Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
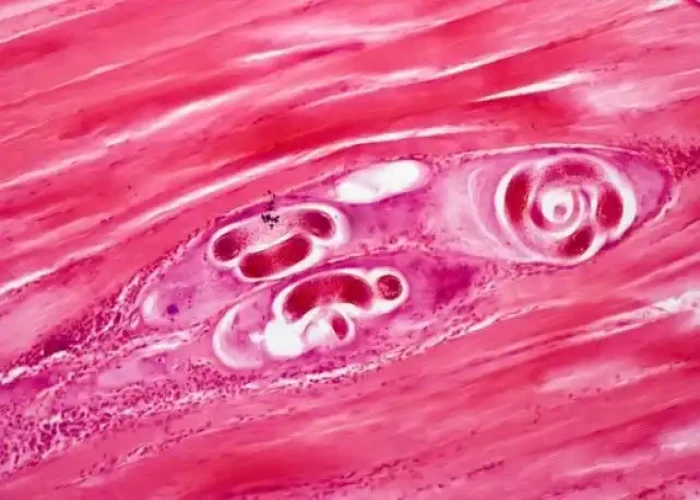
Trichinosis
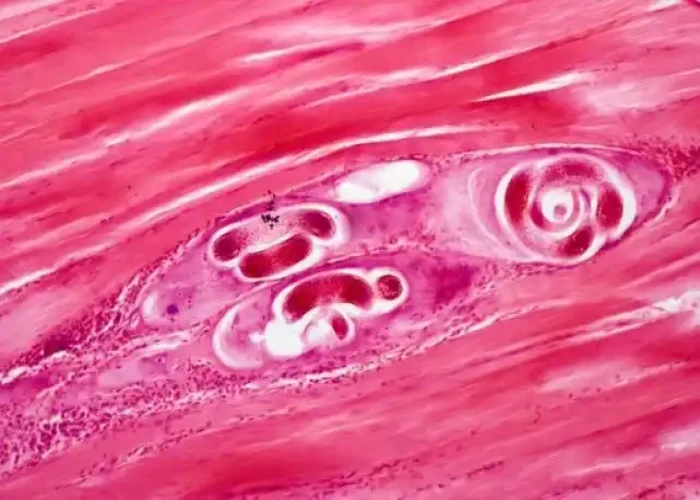
Trichinosis is a parasitic infection caused by the roundworm Trichinella spiralis. The infection is acquired by eating raw or undercooked meat, particularly pork or wild game, that is infected with the parasite.
Symptoms of trichinosis typically appear within a few days after infection and can include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Muscle pain and swelling, particularly in the face and around the eyes, are also common symptoms. In more severe cases, the infection can cause fever, chills, and difficulty coordinating movements.
Diagnosis of trichinosis is typically made through blood tests that detect antibodies to the parasite. Treatment may include medications to kill the parasite and relieve symptoms, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs. In most cases, the infection will resolve on its own within a few months, although in some cases, the symptoms may persist for several years.
Prevention of trichinosis involves cooking meat to a temperature of at least 160°F (71°C) to kill the parasite, and avoiding consumption of raw or undercooked meat, particularly pork and wild game. It is also important to practice good food safety and hygiene practices, such as washing hands and kitchen surfaces thoroughly after handling raw meat.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Diarrhea
- Pink eye (conjunctivitis)
- Sensitivity to light (Photophobia)
- Headaches
- Weakness
- Swollen eyelid
- Abdominal tenderness
- Muscle pain
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Abdomen pain
- An often foul-smelling vaginal discharge — which might be white, gray, yellow or green
Disease Causes
Trichinosis
People get trichinosis when they eat undercooked meat — such as pork, bear, walrus or horse — that is infected with the immature form (larvae) of the trichinella roundworm. In nature, animals are infected when they feed on other infected animals. Pigs and horses can become infected with trichinosis when they feed on garbage containing infected meat scraps. Cattle don't eat meat, but some cases of trichinosis in humans have been linked to eating beef that was mixed with infected pork or ground in a grinder previously used for contaminated pork.
Due to increased regulation of pork feed and products in the United States, pigs have become a less common source of infection. Wild animals, including bear, continue to be sources of infection.
Disease Prevents
Trichinosis
The best defense against trichinosis is proper food preparation. Follow these tips to avoid trichinosis:
- Avoid undercooked meat. Be sure to thoroughly cook cuts of meat until brown. Cook pork and meat from wild animals to an internal temperature of 160 F (71 C) throughout. For whole cuts and ground varieties of poultry, cook to a temperature of at least 165 F (74 C). Don't cut or eat the meat for at least three minutes after you've removed it from the heat.
- Use a meat thermometer to ensure that the meat is thoroughly cooked.
- Freeze pork. Freezing pork that is less than six inches thick for three weeks will kill parasites. However, trichinella parasites in wild-animal meat are not killed by freezing, even over a long period.
- Know that other processing methods don't kill parasites. Other methods of meat processing or preserving, such as smoking, curing and pickling, don't kill trichinella parasites in infected meat.
- Clean meat grinders thoroughly. If you grind your own meat, make sure the grinder is cleaned after each use.
Disease Treatments
Trichinosis usually isn't serious and often gets better on its own, usually within a few months. However, fatigue, mild pain, weakness and diarrhea may linger for months or years. Your doctor may prescribe medications depending on your symptoms and the severity of infection.
- Anti-parasitic medication. Anti-parasitic medication is the first line of treatment for trichinosis. If the trichinella parasite is discovered early, albendazole (Albenza) or mebendazole (Emverm) can be effective in eliminating the worms and larvae in the intestine. You may have mild gastrointestinal side effects during the course of treatment.
- If the disease is discovered after the larvae bury themselves in muscle tissues, the benefit of anti-parasitic medications is less certain. Your doctor might prescribe one if you have central nervous system, cardiac or respiratory problems as a result of the invasion.
- Pain relievers. After muscle invasion, your doctor may prescribe pain relievers to help relieve muscle aches. Eventually, the larvae cysts in your muscles tend to calcify, resulting in destruction of the larvae and the end of muscle aches and fatigue.
- Corticosteroids. Some cases of trichinosis cause allergic reactions when the parasite enters muscle tissue or when dead or dying larvae release chemicals in your muscle tissue. Your doctor might prescribe a corticosteroid to control inflammation.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Trichinosis and Learn More about Diseases

Zollinger-Ellison syndrome

Tetanus

Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)

Herniated disk
Dry macular degeneration
Hernia

Familial hypercholesterolemia
Menorrhagia (Heavy menstrual bleeding)
trichinosis, ট্রাইকিনোসিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.