Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Neurofibromatosis
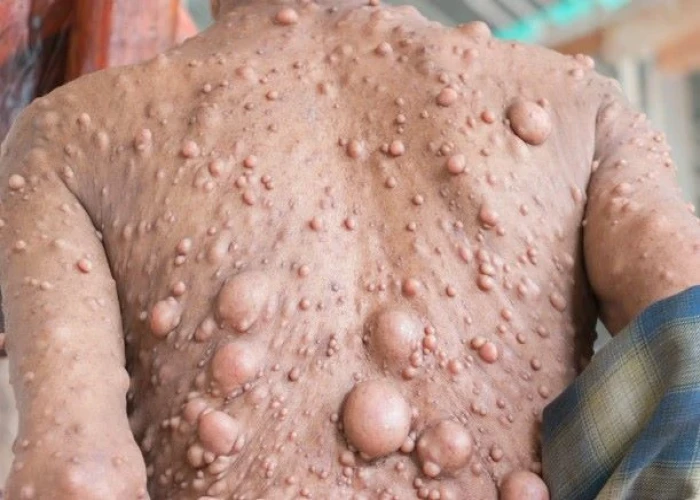
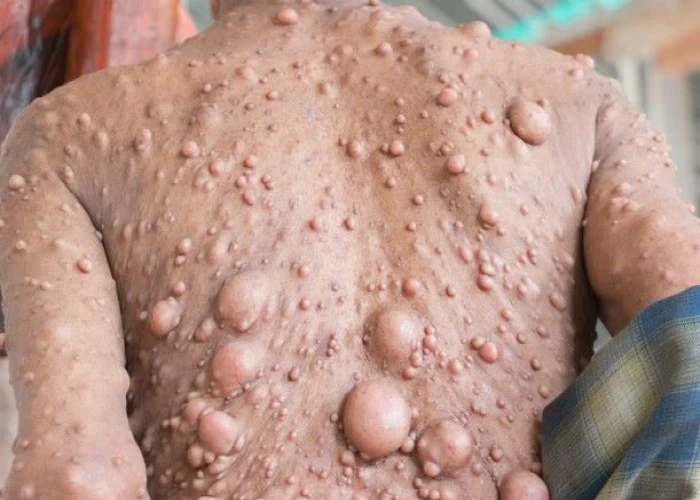
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a genetic disorder that affects the nervous system and can cause tumors to grow on nerves. It is caused by mutations in the genes that regulate cell growth and division. There are three main types of neurofibromatosis:
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1): This is the most common type of NF and affects about 1 in 3,000 people. Symptoms may include café-au-lait spots (flat, light brown birthmarks), neurofibromas (small tumors on or under the skin), scoliosis (curvature of the spine), learning disabilities, and optic nerve gliomas (tumors of the optic nerve).
- Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): This is a rare form of NF that affects about 1 in 25,000 people. It is characterized by the growth of tumors on the nerves that control hearing and balance. Symptoms may include hearing loss, ringing in the ears, balance problems, and facial weakness or numbness.
- Schwannomatosis: This is the rarest form of NF and is characterized by the growth of schwannomas, which are tumors that grow on the nerves that surround the spinal cord and other nerves in the body. Symptoms may include chronic pain, muscle weakness, and numbness.
There is no cure for NF, but treatment can help manage symptoms and complications. Treatment may include surgery to remove tumors, radiation therapy, and medication to manage pain or other symptoms. People with NF may also benefit from genetic counseling and support from healthcare professionals and advocacy organizations.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Deafness (Hearing loss)
- Ringing in ears (tinnitus)
- Lose balance
- Headaches
- Numbness
- Weakness and numbness in legs
- Blurred vision of eye
- Seizures
Disease Causes
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis is caused by genetic defects (mutations) that either are passed on by a parent or occur spontaneously at conception. The specific genes involved depend on the type of neurofibromatosis:
- NF1. The NF1 gene is located on chromosome 17. This gene produces a protein called neurofibromin that helps regulate cell growth. The mutated gene causes a loss of neurofibromin, which allows cells to grow uncontrolled.
- NF2. The NF2 gene is located on chromosome 22, and produces a protein called merlin (also called schwannomin), which suppresses tumors. The mutated gene causes a loss of merlin, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
- Schwannomatosis. So far, two genes are known to cause schwannomatosis. Mutations of the genes SMARCB1 and LZTR1, which suppress tumors, are associated with this type of neurofibromatosis.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
There isn't a cure for neurofibromatosis, but signs and symptoms can be managed. Generally, the sooner someone is under the care of a doctor trained in treating neurofibromatosis, the better the outcome.
Monitoring
If your child has NF1, your doctor is likely to recommend yearly age-appropriate checkups to:
- Assess your child's skin for new neurofibromas or changes in existing ones
- Check for signs of high blood pressure
- Evaluate your child's growth and development — including height, weight and head circumference — according to growth charts available for children who have NF1
- Check for signs of early puberty
- Evaluate your child for any skeletal changes and abnormalities
- Assess your child's learning development and progress in school
- Obtain a complete eye examination
Contact your doctor promptly if you notice any changes in signs or symptoms between visits. Many complications of NF1 can be treated effectively if therapy starts early.
Medication
Selumetinib (Koselugo) is a treatment for plexiform neurofibroma in children. Clinical trials of similar drugs are currently ongoing for children and adults.
Surgery and other procedures
Your doctor might recommend surgery or other procedures to treat severe symptoms or complications of neurofibromatosis.
- Surgery to remove tumors. Symptoms can be relieved by removing all or part of tumors that are compressing nearby tissue or damaging organs. If you have NF2 and have experienced hearing loss, brainstem compression or tumor growth, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove acoustic neuromas that are causing you problems. Complete removal of schwannomas in people with schwannomatosis can ease pain substantially.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery. This procedure delivers radiation precisely to your tumor and doesn't require an incision. Stereotactic radiosurgery might be an option to remove acoustic neuromas if you have NF2. Stereotactic radiosurgery can help preserve your hearing.
- Auditory brainstem implants and cochlear implants. These devices might help improve your hearing if you have NF2 and hearing loss.
Cancer treatment
Malignant tumors and other cancers associated with neurofibromatosis are treated with standard cancer therapies, such as surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Early diagnosis and treatment are the most important factors contributing to a good outcome.
Pain medications
Managing pain is an important part of treatment for schwannomatosis. Your doctor might recommend:
- Drugs for nerve pain such as gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) or pregabalin (Lyrica)
- Tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline
- Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors such as duloxetine (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle)
- Epilepsy medications such as topiramate (Topamax, Qudexy XR, Trokendi XR) or carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Tegretol, others)
Potential future treatments
Researchers are testing gene therapies for NF1. Potential new treatments could include replacing the NF1 gene to restore the function of neurofibromin.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Neurofibromatosis and Learn More about Diseases

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Golfer's elbow

Nickel allergy

Delirium

Generalized anxiety disorder

Complicated grief

Genital herpes

Head and neck cancers
নিউরোফাইব্রোমাটোসিস (এনএফ) একটি জেনেটিক ব্যাধি যা স্নায়ুতন্ত্রকে প্রভাবিত করে এবং স্নায়ুতে টিউমার বৃদ্ধির কারণ হতে পারে।
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.