 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Lip cancer

Lip cancer is a type of cancer that develops on the lips, typically on the lower lip. It is most often a squamous cell carcinoma, which is a type of skin cancer that arises from the thin, flat cells on the surface of the skin.
The most common risk factor for lip cancer is sun exposure, especially in fair-skinned individuals. Other risk factors include smoking, alcohol use, and a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of lip cancer can include a sore or lump on the lip that does not heal, thickening of the lip, red or white patches on the lip, and pain or bleeding in the affected area.
Treatment for lip cancer depends on the size and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Treatment options may include surgery to remove the cancerous tissue, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be used.
Prevention of lip cancer involves protecting the lips from sun exposure, such as wearing a hat and using a lip balm with a high SPF sunscreen. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption can also help reduce the risk of developing lip cancer. Regular dental and medical checkups can also help detect lip cancer early, when it is most treatable.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen lip
- A sore on the lip that won't heal
- Tingling, pain or numbness of the lips or the skin around the mouth
- They commonly occur in the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms and thighs.
- Lip cancer
Disease Causes
Lip cancer
It's not clear what causes lip cancer.
In general, cancer starts when cells develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell the cell what to do. The changes tell the cell to begin multiplying uncontrollably and to continue living when healthy cells would die. The accumulating cells form a tumor that can invade and destroy normal body tissue.
Disease Prevents
Lip cancer
To reduce your risk of lip cancer, you can:
- Stop using tobacco or don't start. If you use tobacco, stop. If you don't use tobacco, don't start. Using tobacco, whether smoked or chewed, exposes the cells in your lips to dangerous cancer-causing chemicals.
- Avoid the sun during the middle of the day. For many people in North America, the sun's rays are strongest between about 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Schedule outdoor activities for other times of the day, even during winter or when the sky is cloudy.
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on cloudy days. Apply sunscreen generously, and reapply every two hours — or more often if you're swimming or perspiring.
- Avoid tanning beds. Tanning beds emit UV rays and can increase your risk of lip cancer.
Disease Treatments
Lip cancer treatments include:
- Surgery. Surgery is used to remove the lip cancer and a margin of healthy tissue that surrounds it. The surgeon then repairs the lip to allow for normal eating, drinking and speaking. Techniques to reduce scarring also are used.
- For small lip cancers, repairing the lip after surgery may be a simple procedure. But for larger lip cancers, skilled plastic and reconstructive surgeons may be needed to repair the lip. Reconstructive surgery may involve moving tissue and skin to the face from another part of the body.
- Surgery for lip cancer may also involve removing cancerous lymph nodes in the neck.
- Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses powerful energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy for lip cancer may be used on its own or it may be used after surgery. The radiation may be aimed only at your lip, or it may also be aimed at the lymph nodes in your neck.
- Radiation therapy for lip cancer most often comes from a large machine that precisely focuses the energy beams. But in some cases, the radiation can be placed directly on your lip and left in place for a short time. This procedure, called brachytherapy, allows doctors to use higher doses of radiation.
- Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells. For lip cancer, chemotherapy is sometimes used in combination with radiation therapy to increase the effectiveness of treatment. In cases of advanced lip cancer that has spread to other areas of the body, chemotherapy may be used to reduce signs and symptoms and make you more comfortable.
- Targeted drug therapy. Targeted drug treatments focus on specific weaknesses present within cancer cells. By blocking these weaknesses, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die. Targeted drug therapy is usually combined with chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is a drug treatment that helps your immune system to fight cancer. Your body's disease-fighting immune system might not attack cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that help them hide from the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. For cancer of the lip, immunotherapy might be considered when the cancer is advanced and other treatments aren't an option.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Lip cancer and Learn More about Diseases
Headaches in children

Sick sinus syndrome

Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Norovirus infection

Bladder stones
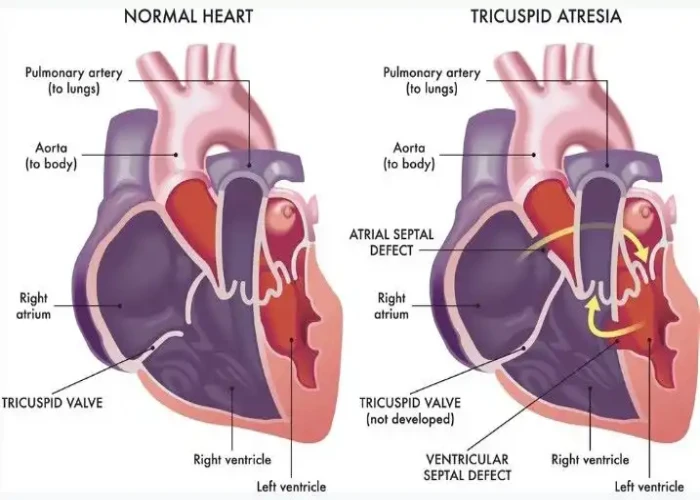
Tricuspid atresia

Orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension)
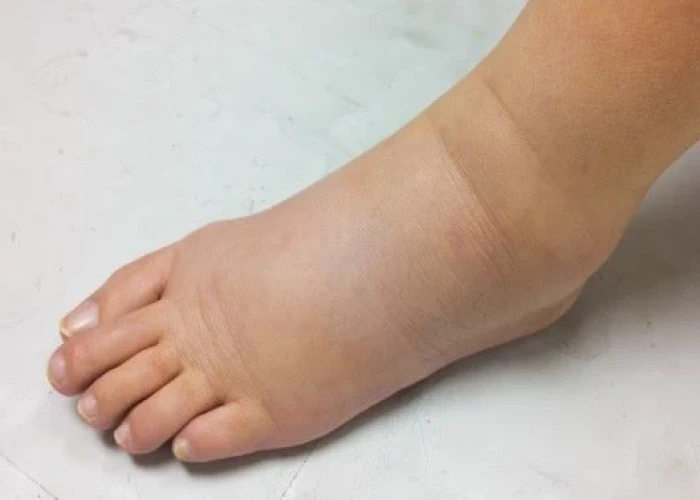
Lymphedema
lip cancer, ঠোঁটের ক্যান্সার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
