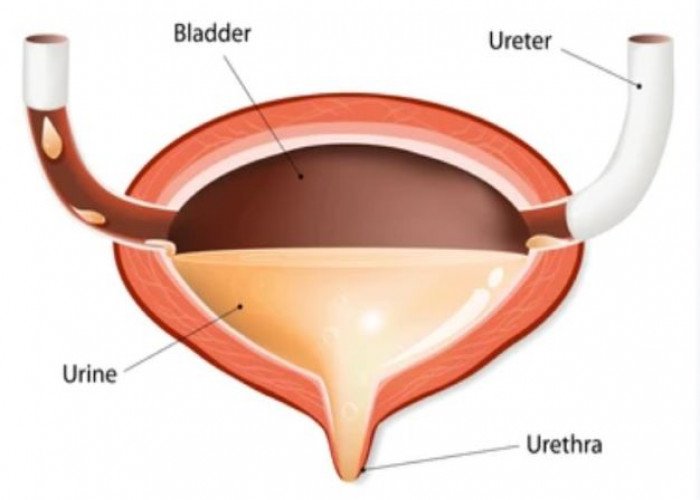
Urethra

Iris Eye
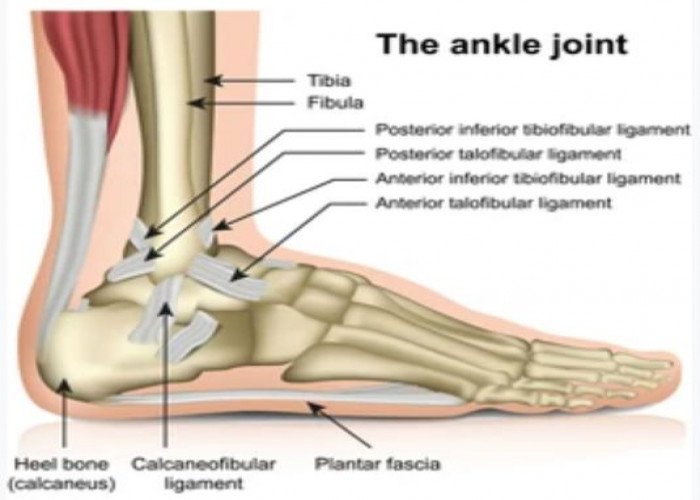
Ankle

Mouth
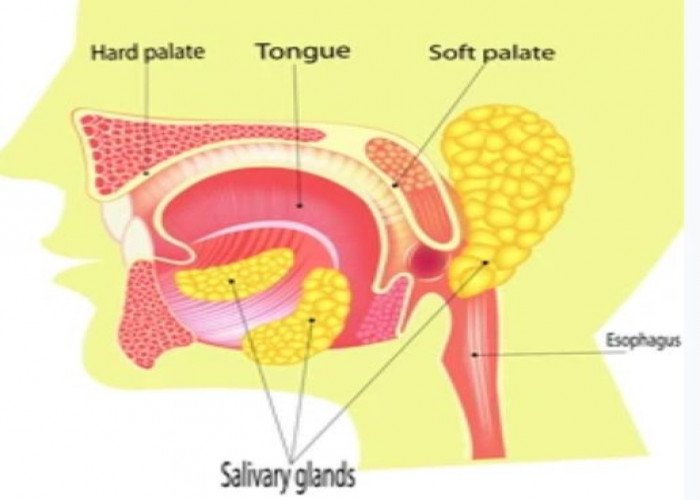
Salivary glands

Retina Eye
Vulva, Itchy vaginal area, Labia majora, Vulva meaning, ভলভা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.