Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
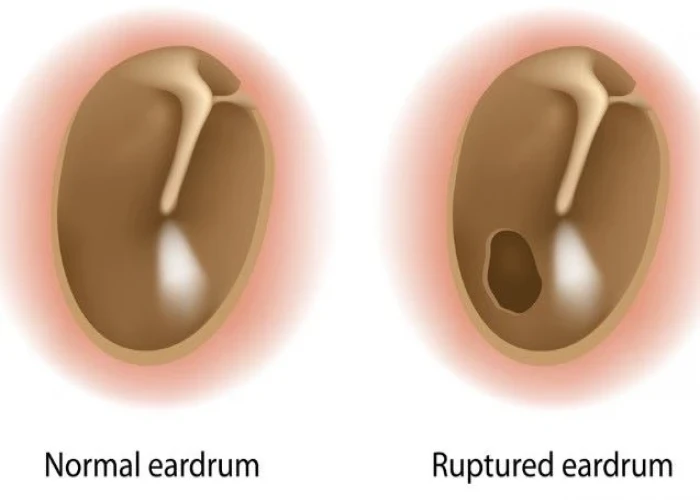
Ruptured eardrum (perforated eardrum)
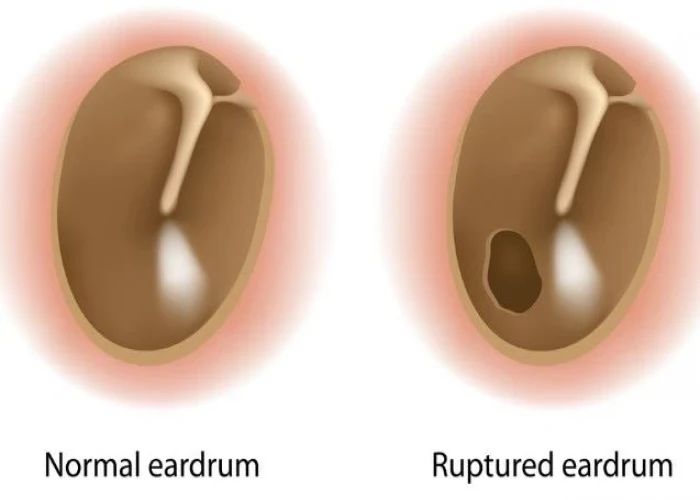
A ruptured eardrum, also known as a perforated eardrum, is a tear or hole in the thin tissue that separates the ear canal from the middle ear. This can occur due to a variety of reasons, such as infection, injury, or changes in air pressure.
Symptoms of a ruptured eardrum may include ear pain, hearing loss, ringing in the ears, fluid drainage from the ear, dizziness or vertigo, and a buzzing or humming sensation in the ear. In some cases, there may be no symptoms at all.
Treatment for a ruptured eardrum may depend on the cause and severity of the injury, but can include antibiotics to treat infection, pain relievers to manage pain, and eardrops to promote healing. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the eardrum.
It is important to avoid inserting any objects into the ear, including cotton swabs, as this can worsen the injury and increase the risk of infection. Additionally, it is important to protect the ear from water, as exposure to water can increase the risk of infection.
Most cases of a ruptured eardrum heal on their own within a few weeks to months, but it is important to follow up with a healthcare provider to monitor the healing process and ensure that there are no further complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Ear pain
- Ear pus
- Deafness (Hearing loss)
- Ringing in ears (tinnitus)
- Dizziness (vertigo)
- Nausea or vomiting
Disease Causes
Ruptured eardrum (perforated eardrum)
Causes of a ruptured (perforated) eardrum may include:
- Middle ear infection (otitis media). A middle ear infection often results in the accumulation of fluids in the middle ear. Pressure from these fluids can cause the eardrum to rupture.
- Barotrauma. Barotrauma is stress exerted on the eardrum when the air pressure in the middle ear and the air pressure in the environment are out of balance. If the pressure is severe, the eardrum can rupture. Barotrauma is most often caused by air pressure changes associated with air travel.
- Other events that can cause sudden changes in pressure — and possibly a ruptured eardrum — include scuba diving and a direct blow to the ear, such as the impact of an automobile air bag.
- Loud sounds or blasts (acoustic trauma). A loud sound or blast, as from an explosion or gunshot — essentially an overpowering sound wave — can rarely cause a tear in the eardrum.
- Foreign objects in your ear. Small objects, such as a cotton swab or hairpin, can puncture or tear the eardrum.
- Severe head trauma. Severe injury, such as a skull base fracture, may cause the dislocation of or damage to middle and inner ear structures, including the eardrum.
Disease Prevents
Ruptured eardrum (perforated eardrum)
Follow these tips to avoid a ruptured (perforated) eardrum:
- Get treatment for middle ear infections. Be aware of the signs and symptoms of middle ear infection, including earache, fever, nasal congestion and reduced hearing. Children with middle ear infections often are fussy and may refuse to eat. Seek prompt evaluation from your provider to prevent potential damage to the eardrum.
- Protect your ears during flight. If possible, don't fly if you have a cold or an active allergy that causes nasal or ear congestion. During takeoffs and landings, keep ears clear with pressure-equalizing earplugs, yawning or chewing gum.
- Or use the Valsalva maneuver — gently pushing air into the nose, as if blowing your nose, while pinching the nostrils and keeping the mouth closed. Don't sleep during ascents and descents.
- Keep your ears free of foreign objects. Never attempt to dig out excess or hardened earwax with items such as a cotton swab, paper clip or hairpin. These items can easily tear or puncture the eardrum. Teach your children about the damage that can be done by putting foreign objects in their ears.
- Guard against explosive noise. Avoid activities that expose the ears to explosions. If your hobbies or work involves planned activities that produce explosive noise, protect your ears from unnecessary damage by wearing protective earplugs or earmuffs.
Disease Treatments
Most ruptured (perforated) eardrums heal without treatment within a few weeks. Your provider may prescribe antibiotic drops if there's evidence of infection. If the tear or hole in the eardrum doesn't heal by itself, treatment will likely involve procedures to close the tear or hole. These may include:
- Eardrum patch. If the tear or hole in the eardrum doesn't close on its own, an ENT specialist may seal it with a paper patch (or a patch made of other material).
- With this office procedure, your ENT doctor may apply a chemical to the edges of the tear, which can promote ear drum healing, and then apply a patch over the hole. The procedure may need to be repeated more than once before the hole closes.
- Surgery. If a patch doesn't result in proper healing or your ENT doctor determines that the tear isn't likely to heal with a patch, he or she may recommend surgery.
- The most common surgical procedure is called tympanoplasty. Your surgeon grafts a patch of your own tissue to close the hole in the eardrum. This procedure is done on an outpatient basis. In an outpatient procedure, you can usually go home the same day unless medical anesthesia conditions require a longer hospital stay.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Ruptured eardrum (perforated eardrum) and Learn More about Diseases
Stomach pain
Atopic dermatitis (eczema)

Bradycardia
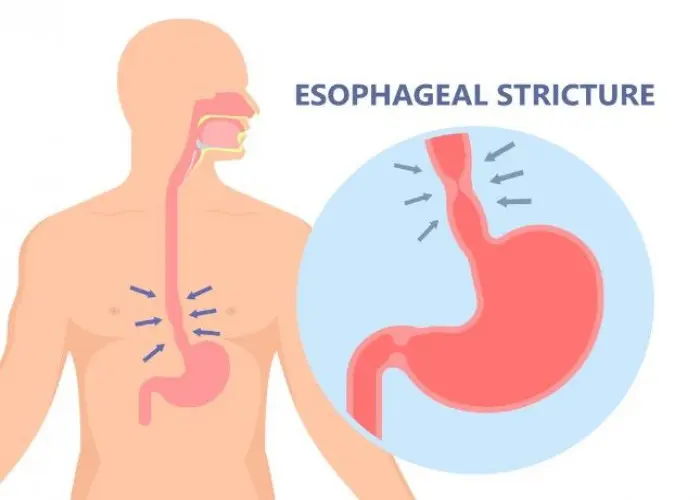
Eosinophilic esophagitis
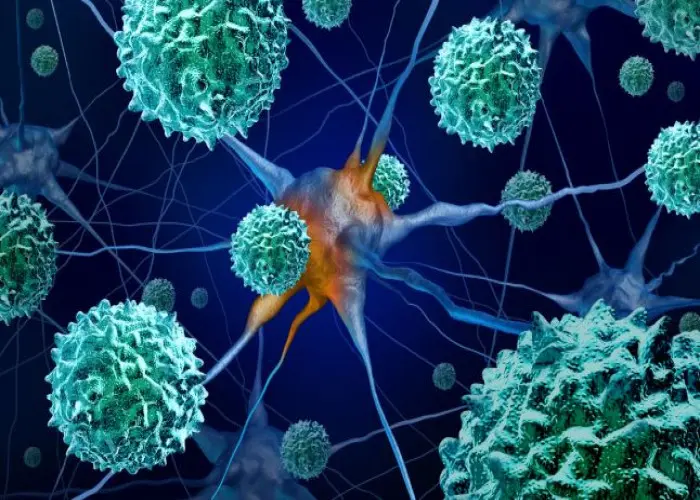
Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM)
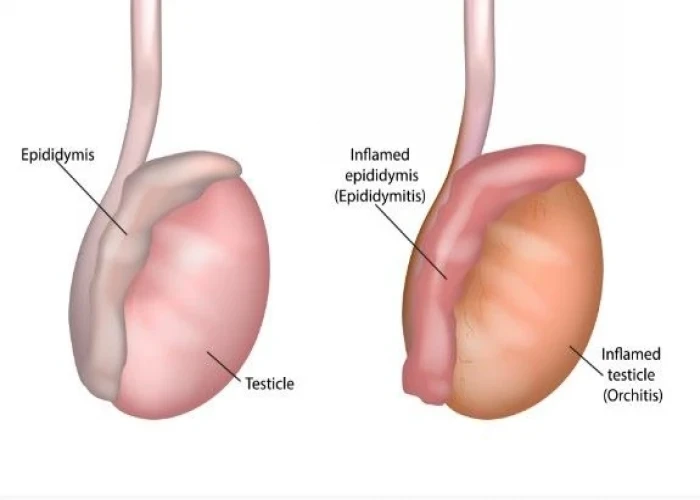
Orchitis

Body lice
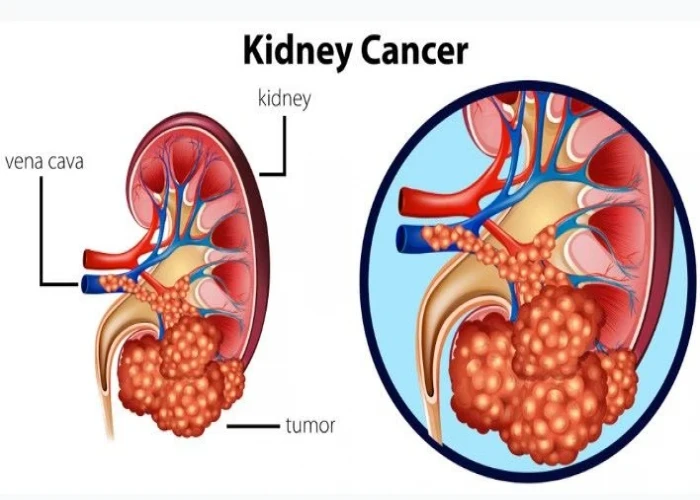
Kidney cancer
ruptured eardrum, perforated eardrum, রাপটার্ড ইয়ারড্রাম, পেপফোরাটেড ইয়ারড্রাম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.