Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
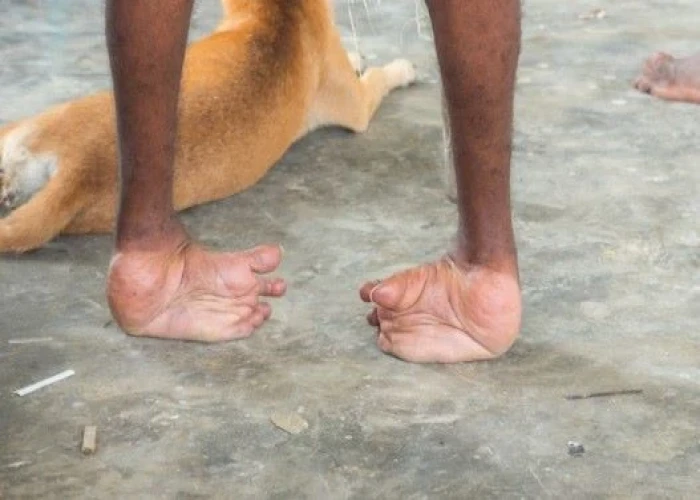
Post-polio syndrome
Post-polio syndrome (PPS) is a condition that can occur in people who have had polio, a viral infection that can affect the nervous system and cause muscle weakness and paralysis. PPS typically develops many years after the initial polio infection and is characterized by new or increased symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, pain, and difficulty with breathing or swallowing.
It is not entirely clear what causes PPS, but it is thought to result from the gradual deterioration of nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain that were initially damaged by the polio virus. The exact prevalence of PPS is unknown, but it is estimated that up to 40% of people who had polio may develop the syndrome.
Treatment for PPS typically focuses on managing symptoms, and may include physical therapy, medications to alleviate pain and fatigue, assistive devices, and in some cases, surgery to correct musculoskeletal problems. It is important for individuals with PPS to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Muscle weakness
- General fatigue and exhaustion with minimal activity
- Sleep-related breathing disorders, such as sleep apnea
- Recurrent, unwanted distressing memories of the traumatic event
Disease Causes
Post-polio syndrome
There are several theories as to what causes post-polio syndrome, but no one knows for sure.
When poliovirus infects your body, it affects nerve cells called motor neurons that carry messages (electrical impulses) between your brain and your muscles. Poliovirus particularly affects the motor neurons in the spinal cord.
Each motor neuron consists of three basic components:
- A cell body
- A major branching fiber (axon)
- Numerous smaller branching fibers (dendrites)
A polio infection often damages or destroys many of these motor neurons. Because there are fewer motor neurons, the remaining neurons sprout new fibers and grow bigger.
This promotes recovery of the use of your muscles, but it also may stress the nerve cell body to nourish the additional fibers. Over the years, this stress may be too much. This may cause the gradual breakdown of the sprouted fibers and, eventually, of the neuron itself.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
There's no one treatment for the various signs and symptoms of post-polio syndrome. The goal of treatment is to manage your symptoms and help make you as comfortable and independent as possible. Here are some treatment options that may help manage your post-polio syndrome symptoms:
- Energy conservation. This involves pacing your physical activity and resting frequently to reduce fatigue. Assistive devices — such as a cane, walker, wheelchair or motor scooter — can help you conserve energy. Having a shower grab bar or raised toilet seat installed also might help. A therapist can show you ways to breathe that help conserve energy.
- Physical therapy. Your doctor or therapist may prescribe exercises for you that strengthen your muscles without fatiguing them. These usually include less strenuous activities, such as swimming or water aerobics, that you perform every other day at a relaxed pace.
- Exercising to maintain fitness is important, but avoid overusing your muscles and joints and exercising to the point of pain or fatigue.
- Speech therapy. A speech therapist can show you ways to compensate for swallowing difficulties. Voice strengthening exercises also might be helpful.
- Sleep disorder treatment. You might need to change your sleeping patterns, such as avoiding sleeping on your back, or use a device that helps open your airway when you sleep. If you have restless legs syndrome, treatment for that disorder may help improve sleep quality and reduce fatigue.
- Medications. Pain relievers — such as aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) — might ease muscle and joint pain.
Other possible treatment options may include the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise), which is often used to treat nerve pain. Chronic opioid pain medications generally shouldn't be used due to their long-term risks. You and your doctor should discuss the right treatment plan for you to manage your pain and symptoms.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Post-polio syndrome and Learn More about Diseases

Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease

Pulmonary atresia
Pituitary tumors

Chronic hives

Mesothelioma
Prediabetes
post-polio syndrome, পোলিও পরবর্তী সিন্ড্রোম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.