 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Radiation sickness

Radiation sickness, also known as acute radiation syndrome (ARS), is a group of symptoms that can occur when a person is exposed to high levels of ionizing radiation in a short period of time, typically in a nuclear or radiological emergency. The severity of the symptoms depends on the amount of radiation exposure.
Symptoms of radiation sickness can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, fatigue, fever, skin burns, hair loss, and reduced organ function. These symptoms can occur within minutes to days after exposure and can become more severe over time. In severe cases, radiation sickness can lead to death within days or weeks.
Treatment for radiation sickness depends on the severity of the symptoms and the level of radiation exposure. In mild cases, treatment may involve medications to manage symptoms, such as anti-nausea drugs or pain relievers. In more severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage symptoms and provide supportive care, such as intravenous fluids or blood transfusions. In some cases, treatment may involve bone marrow or stem cell transplants to help the body produce new blood cells.
Prevention of radiation sickness involves minimizing exposure to ionizing radiation through the use of protective clothing and equipment, as well as following safety protocols and regulations in radiation-related work or activities. In the event of a nuclear or radiological emergency, public health officials may recommend evacuation or sheltering in place to reduce exposure to radiation.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Nausea or vomiting
- Frequent infections
- Hair loss
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Weakness
- Dizziness (vertigo)
- Fever
- Headaches
- Diarrhea
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
Disease Causes
Radiation sickness
Radiation is the energy released from atoms as either a wave or a tiny particle of matter. Radiation sickness is caused by exposure to a high dose of radiation, such as a high dose of radiation received during an industrial accident.
Sources of high-dose radiation
Possible sources of high-dose radiation include the following:
- An accident at a nuclear industrial facility
- An attack on a nuclear industrial facility
- Detonation of a small radioactive device
- Detonation of a conventional explosive device that disperses radioactive material (dirty bomb)
- Detonation of a standard nuclear weapon
Radiation sickness occurs when high-energy radiation damages or destroys certain cells in your body. Regions of the body most vulnerable to high-energy radiation are cells in the lining of your intestinal tract, including your stomach, and the blood cell-producing cells of bone marrow.
Disease Prevents
Radiation sickness
In the event of a radiation emergency, stay tuned to your radio or television to hear what protective actions local, state and federal authorities recommend. Recommended actions will depend on the situation, but you will be told to either stay in place or evacuate your area.
Shelter in place
If you're advised to stay where you are, whether you're at home or work or elsewhere, do the following:
- Close and lock all doors and windows.
- Turn off fans, air conditioners and heating units that bring air in from outside.
- Close fireplace dampers.
- Bring pets indoors.
- Move to an inner room or basement.
- Stay tuned to your emergency response network or local news.
- Stay put for at least 24 hours.
Evacuate
If you're advised to evacuate, follow the instructions provided by your local authorities. Try to stay calm and move quickly and in an orderly manner. In addition, travel lightly, but take supplies, including:
- Flashlight
- Portable radio
- Batteries
- First-aid kit
- Necessary medicines
- Sealed food, such as canned foods, and bottled water
- Manual can opener
- Cash and credit cards
- Extra clothes
Be aware that most emergency vehicles and shelters won't accept pets. Take them only if you're driving your own vehicle and going someplace other than a shelter.
Disease Treatments
The treatment goals for radiation sickness are to prevent further radioactive contamination; treat life-threatening injuries, such as from burns and trauma; reduce symptoms; and manage pain.
Decontamination
Decontamination involves removing external radioactive particles. Removing clothing and shoes eliminates about 90 percent of external contamination. Gently washing with water and soap removes additional radiation particles from the skin.
Decontamination prevents radioactive materials from spreading more. It also lowers the risk of internal contamination from inhalation, ingestion or open wounds.
Treatment for damaged bone marrow
A protein called granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, which promotes the growth of white blood cells, may counter the effect of radiation sickness on bone marrow. Treatment with this protein-based medication, which includes filgrastim (Neupogen), sargramostim (Leukine) and pegfilgrastim (Neulasta), may increase white blood cell production and help prevent subsequent infections.
If you have severe damage to bone marrow, you may also receive transfusions of red blood cells or blood platelets.
Treatment for internal contamination
Some treatments may reduce damage to internal organs caused by radioactive particles. Medical personnel would use these treatments only if you've been exposed to a specific type of radiation. These treatments include the following:
- Potassium iodide (ThyroShield, Iosat). This is a nonradioactive form of iodine.
- Iodine is essential for proper thyroid function. If you're exposed to significant radiation, your thyroid will absorb radioactive iodine (radioiodine) just as it would other forms of iodine. The radioiodine is eventually cleared from the body in urine.
- If you take potassium iodide, it may fill "vacancies" in the thyroid and prevent the absorption of radioiodine. Potassium iodide isn't a cure-all and is most effective if taken within a day of exposure.
- Prussian blue (Radiogardase). This type of dye binds to particles of radioactive elements known as cesium and thallium. The radioactive particles are then excreted in feces. This treatment speeds up the elimination of the radioactive particles and reduces the amount of radiation cells may absorb.
- Diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA). This substance binds to metals. DTPA binds to particles of the radioactive elements plutonium, americium and curium. The radioactive particles pass out of the body in urine, thereby reducing the amount of radiation absorbed.
Supportive treatment
If you have radiation sickness, you may receive additional medications or interventions to treat:
- Bacterial infections
- Headache
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dehydration
- Burns
- Sores or ulcers
End-of-life care
A person who has absorbed very large doses of radiation has little chance of recovery. Depending on the severity of illness, death can occur within two days or two weeks. People with a lethal radiation dose will receive medications to control pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. They may also benefit from psychological or pastoral care.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Radiation sickness and Learn More about Diseases

Lip cancer
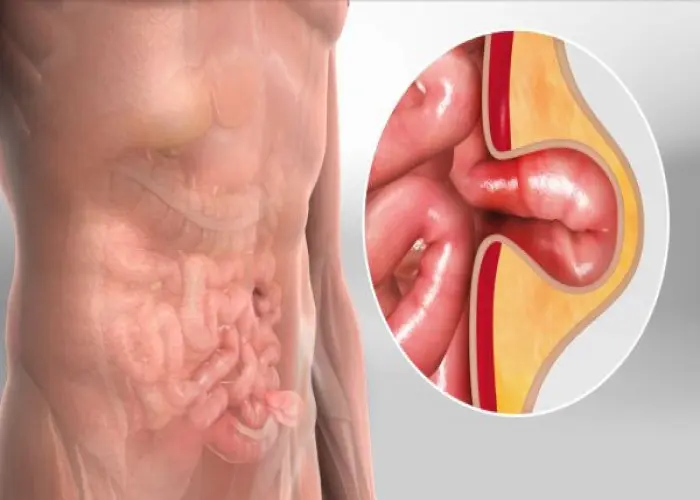
Hernia

Primary biliary cholangitis
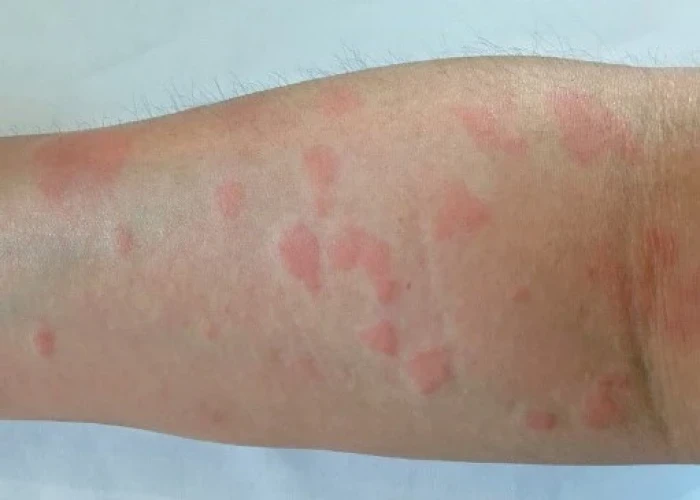
Lupus
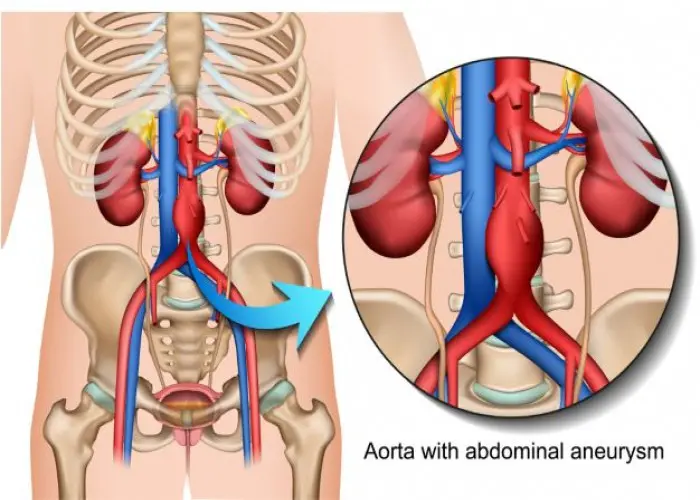
Abdominal aortic aneurysm

Keratitis
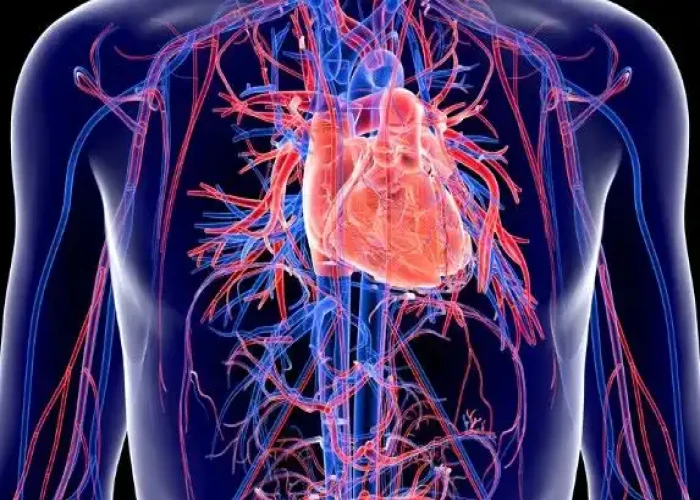
Transposition of the great arteries
Myelofibrosis
radiation sickness, বিকিরণ অসুস্থতা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
