Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Knee bursitis
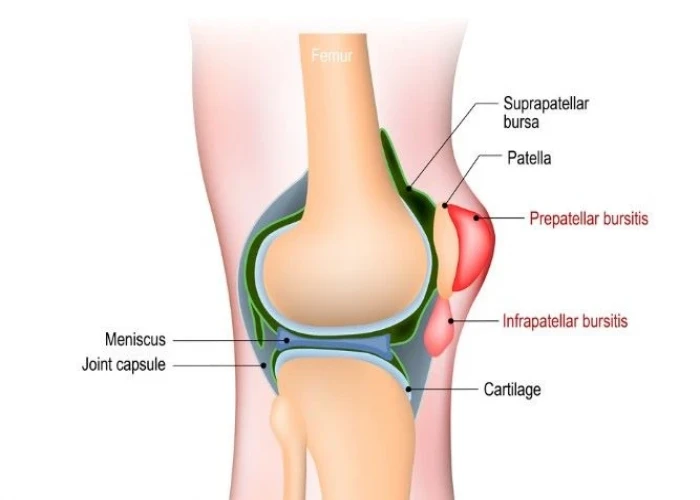
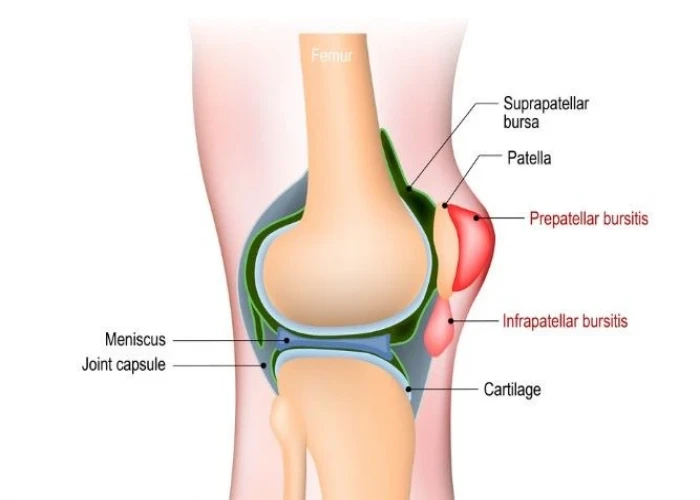
Knee bursitis is a condition that occurs when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones and soft tissues in the knee joint, become inflamed. This inflammation can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the knee, and may limit mobility and range of motion.
There are several different types of knee bursitis, depending on which bursae are affected. Some of the most common types include:
- Prepatellar bursitis: This occurs when the bursa at the front of the knee, just above the kneecap, becomes inflamed. It is often caused by repeated pressure or trauma to the knee, such as kneeling on hard surfaces.
- Infrapatellar bursitis: This occurs when the bursa below the kneecap becomes inflamed. It is often caused by overuse, such as running or jumping.
- Pes anserine bursitis: This occurs when the bursa on the inner side of the knee, just below the joint, becomes inflamed. It is often caused by overuse or poor biomechanics during exercise.
Treatment for knee bursitis typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce inflammation and pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be recommended to help with pain and swelling. In some cases, a doctor may recommend draining the inflamed bursa with a needle and injecting corticosteroids into the joint to reduce inflammation. Physical therapy may also be recommended to help with range of motion and strengthening exercises to prevent future episodes of knee bursitis.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Knee pain
- Swollen knee
- Joints especially knees and wrists might be stiff, painful and inflamed.
Disease Causes
Knee bursitis
Knee bursitis can be caused by:
- Frequent and sustained pressure, such as from kneeling, especially on hard surfaces
- Overuse or strenuous activity
- A direct blow to your knee
- Bacterial infection of the bursa
- Complications from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis or gout in your knee
Disease Prevents
Knee bursitis
To avoid knee bursitis or prevent its recurrence:
- Wear kneepads. If you're working on your knees or participating in sports that put your knees at risk, use padding to cushion and protect your knees.
- Take breaks. If you're on your knees for a period of time, take regular breaks to stretch your legs and rest your knees.
- Avoid excessive squatting. Excessive or repetitious bending of your knees increases the force on your knee joints.
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight. This can help take pressure off your knee joint.
Disease Treatments
Bursitis often improves over time, so treatment is usually aimed at symptom relief. However, depending on the cause of your knee bursitis and which bursa is infected, your doctor might recommend one or more treatment approaches.
Medications
If an infection has caused the knee bursitis, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotic treatment.
Therapy
Your doctor might refer you to a physical therapist or specialist in sports medicine, who can help you improve flexibility and strengthen muscles. This therapy might alleviate pain and reduce your risk of recurring episodes of knee bursitis. Protective knee braces might help if you can't avoid kneeling, and compressive knee sleeves can help reduce swelling.
Surgical and other procedures
More-invasive treatments for knee bursitis treatment include:
- Corticosteroid injection. If the bursitis is persistent and not responding to basic treatments, your doctor might inject a corticosteroid drug into an affected bursa to reduce inflammation. The inflammation usually subsides rapidly, but you might have pain and swelling from the injection for a couple of days.
- Aspiration. Your doctor might aspirate a bursa to reduce excess fluid and treat inflammation. He or she will insert a needle into the affected bursa and draw fluid into the syringe. Aspiration might cause short-term pain and swelling, and you might need to wear a knee immobilizer for a short period after the injection to reduce the chance of recurrent swelling.
- Surgery. If you have severe chronic or recurrent bursitis and don't respond to other treatments, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove the bursa.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Knee bursitis and Learn More about Diseases

Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
Lupus

Alcohol poisoning
Spinal headaches
Flatfeet

Night Discharge

Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)

Scleroderma
knee bursitis, হাঁটু বার্সাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.