 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
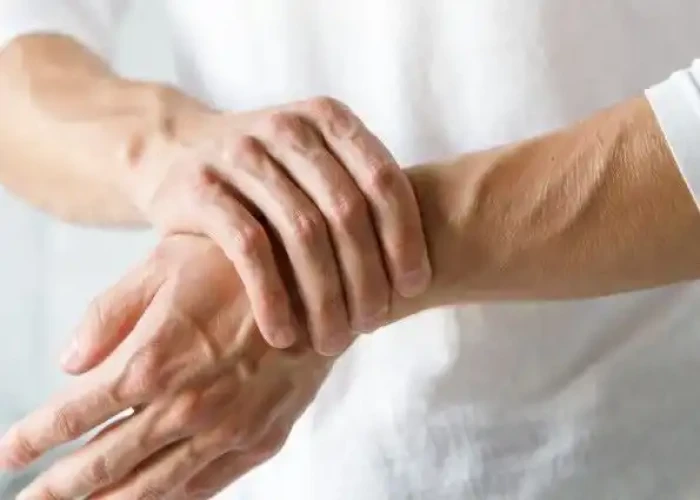
Wrist pain

Wrist pain is a common condition that can result from a variety of causes. It can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and can interfere with daily activities. Some of the most common causes of wrist pain include:
- Repetitive strain injuries: These injuries occur when the wrist is subjected to repetitive movements, such as typing, playing sports, or using tools, which can cause inflammation and pain in the wrist.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: This condition occurs when the median nerve, which runs through the wrist, is compressed or pinched, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in the wrist and hand.
- Sprains and strains: Wrist sprains and strains are common injuries that can result from falls or sudden twisting movements, causing damage to the ligaments and muscles in the wrist.
- Arthritis: Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation and pain in the joints, including the wrist, and can result in reduced mobility and stiffness.
- Tendinitis: Tendinitis is inflammation of the tendons in the wrist and can result from repetitive movements, injury, or overuse.
- Fractures: Fractures, or broken bones, can occur in any of the bones in the wrist, resulting in pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Treatment for wrist pain depends on the underlying cause of the pain. In some cases, rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications may be sufficient to relieve the pain. Other treatment options include physical therapy, splinting or bracing, corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases, surgery. It is important to see a healthcare professional if the pain persists or is severe, as prompt treatment can prevent further damage and promote healing.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Wrist pain
- Toothache
Disease Causes
Wrist pain
Damage to any of the parts of your wrist can cause pain and affect your ability to use your wrist and hand.
Injuries
- Sudden impacts. Wrist injuries often occur when you fall forward onto your outstretched hand. This can cause sprains, strains and even fractures. A scaphoid fracture involves a bone on the thumb side of the wrist. This type of fracture may not show up on X-rays immediately after the injury.
- Repetitive stress. Any activity that involves repetitive wrist motion — from hitting a tennis ball or bowing a cello to driving cross-country — can inflame the tissues around joints or cause stress fractures, especially when you perform the movement for hours on end without a break. De Quervain's disease is a repetitive stress injury that causes pain at the base of the thumb.
Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis. This type of arthritis occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones deteriorates over time. Osteoarthritis in the wrist is uncommon and usually occurs only in people who have injured that wrist in the past.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. A disorder in which the body's immune system attacks its own tissues, rheumatoid arthritis commonly involves the wrist. If one wrist is affected, the other one usually is, too.
Other diseases and conditions
- Carpal tunnel syndrome. Carpal tunnel syndrome develops when there's increased pressure on the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel, a passageway in the palm side of your wrist.
- Ganglion cysts. These soft tissue cysts occur most often on the part of your wrist opposite your palm. Ganglion cysts may be painful, and pain may either worsen or improve with activity.
- Kienbock's disease. This disorder typically affects young adults and involves the progressive collapse of one of the small bones in the wrist. Kienbock's disease occurs when the blood supply to this bone is compromised.
Disease Prevents
Wrist pain
It's impossible to prevent the unforeseen events that often cause wrist injuries, but these basic tips may offer some protection:
- Build bone strength. Getting adequate amounts of calcium — 1,000 milligrams a day for most adults and at least 1,200 milligrams a day for women over age 50, — can help prevent fractures.
- Prevent falls. Falling forward onto an outstretched hand is the main cause of most wrist injuries. To help prevent falls, wear sensible shoes. Remove home hazards. Light up your living space. And install grab bars in your bathroom and handrails on your stairways, if necessary.
- Use protective gear for athletic activities. Wear wrist guards for high-risk activities, such as football, snowboarding and rollerblading.
- Pay attention to ergonomics. If you spend long periods at a keyboard, take regular breaks. When you type, keep your wrist in a relaxed, neutral position. An ergonomic keyboard and foam or gel wrist support may help.
Disease Treatments
Treatments for wrist problems vary greatly based on the type, location and severity of the injury, as well as on your age and overall health.
Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), may help reduce wrist pain. Stronger pain relievers are available by prescription.
Therapy
A physical therapist can implement specific treatments and exercises for wrist injuries and tendon problems. If you need surgery, your physical therapist can also help with rehabilitation after the operation. You may also benefit from having an ergonomic evaluation that addresses workplace factors that may be contributing to wrist pain.
If you have a broken bone in your wrist, the pieces will need to be aligned so that the bone can heal properly. A cast or splint can help hold the bone fragments together while they heal.
If you have sprained or strained your wrist, you may need to wear a splint to protect the injured tendon or ligament while it heals. Splints are particularly helpful with overuse injuries caused by repetitive motions.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary. Examples include:
- Bone fractures. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to stabilize bone fractures to permit healing. A surgeon may need to connect the fragments of bone together with metal hardware.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome. If your symptoms are severe, you may need to have the ligament that forms the roof of the tunnel cut open to relieve the pressure on the nerve.
- Tendon or ligament repair. Surgery is sometimes necessary to repair tendons or ligaments that have ruptured.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Wrist pain and Learn More about Diseases

Glucoma

Sick sinus syndrome

Plague
Congenital myasthenic syndromes

Serotonin syndrome
Jaw tumors and cysts

Yeast infection (vaginal)

Ice cream headaches
wrist pain, কব্জি ব্যথা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
