Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
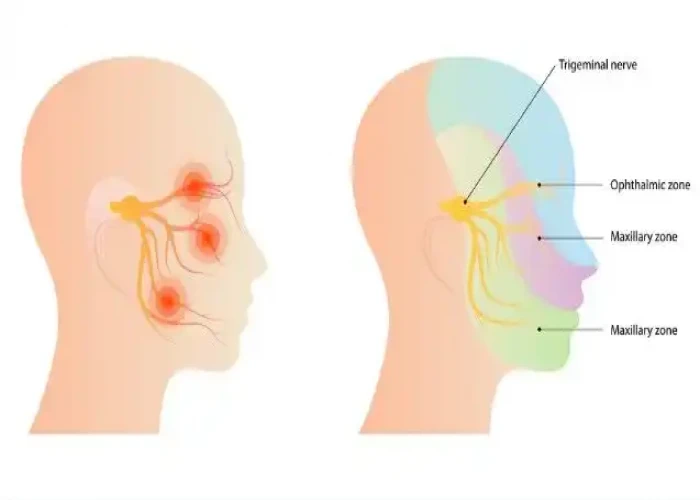
Trigeminal neuralgia

Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the face to the brain. The condition is characterized by intense, shooting or electric shock-like pain in the face, typically in the area of the cheek, jaw, or forehead.
The pain is often triggered by everyday activities such as talking, eating, or brushing teeth, and can be debilitating. Trigeminal neuralgia is most common in people over the age of 50, and is more common in women than in men.
The cause of trigeminal neuralgia is not fully understood, but it is believed to be caused by compression of the trigeminal nerve by a blood vessel or tumor. Other possible causes include multiple sclerosis and other neurological disorders.
Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia typically includes medications to manage pain, such as anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants. In severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerve. Treatment may also involve lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers and practicing stress-reducing techniques.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Jaw pain
- Pain focused in one spot or spread in a wider pattern
- Pain affecting one side of the face at a time, though may rarely affect both sides of the face
- Pain in areas supplied by the trigeminal nerve, including the cheek, jaw, teeth, gums, lips, or less often the eye and forehead
- Constant aching, burning feeling that may occur before it evolves into the spasm-like pain of trigeminal neuralgia
- Episodes of several attacks lasting days, weeks, months or longer — some people have periods when they experience no pain
- Bouts of pain lasting from a few seconds to several minutes
- Spontaneous attacks of pain or attacks triggered by things such as touching the face, chewing, speaking or brushing teeth
- Episodes of severe, shooting or jabbing pain that may feel like an electric shock
- Gum pain
- Toothache
- Attacks that become more frequent and intense over time
Disease Causes
Trigeminal neuralgia
In trigeminal neuralgia, also called tic douloureux, the trigeminal nerve's function is disrupted. Usually, the problem is contact between a normal blood vessel — in this case, an artery or a vein — and the trigeminal nerve at the base of your brain. This contact puts pressure on the nerve and causes it to malfunction.
While compression by a blood vessel is one of the more common causes of trigeminal neuralgia, there are many other potential causes as well. Some may be related to multiple sclerosis or a similar disorder that damages the myelin sheath protecting certain nerves. Trigeminal neuralgia can also be caused by a tumor compressing the trigeminal nerve.
Some people may experience trigeminal neuralgia due to a brain lesion or other abnormalities. In other cases, surgical injuries, stroke or facial trauma may be responsible for trigeminal neuralgia.
Triggers
A variety of triggers may set off the pain of trigeminal neuralgia, including:
- Shaving
- Touching your face
- Eating
- Drinking
- Brushing your teeth
- Talking
- Putting on makeup
- Breeze lightly blowing over your face
- Smiling
- Washing your face
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Trigeminal neuralgia and Learn More about Diseases
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma

Desmoid tumors

Hay fever
Supraventricular tachycardia
Granuloma annulare

Mosquito bites

Rheumatic fever

Progeria
trigeminal neuralgia, ট্রাইজেমিনাল নিউরালজিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.