 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Epididymis - Diseases
The epididymis is a coiled tube that is part of the male reproductive system. It is located on the posterior aspect of each testicle and is connected to the vas deferens, which transports sperm from the testicles to the urethra.
The epididymis is composed of three parts: the head, the body, and the tail. Sperm produced in the testicles travel through the epididymis, where they mature and are stored until they are ready to be ejaculated.
During its journey through the epididymis, sperm undergo a series of changes that allow them to become fully motile and capable of fertilizing an egg. These changes are facilitated by the fluid and secretions produced by the epididymal cells.
The epididymis is a highly specialized and essential part of the male reproductive system, and any damage or blockage to this structure can result in infertility or other reproductive problems. Infections, injury, and certain medical conditions can all affect the function of the epididymis and may require medical intervention to restore normal reproductive function.
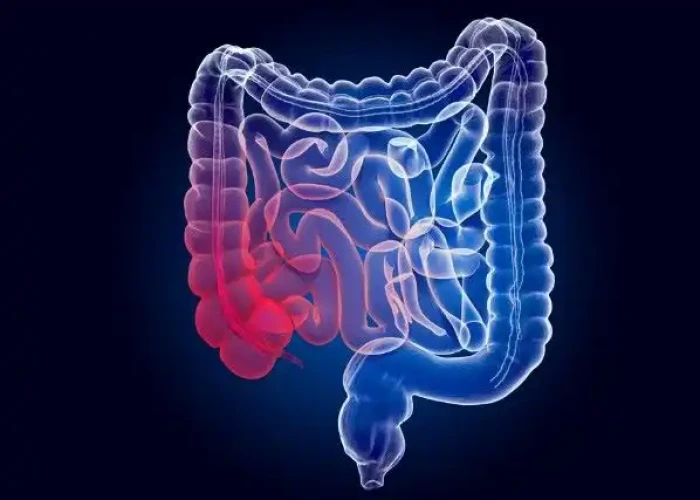
Duodenum intestine

Rectum
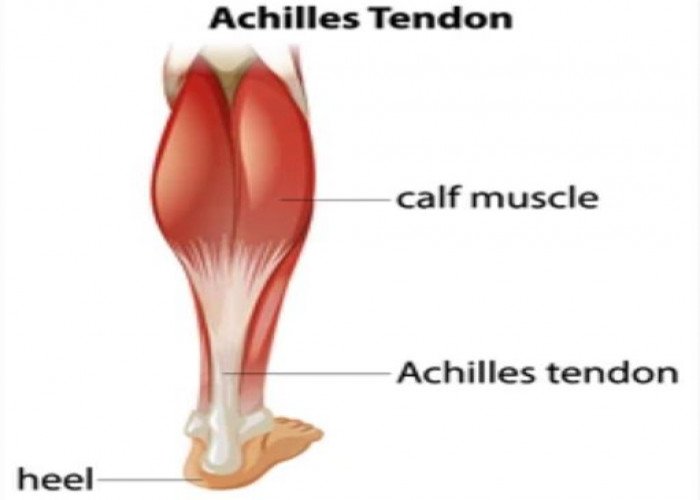
Tendons
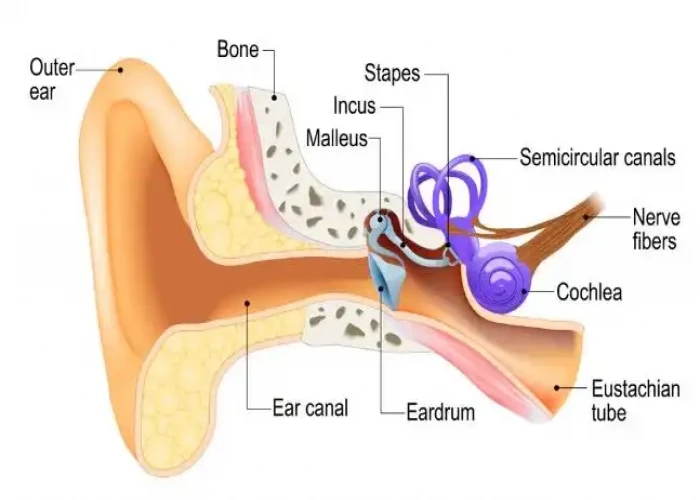
Ossicles Middle ear
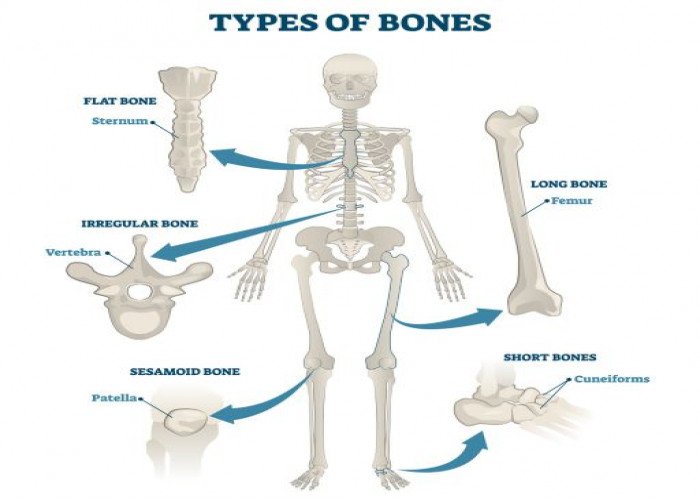
Bones
Transverse colon intestine
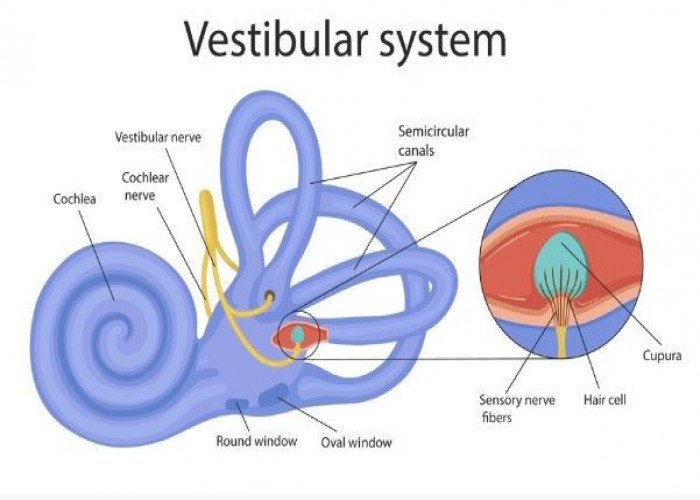
Vestibule of the Inner ear
Jaw
Epididymis, Spermatoceles, Cystic epididymis, এপিডিডাইমিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.