Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Frostbite
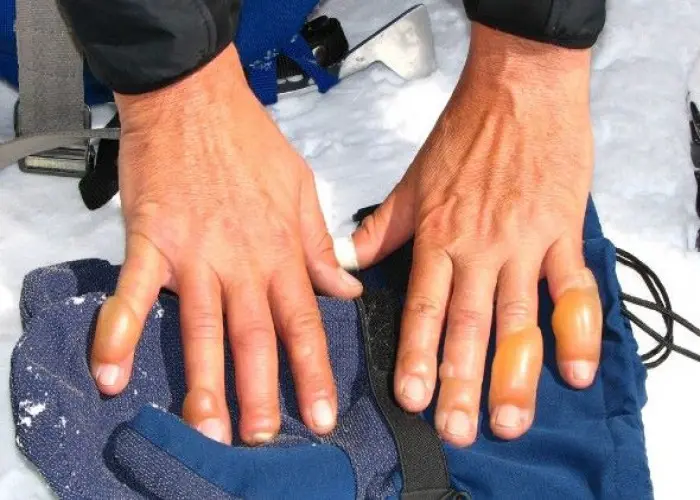
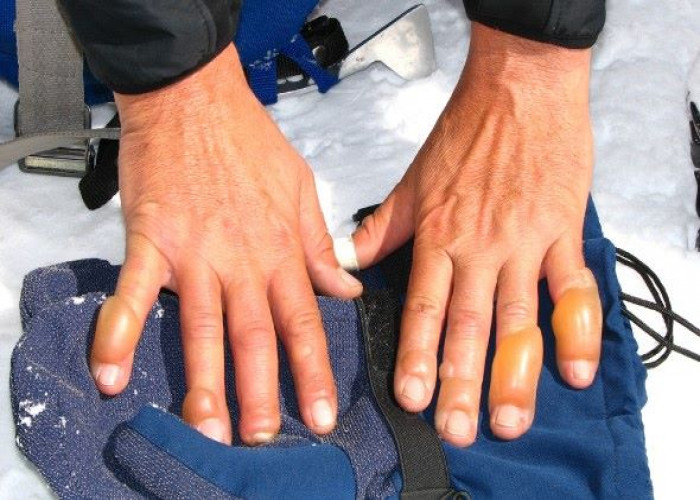
Frostbite is a condition that occurs when the skin and underlying tissues freeze due to exposure to extremely cold temperatures. The most commonly affected areas are the hands, feet, nose, and ears.
The symptoms of frostbite can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Numbness or tingling in the affected area
- Cold, pale, or blue skin
- Hard or waxy-looking skin
- Blisters or open sores
- Swelling
- Pain
In severe cases of frostbite, the affected tissue may die, which can lead to gangrene and the need for amputation.
Prevention is key in avoiding frostbite. When exposed to cold temperatures, it is important to wear appropriate clothing and limit the amount of time spent outside. Layers of loose-fitting, lightweight clothing help to trap warm air between layers and provide better insulation. Covering the head, hands, and feet is especially important. It is also important to avoid consuming alcohol or smoking, which can increase the risk of frostbite.
If you suspect that you have frostbite, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment may include rewarming the affected area, pain management, and in severe cases, surgical intervention. It is important to keep the affected area dry, and elevated, and to avoid rubbing or massaging the area, as this can cause further damage to the affected tissues.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- At first, cold skin and a prickling feeling
- Numbness
- Red skin
- Waxy skin
- Muscle stiffness may occur in any part of the body.
- Red, white, bluish-white or grayish-yellow skin
- Fever
Disease Causes
Frostbite
Frostbite occurs when skin and underlying tissues freeze. The most common cause of frostbite is exposure to cold-weather conditions. But it can also be caused by direct contact with ice, freezing metals or very cold liquids.
Specific conditions that lead to frostbite include:
- Wearing clothing that isn't suitable for the conditions you're in — for example, it doesn't protect against cold, windy or wet weather or it's too tight.
- Staying out in the cold and wind too long. Risk increases as air temperature falls below 5 F (minus 15 C), even with low wind speeds. In wind chill of minus 16.6 F (minus 27 C), frostbite can occur on exposed skin in less than 30 minutes.
Disease Prevents
Frostbite
Frostbite can be prevented. Here are tips to help you stay safe and warm.
- Limit time outdoors in cold, wet or windy weather. Pay attention to weather forecasts and wind chill readings. In very cold, windy weather, exposed skin can develop frostbite in a matter of minutes.
- Dress in several layers of loose, warm clothing. Air trapped between the layers of clothing acts as insulation against the cold. Wear windproof and waterproof outer garments to protect against wind, snow and rain. Choose undergarments that wick moisture away from the skin. Change out of wet clothing — particularly gloves, hats and socks — as soon as possible.
- Wear a hat or headband that fully covers the ears. Heavy woolen or windproof materials make the best headwear for cold protection.
- Wear mittens rather than gloves. Mittens provide better protection. Or try a thin pair of glove liners made of a wicking material (such as polypropylene) under a pair of heavier gloves or mittens.
- Wear socks and sock liners that fit well, wick moisture and provide insulation. Consider hand and foot warmers as well. Be sure foot warmers don't make boots too tight, restricting blood flow.
- Watch for signs of frostbite. Early signs of frostbite include changes in skin color, prickling and numbness. Seek warm shelter if you notice signs of frostbite.
- Plan to protect yourself. When traveling in cold weather, carry emergency supplies and warm clothing in case you become stranded. If you'll be in remote territory, tell others your route and expected return date.
- Don't drink alcohol if you plan to be outdoors in cold weather. Alcoholic beverages cause the body to lose heat faster.
- Eat well-balanced meals and stay hydrated. Doing this even before you go out in the cold will help you stay warm.
- Keep moving. Exercise can get the blood flowing and help you stay warm, but don't do it to the point of exhaustion.
Disease Treatments
Mild frostbite (frostnip) can be treated at home with first-aid care. For all other frostbite, after appropriate first aid and assessment for hypothermia, medical treatment may involve rewarming, medications, wound care, surgery and various therapies, depending on the severity of the injury.
- Rewarming of the skin. If the skin hasn't been rewarmed already, your doctor will rewarm the area using a warm-water bath for 15 to 30 minutes. The skin may turn soft. You may be encouraged to gently move the affected area as it rewarms.
- Oral pain medicine. Because the rewarming process can be painful, your doctor will likely give you a drug to ease the pain.
- Protecting the injury. Once the skin thaws, your doctor may loosely wrap the area with sterile sheets, towels or dressings to protect the skin. Or the doctor may protect your fingers or toes as they thaw by gently separating them from each other. And you may need to elevate the affected area to reduce swelling.
- Removal of damaged tissue (debridement). To heal properly, frostbitten skin needs to be free of damaged, dead or infected tissue. To better distinguish between healthy and dead tissue, your doctor may wait 1 to 3 months before removing damaged tissue.
- Whirlpool therapy or physical therapy. Soaking in a whirlpool bath (hydrotherapy) can aid healing by keeping skin clean and naturally removing dead tissue. You may be encouraged to gently move the affected area.
- Infection-fighting drugs. If the skin or blisters appear infected, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics.
- Clot-busting drugs. You may receive an intravenous (IV) injection of a drug that helps restore blood flow (thrombolytic), such as tissue plasminogen activator (TPA). Studies of people with severe frostbite show that TPA lowers the risk of amputation. But these drugs can cause serious bleeding and are typically used only in the most serious situations and within 24 hours of exposure.
- Wound care. A variety of wound care techniques may be used, depending on the extent of injury.
- Surgery. People who have experienced severe frostbite may in time need surgery or amputation to remove dead or decaying tissue.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room. Some patients show improved symptoms after this therapy. But more study is needed.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Frostbite and Learn More about Diseases

Chronic exertional compartment syndrome

Stickler syndrome
Diphtheria

Heart arrhythmia
Acne
Gastric Ulcer
Median arcuate ligament syndrome (MALS)

Common cold
Frostbite, ফ্রস্ট বাইট, তুষারস্পর্শে দেহের প্রদাহ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.