Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Cor Pulmonale
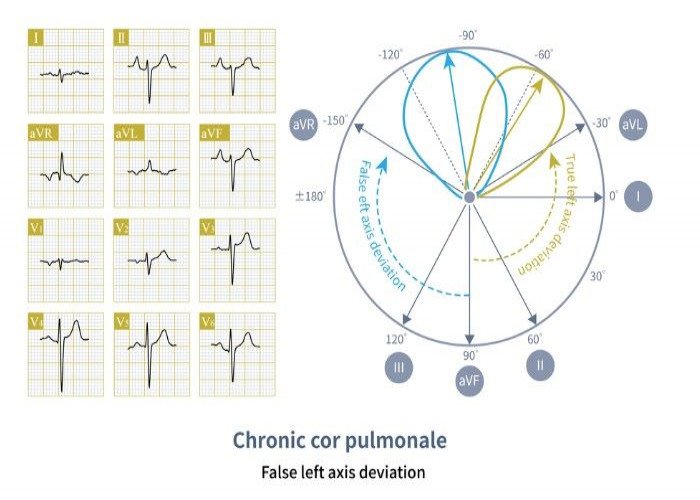
Cor pulmonale, also known as pulmonary heart disease, is a condition that occurs when the right side of the heart becomes enlarged or weakened due to long-term high blood pressure in the pulmonary artery and lungs. This increased pressure is often caused by chronic lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary embolism, or pulmonary fibrosis.
The symptoms of cor pulmonale can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but may include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Fatigue or weakness
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness or fainting
Diagnosis of cor pulmonale may involve a combination of tests, such as an echocardiogram, electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, and pulmonary function tests.
Treatment for cor pulmonale typically focuses on managing the underlying lung condition and improving symptoms of heart failure. This may involve the use of oxygen therapy, diuretics to reduce fluid buildup, and medications such as vasodilators or blood thinners to improve blood flow and reduce the risk of blood clots.
In some cases, surgery or other interventions such as a pulmonary thromboendarterectomy may be necessary to treat underlying conditions such as pulmonary embolism or pulmonary hypertension.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent symptoms of cor pulmonale, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Lack of sleep (Sleep apnea)
- Frequent urination
- Fainting (syncope)
- Swollen leg
- Chest pain
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or faintness
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Cor Pulmonale
Disease Causes
Cor Pulmonale
High blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs is called pulmonary hypertension. It is the most common cause of cor pulmonale.
In people who have pulmonary hypertension, changes in the small blood vessels inside the lungs can lead to increased blood pressure in the right side of the heart. This makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the lungs. If this high pressure continues, it puts a strain on the right side of the heart. That strain can cause cor pulmonale.
Lung conditions that cause a low blood oxygen level in the blood over a long time can also lead to cor pulmonale. Some of these are:
- Autoimmune diseases that damage the lungs, such as scleroderma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Chronic blood clots in the lungs
- Cystic fibrosis (CF)
- Severe bronchiectasis
- Scarring of the lung tissue (interstitial lung disease)
- Severe curving of the upper part of the spine (kyphoscoliosis)
- Obstructive sleep apnea, which causes stops in breathing because of airway inflammation
- Idiopathic (no specific cause) tightening (constriction) of the blood vessels of the lungs
- Severe left-sided heart failure
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Ampicillin Sodium
High potency end antibiotics should be taken.
1 service every 8 hours.
-
Doxycycline Hydrochloride
1 capsule 2 times a day for 8-10 days.
-
Cephalexin
A high-potency antibiotic should be taken first.
1 capsule after 6 hours for 7-10 days or 1+1+1.
-
Ciprofloxacin
A high-potency antibiotic should be taken first.
1+1+1.
-
Clobazam
Medicines containing clobazam for restlessness, sleep, anxiety, depression etc.
1 pill 2 times a day.
-
Diazepam
Medicines containing clobazam for restlessness, sleep, anxiety, depression etc.
1 pill 2/3 times a day.
-
Aminophylline
Medication containing aminophylline for patient's respiratory distress.
1 2/3 times a day after meals or Aminomol-R 1/2 pill 1 time a day.
-
Theophylline
1 each 2 times a day. Older adults: Unicontin 1/2+0+1/2 or just 1/2 pill at night.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Cor Pulmonale and Learn More about Diseases

Persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)

Mammary duct ectasia

Drug addiction (substance use disorder)

Tendinitis

Suspicious breast lumps
Ischemic colitis

Tetanus
Myasthenia gravis
cor pulmonale, ফুসফুসীয় হৃদরোগ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.