Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
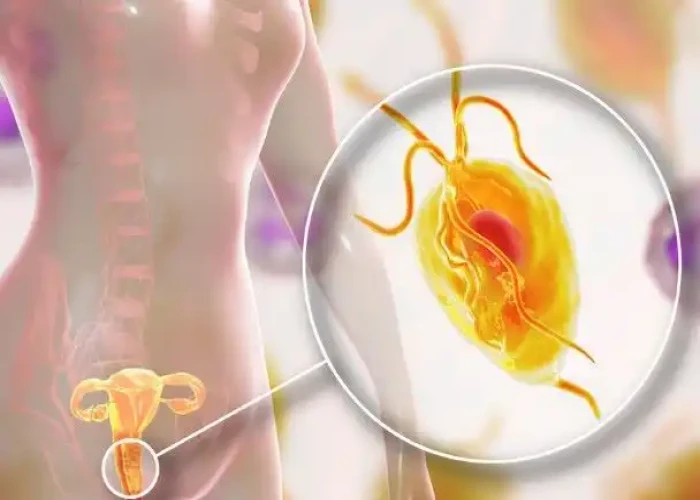
Trichomoniasis
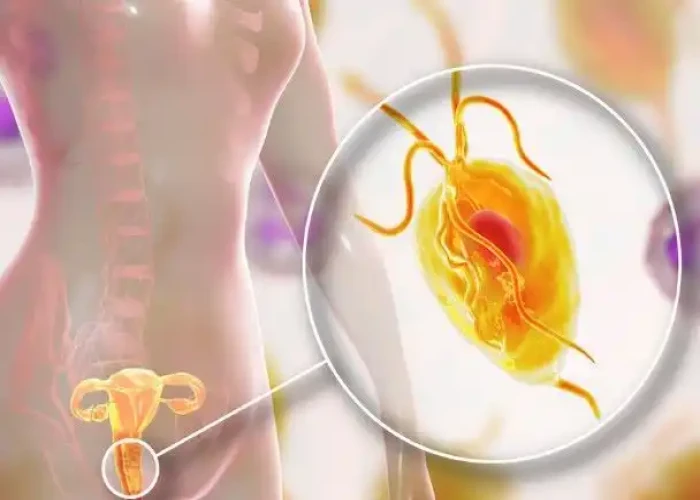
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. It is a common STI, particularly among sexually active women and men.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis can include vaginal discharge (which may be yellow, green, or gray), itching or burning in the genital area, and pain during sexual intercourse or urination. In men, symptoms may include discharge from the penis and pain or burning during urination. However, many people with trichomoniasis may not have any symptoms at all.
Trichomoniasis is diagnosed through laboratory tests that detect the parasite in samples of vaginal fluid or semen. Treatment for trichomoniasis typically involves taking prescription medication, such as metronidazole or tinidazole, to kill the parasite. Sexual partners should also be treated to prevent reinfection.
Prevention strategies for trichomoniasis include using latex condoms or other barriers during sexual activity to reduce the risk of transmission, and limiting sexual partners. It is also important to practice good hygiene, such as washing the genital area regularly with soap and water, to reduce the risk of infection.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Foul menstruation or vaginal discharge
- Menstruation is white
- Itching
- Painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Ejaculation
- Discharge from penis
- An often foul-smelling vaginal discharge — which might be white, gray, yellow or green
Disease Causes
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is caused by a one-celled protozoan, a type of tiny parasite that travels between people during sexual intercourse. The incubation period between exposure and infection is unknown, but it's thought to range from four to 28 days.
Disease Prevents
Trichomoniasis
As with other sexually transmitted infections, the only way to prevent trichomoniasis is to abstain from sex. To lower your risk, use condoms correctly every time you have sex.
Disease Treatments
The most common treatment for trichomoniasis, even for pregnant women, is to swallow one megadose of either metronidazole (Flagyl) or tinidazole (Tindamax). In some cases, your doctor might recommend a lower dose of metronidazole two times a day for seven days.
Both you and your partner need treatment. And you need to avoid sexual intercourse until the infection is cured, which takes about a week.
Don't drink alcohol for 24 hours after taking metronidazole or 72 hours after taking tinidazole, because it can cause severe nausea and vomiting.
Your doctor will likely want to retest you for trichomoniasis from two weeks to three months after treatment to be sure you haven't been reinfected.
Untreated, trichomoniasis can last for months to years.
Preparing for your appointment
Your family doctor, gynecologist or a medical practitioner at an urgent care center can diagnose and prescribe treatment for trichomoniasis.
What you can do
Before the appointment, you might prepare a list that includes:
- A detailed description of your symptoms, including when they started
- Sexually transmitted infections you've had
- The number of sexual partners you've had during the past few years
What to expect from your doctor
For women, your doctor will perform a pelvic exam and may take a sample of your vaginal fluids for testing. Men will need to provide a urine sample.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Trichomoniasis and Learn More about Diseases
Cradle cap

Phenylketonuria (PKU)

Sacral dimple
Spinal headaches
Sprains
Boils (Absces or Carbuncles)

N/A

Alzheimers disease
trichomoniasis, ট্রাইকোমোনিয়াসিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.