 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)

Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) refers to a range of physical and emotional symptoms that many women experience in the days or weeks before their menstrual period. PMS is a common condition that affects up to 75% of women at some point in their lives.
Symptoms of PMS can vary from woman to woman, but may include mood changes, such as irritability, anxiety, or depression, as well as physical symptoms such as bloating, breast tenderness, and headaches. These symptoms typically resolve after the menstrual period begins.
The exact causes of PMS are not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can affect brain chemistry and lead to the symptoms of PMS.
Treatment for PMS may involve lifestyle changes, such as exercise, dietary changes, and stress management techniques, which can help reduce symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may also be helpful for relieving physical symptoms.
In some cases, hormonal birth control, such as the pill, patch, or ring, may be recommended to help regulate hormone levels and reduce PMS symptoms. For women with severe PMS, medications such as antidepressants or diuretics may be prescribed.
It is important for women who are experiencing symptoms of PMS to talk to their healthcare provider, who can help identify the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Anxiety
- Rapid mood chang
- Irritability
- Excessive anger
- Alcohol intolerance
Disease Causes
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Exactly what causes premenstrual syndrome is unknown, but several factors may contribute to the condition:
- Cyclic changes in hormones. Signs and symptoms of premenstrual syndrome change with hormonal fluctuations and disappear with pregnancy and menopause.
- Chemical changes in the brain. Fluctuations of serotonin, a brain chemical (neurotransmitter) that's thought to play a crucial role in mood states, could trigger PMS symptoms. Insufficient amounts of serotonin may contribute to premenstrual depression, as well as to fatigue, food cravings and sleep problems.
- Depression. Some women with severe premenstrual syndrome have undiagnosed depression, though depression alone does not cause all of the symptoms
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
For many women, lifestyle changes can help relieve PMS symptoms. But depending on the severity of your symptoms, your doctor may prescribe one or more medications for premenstrual syndrome.
The success of medications in relieving symptoms varies among women. Commonly prescribed medications for premenstrual syndrome include:
- Antidepressants. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) — which include fluoxetine (Prozac), paroxetine (Paxil, Pexeva), sertraline (Zoloft) and others — have been successful in reducing mood symptoms. SSRIs are the first line treatment for severe PMS or PMDD. These medications are generally taken daily. But for some women with PMS, use of antidepressants may be limited to the two weeks before menstruation begins.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Taken before or at the onset of your period, NSAIDs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve) can ease cramping and breast discomfort.
- Diuretics. When exercise and limiting salt intake aren't enough to reduce the weight gain, swelling and bloating of PMS, taking water pills (diuretics) can help your body shed excess fluid through your kidneys. Spironolactone (Aldactone) is a diuretic that can help ease some of the symptoms of PMS.
- Hormonal contraceptives. These prescription medications stop ovulation, which may bring relief from PMS symptoms.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and Learn More about Diseases

Anorgasmia in women
Broken ankle

Primary ovarian insufficiency
Bone metastasis
Norovirus infection
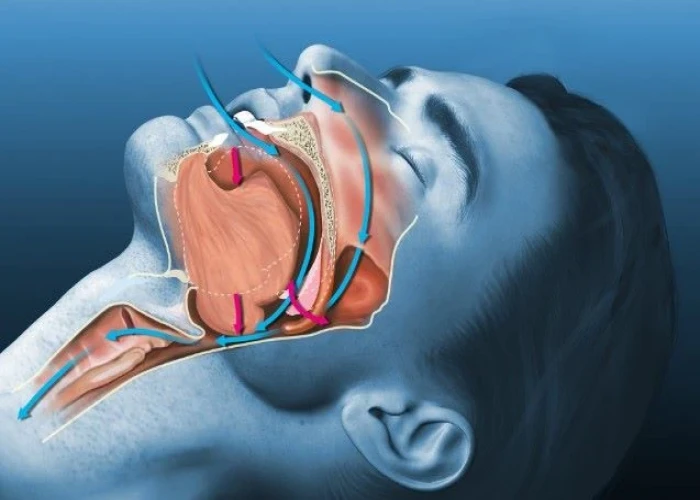
Obstructive sleep apnea

Scleroderma

Thunderclap headaches
Premenstrual syndrome, pms, প্রাক মাসিক সিনড্রোম, পিএমএস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
