 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Appendix - Diseases
The appendix is a small, finger-like organ that is attached to the cecum, which is the beginning of the large intestine. It is located in the lower right side of the abdomen. The appendix is a vestigial organ, meaning that it is a remnant of a structure that was once functional in our evolutionary past, but now has no known important role in the body.
The function of the appendix is not well understood, but it is believed to play a role in immune system function and the maintenance of gut bacteria. However, it is not essential for survival, and it can be removed without causing any significant health problems.
In some cases, the appendix can become inflamed, a condition known as appendicitis. Appendicitis is usually caused by a blockage in the appendix, which leads to the growth of bacteria and inflammation. The symptoms of appendicitis include abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting. If left untreated, appendicitis can cause the appendix to rupture, which can lead to a serious infection in the abdomen. The treatment for appendicitis is typically surgical removal of the appendix, a procedure called an appendectomy.
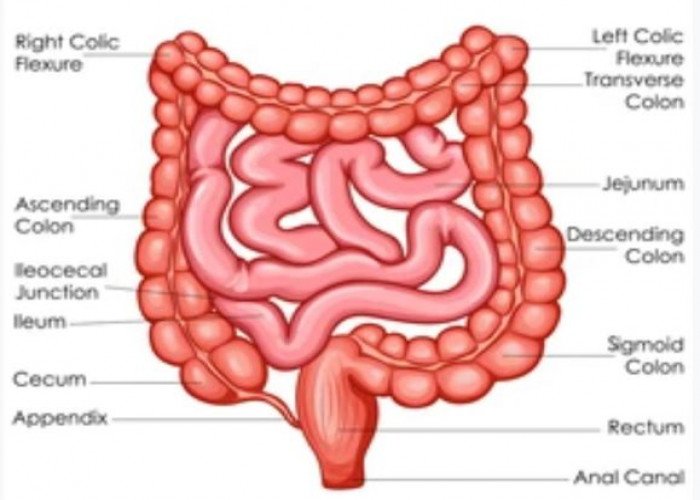
Intestine

Muscles
Shoulder

Bulbourethral glands
Muscles of breathing
Jaw

Hand

Mental
Appendix, Appendicitis, Appendectomy, Appendix meaning, এ্যাপেন্ডিক্স
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.