Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)
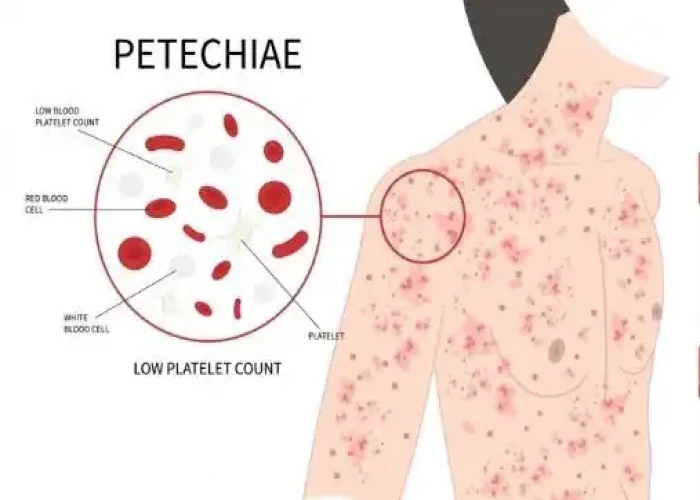
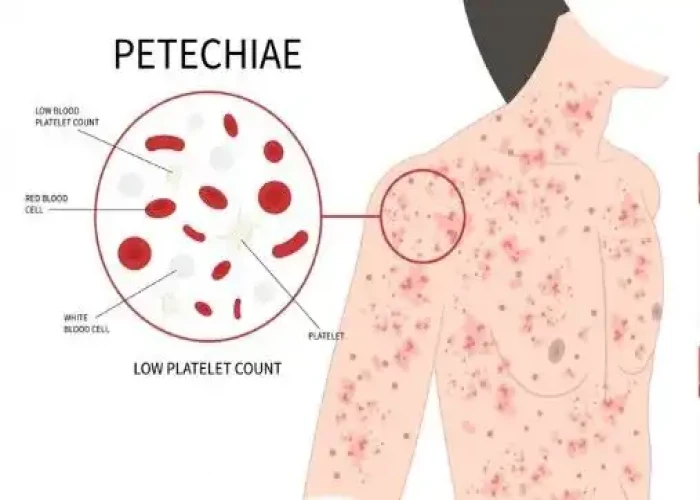
Thrombocytopenia is a medical condition characterized by a low platelet count, which can lead to abnormal bleeding or bruising. Platelets are small blood cells that help form clots to stop bleeding. A platelet count below 150,000 platelets per microliter of blood is considered low.
There are several possible causes of thrombocytopenia, including:
- Decreased production of platelets in the bone marrow due to conditions such as leukemia, viral infections, and chemotherapy or radiation treatment.
- Increased destruction of platelets due to autoimmune disorders, medications, or infections such as HIV or hepatitis C.
- Sequestration of platelets in the spleen due to conditions such as liver cirrhosis or other diseases that cause an enlarged spleen.
The symptoms of thrombocytopenia can include easy bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin), nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual bleeding.
Diagnosis of thrombocytopenia typically involves a complete blood count (CBC) and examination of a peripheral blood smear. Other tests may be performed to determine the underlying cause.
Treatment for thrombocytopenia depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Mild cases may not require any treatment, while more severe cases may require medication, blood transfusions, or in some cases, surgical removal of the spleen. In addition, avoiding medications that can cause or worsen thrombocytopenia, and following good hygiene and safety practices to prevent infections can also help manage the condition.
It is important to seek medical attention if any symptoms of thrombocytopenia are experienced, as untreated cases can be life-threatening.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Bleeding from gums
- Nose bleeding
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Blood in stool
- Heavy menstrual period or bleeding
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Enlarged liver and spleen
Disease Causes
Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)
Thrombocytopenia means you have fewer than 150,000 platelets per microliter of circulating blood. Because each platelet lives only about 10 days, your body normally renews your platelet supply continually by producing new platelets in your bone marrow.
Thrombocytopenia rarely is inherited; or it can be caused by a number of medications or conditions. Whatever the cause, circulating platelets are reduced by one or more of the following processes: trapping of platelets in the spleen, decreased platelet production or increased destruction of platelets.
Trapped platelets
The spleen is a small organ about the size of your fist situated just below your rib cage on the left side of your abdomen. Normally, your spleen works to fight infection and filter unwanted material from your blood. An enlarged spleen — which can be caused by a number of disorders — can harbor too many platelets, which decreases the number of platelets in circulation.
Decreased production of platelets
Platelets are produced in your bone marrow. Factors that can decrease platelet production include:
- Leukemia and other cancers
- Some types of anemia
- Viral infections, such as hepatitis C or HIV
- Chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy
- Heavy alcohol consumption
Increased breakdown of platelets
Some conditions can cause your body to use up or destroy platelets faster than they're produced, leading to a shortage of platelets in your bloodstream. Examples of such conditions include:
- Pregnancy. Thrombocytopenia caused by pregnancy is usually mild and improves soon after childbirth.
- Immune thrombocytopenia. Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, cause this type. The body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys platelets. If the exact cause of this condition isn't known, it's called idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. This type more often affects children.
- Bacteria in the blood. Severe bacterial infections involving the blood (bacteremia) can destroy platelets.
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. This is a rare condition that occurs when small blood clots suddenly form throughout your body, using up large numbers of platelets.
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome. This rare disorder causes a sharp drop in platelets, destruction of red blood cells and impairs kidney function.
- Medications. Certain medications can reduce the number of platelets in your blood. Sometimes a drug confuses the immune system and causes it to destroy platelets. Examples include heparin, quinine, sulfa-containing antibiotics and anticonvulsants.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Thrombocytopenia can last for days or years. People with mild thrombocytopenia might not need treatment. For people who do need treatment for thrombocytopenia, treatment depends on its cause and how severe it is.
If your thrombocytopenia is caused by an underlying condition or a medication, addressing that cause might cure it. For example, if you have heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, your doctor can prescribe a different blood-thinning drug.
Other treatments might involve:
- Blood or platelet transfusions. If your platelet level becomes too low, your doctor can replace lost blood with transfusions of packed red blood cells or platelets.
- Medications. If your condition is related to an immune system problem, your doctor might prescribe drugs to boost your platelet count. The first-choice drug might be a corticosteroid. If that doesn't work, stronger medications can be used to suppress your immune system.
- Surgery. If other treatments don't help, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove your spleen (splenectomy).
- Plasma exchange. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura can result in a medical emergency requiring plasma exchange.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) and Learn More about Diseases
Hip dysplasia

Conjoined twins
Milia
Morton's neuroma
Asbestosis
Adnexal tumors

Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)
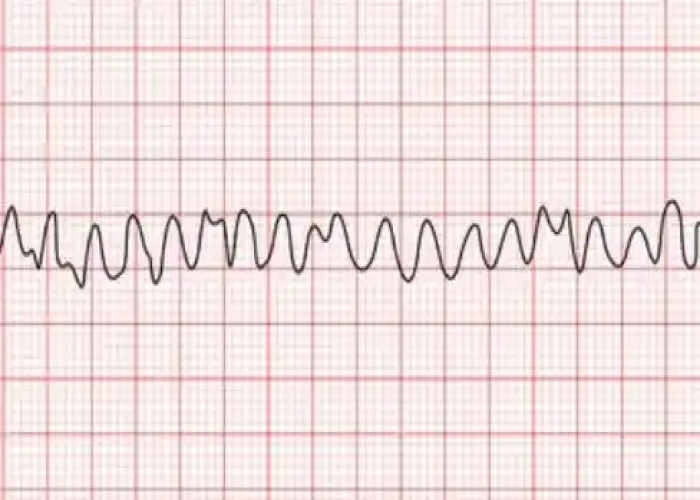
Ventricular fibrillation
thrombocytopenia, low platelet count, থ্রোমোসাইটোপেনিয়া, কম প্লেটলেট গণনা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.