Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
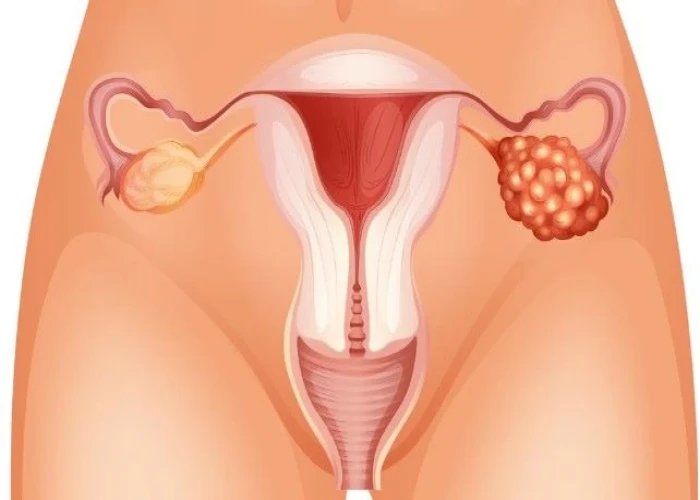
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the ovaries, which are female reproductive organs that produce eggs and hormones. It is the fifth leading cause of cancer deaths in women.
Symptoms of ovarian cancer may include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
- Urinary symptoms, such as urgency or frequency
- Fatigue
- Back pain
- Menstrual changes or postmenopausal bleeding
However, many of these symptoms can also be caused by other, less serious conditions, so it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Risk factors for ovarian cancer include:
- Age: the risk of ovarian cancer increases with age, particularly after menopause
- Family history: women with a family history of ovarian cancer or certain inherited genetic mutations are at increased risk
- Personal history: women who have had breast, uterine, or colon cancer may be at increased risk
- Reproductive history: women who have never been pregnant or who have had infertility treatments may be at increased risk
- Hormone therapy: long-term use of estrogen without progesterone may increase the risk of ovarian cancer
Diagnosis of ovarian cancer may involve a physical exam, imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan, and a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of ovarian cancer typically involves surgery to remove the affected ovary or ovaries, as well as any other affected tissues or organs, followed by chemotherapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
Prevention of ovarian cancer may involve genetic counseling and testing for women with a family history of ovarian cancer or certain genetic mutations, as well as the use of oral contraceptives, which have been shown to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Abdomen bloating
- Abdomen pain
- Abdomen cancer
- Weight loss
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Back pain
- Frequent urination
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
- Painful urination or an urgent or frequent need to urinate
Disease Causes
Ovarian cancer
It's not clear what causes ovarian cancer, though doctors have identified things that can increase the risk of the disease.
Doctors know that ovarian cancer begins when cells in or near the ovaries develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell the cell what to do. The changes tell the cells to grow and multiply quickly, creating a mass (tumor) of cancer cells. The cancer cells continue living when healthy cells would die. They can invade nearby tissues and break off from an initial tumor to spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
Types of ovarian cancer
The type of cell where the cancer begins determines the type of ovarian cancer you have and helps your doctor determine which treatments are best for you. Ovarian cancer types include:
- Epithelial ovarian cancer. This type is the most common. It includes several subtypes, including serous carcinoma and mucinous carcinoma.
- Stromal tumors. These rare tumors are usually diagnosed at an earlier stage than other ovarian cancers.
- Germ cell tumors. These rare ovarian cancers tend to occur at a younger age.
Disease Prevents
Ovarian cancer
Symptoms and causes
There's no sure way to prevent ovarian cancer. But there may be ways to reduce your risk:
- Consider taking birth control pills. Ask your doctor whether birth control pills (oral contraceptives) may be right for you. Taking birth control pills reduces the risk of ovarian cancer. But these medications do have risks, so discuss whether the benefits outweigh those risks based on your situation.
- Discuss your risk factors with your doctor. If you have a family history of breast and ovarian cancers, bring this up with your doctor. Your doctor can determine what this may mean for your own risk of cancer. You may be referred to a genetic counselor who can help you decide whether genetic testing may be right for you. If you're found to have a gene change that increases your risk of ovarian cancer, you may consider surgery to remove your ovaries to prevent cancer.
Disease Treatments
Treatment of ovarian cancer usually involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Other treatments may be used in certain situations.
Surgery
Operations to remove ovarian cancer include:
- Surgery to remove one ovary. For early-stage cancer that hasn't spread beyond one ovary, surgery may involve removing the affected ovary and its fallopian tube. This procedure may preserve your ability to have children.
- Surgery to remove both ovaries. If cancer is present in both your ovaries, but there are no signs of additional cancer, your surgeon may remove both ovaries and both fallopian tubes. This procedure leaves your uterus intact, so you may still be able to become pregnant using your own frozen embryos or eggs or with eggs from a donor.
- Surgery to remove both ovaries and the uterus. If your cancer is more extensive or if you don't wish to preserve your ability to have children, your surgeon will remove the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, the uterus, nearby lymph nodes and a fold of fatty abdominal tissue (omentum).
- Surgery for advanced cancer. If your cancer is advanced, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove as much of the cancer as possible. Sometimes chemotherapy is given before or after surgery in this situation.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill fast-growing cells in the body, including cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs can be injected into a vein or taken by mouth.
Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might remain. It can also be used before surgery.
In certain situations, chemotherapy drugs may be heated and infused into the abdomen during surgery (hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy). The drugs are left in place for a certain amount of time before they're drained. Then the operation is completed.
Targeted therapy
Targeted drug treatments focus on specific weaknesses present within cancer cells. By attacking these weaknesses, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die.
If you're considering targeted therapy for ovarian cancer, your doctor may test your cancer cells to determine which targeted therapy is most likely to have an effect on your cancer.
Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy uses drugs to block the effects of the hormone estrogen on ovarian cancer cells. Some ovarian cancer cells use estrogen to help them grow, so blocking estrogen may help control the cancer.
Hormone therapy might be a treatment option for some types of slow-growing ovarian cancers. It may also be an option if the cancer comes back after initial treatments.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy uses the immune system to fight cancer. The body's disease-fighting immune system may not attack cancer cells because they produce proteins that help them hide from the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process.
Immunotherapy might be an option for treating ovarian cancer in certain situations.
Supportive (palliative) care
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care. Palliative care can be used while undergoing other aggressive treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy.
When palliative care is used along with all of the other appropriate treatments, people with cancer may feel better and live longer.
Palliative care is provided by a team of doctors, nurses and other specially trained professionals. Palliative care teams aim to improve the quality of life for people with cancer and their families. This form of care is offered alongside curative or other treatments you may be receiving.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Ovarian cancer and Learn More about Diseases
Epilepsy
Acanthosis nigricans
Chagas disease
Inherited metabolic disorders

Teen depression

Low sex drive in women

Bee sting
Endometrial cancer
ovarian cancer, ডিম্বাশয়ের ক্যান্সার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.